堆中的路径 java描述
将一系列给定数字插入一个初始为空的小顶堆H[]。随后对任意给定的下标i,打印从H[i]到根结点的路径。
输入格式:
每组测试第1行包含2个正整数N和M(≤1000),分别是插入元素的个数、以及需要打印的路径条数。下一行给出区间[-10000, 10000]内的N个要被插入一个初始为空的小顶堆的整数。最后一行给出M个下标。
输出格式:
对输入中给出的每个下标i,在一行中输出从H[i]到根结点的路径上的数据。数字间以1个空格分隔,行末不得有多余空格。
输入样例:
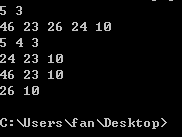
5 3
46 23 26 24 10
5 4 3
输出样例:
24 23 10
46 23 10
26 10
思路:堆是一个完全二叉树,用数组来存放堆中数据,角标为1代表堆顶。若当前角标为i,左儿子为2i,右儿子为2i+1,父节点为i/2。
每插入一个元素,把他放在完全二叉树最后一个位置,使其与父节点比较,若小于父节点,父节点值和插入元素互换,继续循
环比较,因为设置了哨兵arr[0]=-10001, 所以插入的数据角标最小只可能为1,不可能为0.
import java.util.Scanner; //声明一个堆类 class heap { //堆中数据内容有一个数组和一个表示堆大小的size int[] arr; int size; //初始化堆,因为N取值是-10000到10000,取10001是为了数组能满足题目要求,arr[0]=-10001作为哨兵,使数组从角标为1开始存放数据 //一开始堆是空的,所以size=0 public heap() { arr=new int[10001]; arr[0]=-10001; size=0; } //向堆中插入数据,堆的数据结构是一个完全二叉树 public void insert(int num) { if (size==0) { arr[1]=num; size++; } else { arr[++size]=num; //恢复t int t=size; while (num<arr[t/2]) { int temp=arr[t/2]; arr[t/2]=num; arr[t]=temp; t=t/2; } } } //取得从给定角标到堆顶的路径 public void road(int num) { while (num!=0) { System.out.print(arr[num]+" "); num=num/2; } if (num==0) { System.out.println(); } } } //测试类 class test { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); heap h=new heap(); int N=sc.nextInt(); int M=sc.nextInt(); for (int i=0;i<N ;i++ ) { int num=sc.nextInt(); h.insert(num); } for (int i=0;i<M ;i++ ) { int r=sc.nextInt(); h.road(r); } } }
打印结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号