hdu 1272 小希的迷宫(java实现)
小希的迷宫
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 19599 Accepted Submission(s): 5993
Problem Description
上次Gardon的迷宫城堡小希玩了很久(见Problem B),现在她也想设计一个迷宫让Gardon来走。但是她设计迷宫的思路不一样,首先她认为所有的通道都应该是双向连通的,就是说如果有一个通道连通了房间A和B,那么既可以通过它从房间A走到房间B,也可以通过它从房间B走到房间A,为了提高难度,小希希望任意两个房间有且仅有一条路径可以相通(除非走了回头路)。小希现在把她的设计图给你,让你帮忙判断她的设计图是否符合她的设计思路。比如下面的例子,前两个是符合条件的,但是最后一个却有两种方法从5到达8。
![]()
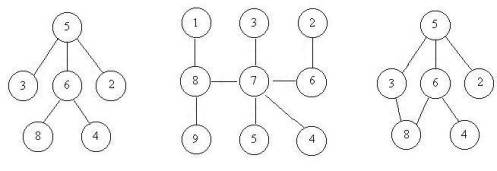
Input
输入包含多组数据,每组数据是一个以0 0结尾的整数对列表,表示了一条通道连接的两个房间的编号。房间的编号至少为1,且不超过100000。每两组数据之间有一个空行。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
整个文件以两个-1结尾。
Output
对于输入的每一组数据,输出仅包括一行。如果该迷宫符合小希的思路,那么输出"Yes",否则输出"No"。
Sample Input
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4
5 6 0 0
8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5
7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
3 8 6 8 6 4
5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
-1 -1
Sample Output
Yes
Yes
No
//判断是否为连通图,然后删边问题,其实不用判断是否为连通图就可以AC、具体请看最后一个代码
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {//先判断是否为连通图,然后是删边问题,M-(n-1)==0
private static int str[];
private static boolean s[];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
HashSet<Integer> Hs=new HashSet<Integer>();
int m=0;
str = new int[100001];
s=new boolean[100001];//标记这个顶点是否出现过
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++)
str[i] = i;
int a = input.nextInt();
int b = input.nextInt();
if(a==0&&b==0){//0 0情况是一个点也没有,也属于满足条件
System.out.println("Yes");
continue;
}
if (a == -1 && b == -1)
break;
while (!(a == 0 && b == 0)) {
//记录边的条数
m++;
//记录顶点个数
Hs.add(a);
Hs.add(b);
s[a]=true;
s[b]=true;
heBing(a, b);//并查集,合并区间
a = input.nextInt();
b = input.nextInt();
}
int sum=0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++)//判断有多少区间
if(s[i]&&str[i] == i)
sum++;
if(sum==1&&(m-Hs.size()==-1)){//一个区间,且边减顶点等于-1,则最优
System.out.println("Yes");
}
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
private static void heBing(int x, int y) {
int x1 = find(x);
int y1 = find(y);
if (x1 != y1)
str[x1] = y1;
}
private static int find(int x) {
while (str[x] != x) {
x = str[x];
}
return x;
}
}
//并查集
//8833413 2013-08-05 12:43:52 Accepted 1272 687MS 6996K 1511 B Java zhangyi
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {//优化过后
private static int str[];
private static boolean ok = true;
private static boolean s[];
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int max=Integer.MIN_VALUE;
ok = true;//记录是否有相同的父节点
str = new int[100001];
s=new boolean[100001];
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++)
str[i] = i;
int a = input.nextInt();
int b = input.nextInt();
if(a==0&&b==0){//特殊情况
System.out.println("Yes");
continue;
}
if (a == -1 && b == -1)
break;
while (!(a == 0 && b == 0)) {
//找出最大顶点和最小顶点
if(a>max)
max=a;
if(b>max)
max=b;
if(a<min)
min=a;
if(b<min)
min=b;
//标记顶点是否出现过
s[a]=true;
s[b]=true;
heBing(a, b);//并查集,合并区间
a = input.nextInt();
b = input.nextInt();
}
int sum=0;
for (int i = min; i <= max; i++)//c查找区间个数
if(s[i]&&str[i] == i)
sum++;
if (sum==1&&ok)//如果一个区间,且每个顶点没有重复父节点(边)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
private static void heBing(int x, int y) {
int x1[]=new int[2];
int y1[]=new int[2];
x1=find(x);
y1=find(y);
if(x1[0]!=y1[0])
//深度小的合并到深度大的上边
if(x1[1]<y1[1]){
str[x1[0]]=y1[0];
//把此节点也连到父节点上
str[x]=y1[0];
}
else{
str[y1[0]]=x1[0];
str[y]=x1[0];
}
else//说明有相同父节点,即有连通图
ok=false;
}
private static int[] find(int x) {
int b[]=new int[2];
b[0]=x;b[1]=0;
while(str[b[0]]!=b[0]){
b[0]=str[b[0]];
b[1]++;//记录深度
}
return b;
}
}
//AC代码-删边问题
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{//AC 原来系统保证图是连通图
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
HashSet<Integer> HS=new HashSet<Integer>();
int m=0;
int a=input.nextInt();
int b=input.nextInt();
if(a==-1&&b==-1)
break;
while(!(a==0&&b==0)){
HS.add(a);
HS.add(b);
m++;
a=input.nextInt();
b=input.nextInt();
}
// System.out.println(m+"-----"+HS.size());
if(m==0||m-(HS.size()-1)==0)
System.out.println("Yes");
else
System.out.println("No");
}
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号