Codeforces_765_D. Artsem and Saunders_(数学)
Artsem has a friend Saunders from University of Chicago. Saunders presented him with the following problem.
Let [n] denote the set {1, ..., n}. We will also write f: [x] → [y] when a function f is defined in integer points 1, ..., x, and all its values are integers from 1 to y.
Now then, you are given a function f: [n] → [n]. Your task is to find a positive integer m, and two functions g: [n] → [m], h: [m] → [n], such that g(h(x)) = x for all 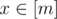 , and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all
, and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all  , or determine that finding these is impossible.
, or determine that finding these is impossible.
The first line contains an integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105).
The second line contains n space-separated integers — values f(1), ..., f(n) (1 ≤ f(i) ≤ n).
If there is no answer, print one integer -1.
Otherwise, on the first line print the number m (1 ≤ m ≤ 106). On the second line print n numbers g(1), ..., g(n). On the third line print m numbers h(1), ..., h(m).
If there are several correct answers, you may output any of them. It is guaranteed that if a valid answer exists, then there is an answer satisfying the above restrictions.
3
1 2 3
3
1 2 3
1 2 3
3
2 2 2
1
1 1 1
2
2
2 1
-1[]
题意:f:[n]-->[m];g:[n]-->[m];h:[m]-->[n].给定n和f[1--n]的值,求一个m,使得g[h[x]]==x,h[g[x]]==f[x]。
比赛中看到这道题时,心里有点害怕,感觉做不出来,毕竟不太擅长这种题。然后第二天冷静了一下,AC掉。
思路:
由g[h[x]]==x和h[g[x]]==f[x]可知,只有当f[x]==x的x(或f[x])值可以做h[1--m]的值域中的元素,
所以由f[x]==x可以确定h[x]和m的值;有了h[x],由h[g[x]]==f[x]可以确定g[x]。
并且h[1--m]的值域和f[1--n]的值域应该完全相同,否则不可能。因为若f[1--n]的值域中存在一个I,但不在h[1--m]的值域中,那么就存在一个
g[t]不能被确定。
不可能的情况什么时候发生? 由以上思路,及由h[1--m]和f[1--n]若存在一个g[i]不能被确定,那么就是不可能的情况。
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #include<map> using namespace std; #define N 100005 int f[N],g[N],h[N]; map<int,int>maph; bool vis[N]; int main() { int n,cntg; scanf("%d",&n); int m,last=0; cntg=1; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { scanf("%d",&f[i]); if(f[i]==i) { vis[f[i]]=1; } } //numg[cntg-1]+=n-last; m=0; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) if(vis[i]==1) { m++; h[m]=i; maph[i]=m; //值域到定义域的映射 } int flag=1; for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { if(maph[f[i]]>0) g[i]=maph[f[i]]; else flag=0; } if(flag) { printf("%d\n",m); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { printf("%d",g[i]); if(i==n) printf("\n"); else printf(" "); } for(int i=1; i<=m; i++) { printf("%d",h[i]); if(i==m) printf("\n"); else printf(" "); } } else printf("-1\n"); return 0; }



