File Transfer (并查集) Java实现
题目描述
We have a network of computers and a list of bi-directional connections. Each of these connections allows a file transfer from one computer to another. Is it possible to send a file from any computer on the network to any other?
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each test case, the first line contains N (2<=N<=104), the total number of computers in a network. Each computer in the network is then represented by a positive integer between 1 and N. Then in the following lines, the input is given in the format:
I c1 c2
where I stands for inputting a connection between c1 andc2; or
C c1 c2
where C stands for checking if it is possible to transfer files betweenc1 and c2; or
S
where S stands for stopping this case.
Output Specification:
For each C case, print in one line the word "yes" or "no" if it is possible or impossible to transfer files betweenc1 and c2, respectively. At the end of each case, print in one line "The network is connected." if there is a path between any pair of computers; or "There are k components." wherek is the number of connected components in this network.
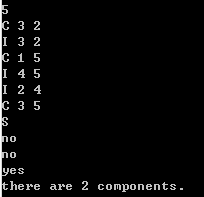
Sample Input 1:
5 C 3 2 I 3 2 C 1 5 I 4 5 I 2 4 C 3 5 S
Sample Output 1:
no no yes There are 2 components.
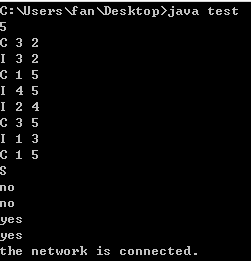
Sample Input 2:
5 C 3 2 I 3 2 C 1 5 I 4 5 I 2 4 C 3 5 I 1 3 C 1 5 S
Sample Output 2:
no no yes yes The network is connected.
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
思路:用数组角标来表示不同的电脑,角标所对应的值表示当前电脑的父节点。若当前角标所对应的值为-1,则当前角标为根节点。
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; //声明集合类 class gather { int[] arr; //初始化集合 public gather(int N) { //为了使角标与电脑的对应关系更加清晰,从1开始表示,角标数即为电脑标号 arr=new int[N+1]; arr[0]=-1; //创建新的集合时,集合中每一个角标都是根节点,所以对应元素为-1 for (int i=1;i<N+1 ;i++ ) { arr[i]=-1; } } //判断两台电脑是否连接 public boolean check(int a,int b) { int aroot=find(a); int broot=find(b); return aroot==broot; } //寻找当前电脑的根 public int find(int data) { int temp=data; while (arr[temp]!=-1) { temp=arr[temp]; } return temp; } //连接两台电脑,若二者已经相连(间接相连),则不做处理,否则将b连到a上 public void connect(int a,int b) { if (!check(a,b)) {
//把b的根节点连到a上 arr[find(b)]=a; } } //整个网络的连接状况 public void isConnected(int N) { int count=0; for (int i=1;i<N+1 ;i++ ) { if (arr[i]==-1) { count++; } } if (count==1) { System.out.print("the network is connected."); } else { System.out.print("there are "+count+" components."); } } } class test { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); int N=sc.nextInt(); gather g=new gather(N); String flag; //用来存放check的结果,方便输入S之后将所有check结果输出 ArrayList<String> arr=new ArrayList<String>(); do { flag=sc.next(); if (flag.equals("S")) { break; } int a=sc.nextInt(); int b=sc.nextInt(); if (flag.equals("I")) { g.connect(a,b); } if (flag.equals("C")) { if (g.check(a,b)) { arr.add("yes"); } else arr.add("no"); } } while (true); for (int i=0;i<arr.size() ; i++) { System.out.println(arr.get(i)); } g.isConnected(N); } }
打印结果


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号