为 static 变量分配空间,设置默认值(准备阶段)
话不多说直接上代码:
package com.beyond.dhl;
class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance; // 懒汉式所以不会进行实例化对象
private Singleton() {
System.out.println("构造方法:" + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public static Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> Singleton.getInstance(), "线程A").start();
new Thread(() -> Singleton.getInstance(), "线程B").start();
new Thread(() -> Singleton.getInstance(), "线程C").start();
new Thread(() -> Singleton.getInstance(), "线程D").start();
new Thread(() -> Singleton.getInstance(), "线程E").start();
}
}
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 10; //十进制
int i2 = 010; //八进制0
int i3 = 0x10; //十六进制0x
int i4 = 0b10; //二进制0b
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(i2);
System.out.println(i3);
System.out.println(i4);
}
}
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float f = 0.1f;
double d = 1.0/10;
System.out.println(f == d);
System.out.println(f);
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println("========================================");
float d1 = 233333333333333333F;
float d2 = d1 + 1;
System.out.println(d1 == d2);
}
}
public class MyClass {
static int num;
}
public class Test_MyClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//可直接通过 类名.属性名 进行访问
MyClass.num=10;
MyClass m1 = new MyClass();
m1.num=20;
System.out.println(m1.num);//num=20
MyClass m2 = new MyClass();
m2.num=30;
System.out.println(m2.num);//num=30
System.out.println(m1.num);//num=30
}
}
package com.soder;
public class Soder1 extends Soders{
public Soder1() {
p--;
System.out.println("子类构造方法\t"+p);
}
{
System.out.println("子类代码块\t"+p);
}
static {
System.out.println("子类静态代码块\t"+p);
}
public static void m1() {
System.out.println("子类静态指令m1\t"+p);
}
public void m2() {
System.out.println("子类指令m2\t"+p);
}
}
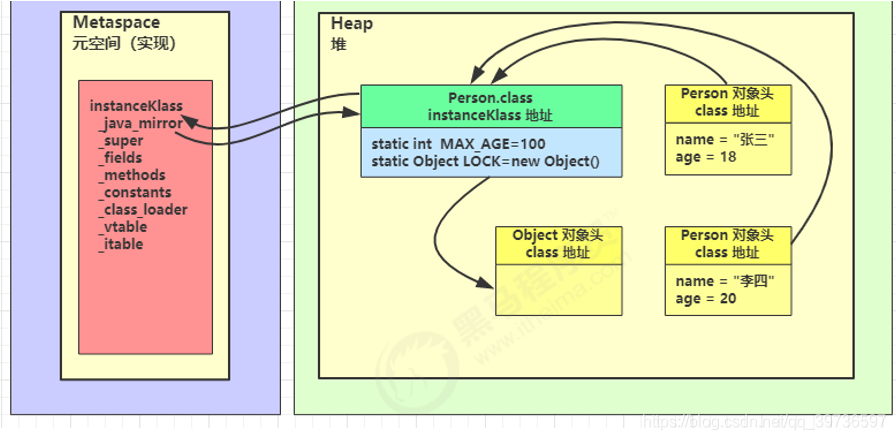
tips:当类被加载时,类的所有信息(包名,类名,属性,方法等)都会被加载到方法区,而其中的静态属性方法又会被调进静态域,可通过类名直接调用出来



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号