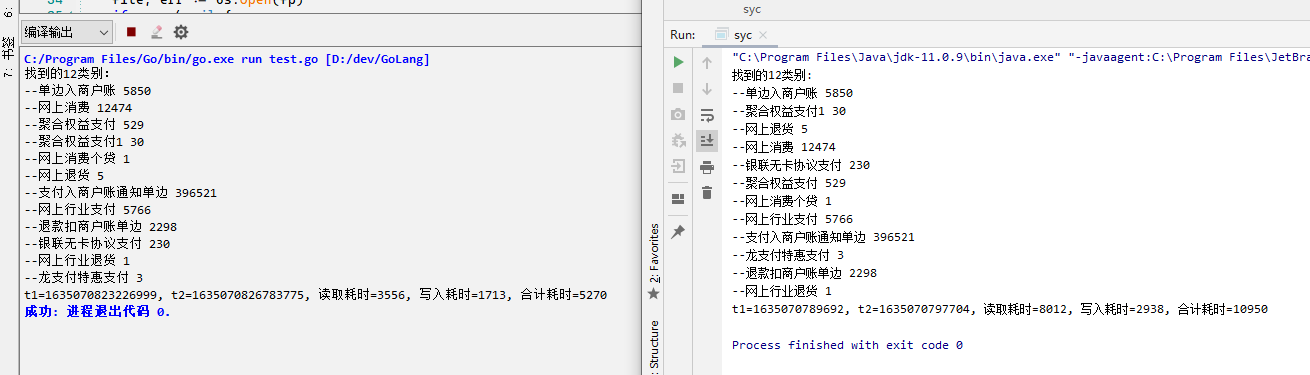
同样环境与 java 做了个对比,差的不是一星半点!先看执行结果,同样环境下读取同一个400M左右数据文件,以下截图是测试结果:
JAVA 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 | package ccb;import java.io.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.List;import java.util.Map;public class syc{ static String fp = "D:\\ccb\\ONL_STLM_JNL_410_20190625.dat";// static String fp = "D:\\ccb\\ONL.dat"; static File sourceFile = new File(fp); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { long s0 = System.currentTimeMillis(); long lnu = get_line_number(); System.out.println(String.format("文件共有:%s行", lnu)); long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(String.format("统计文件行数用时:%s", (s1-s0))); long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 读取文件内容,并进行归类 Map<String, List<String>> mapList = read_data(); long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 将文件内容写入磁盘 write_data(mapList); long t3 = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(String.format("t1=%s, t2=%s, 读取耗时=%s, 写入耗时=%s, 合计耗时=%s", t1, t2, (t2-t1), (t3-t2), (t3-t1))); } /** * 带缓存读取文件,归类 * @return Map */ @SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" }) public static Map<String, List<String>> read_data() { Map<String, List<String>> mapList = new HashMap<>(); // 带缓存的输入流读取 BufferedReader buff = null; try { buff = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(sourceFile)); String line = ""; while ((line = buff.readLine()) != null) { String[] items = line.split("\\|@\\|"); String type_name = items[1]; if (mapList.containsKey(type_name)) { List tempList = mapList.get(type_name); tempList.add(line); mapList.put(type_name, tempList); } else { List lines = new ArrayList<>(); lines.add(line); mapList.put(type_name, lines); } } buff.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (buff != null) { try { buff.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } System.out.println(String.format("找到的%s类别:", mapList.size())); return mapList; } /** * 带缓存写入文件 * @param mapList * @throws IOException */ public static void write_data(Map<String, List<String>> mapList) throws IOException { FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter(sourceFile + ".result"); BufferedWriter buff = new BufferedWriter(fWriter); for (Map.Entry<String, List<String>> entry : mapList.entrySet()) { List<String> lines = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(String.format("--%s %s", entry.getKey(), lines.size())); for (String line : lines) { buff.write(line + "\n"); } } try { buff.close(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } /** * 返回文件的总行数 * @return */ public static long get_line_number() throws IOException { File file = new File(fp); FileReader reader = new FileReader(file); LineNumberReader line_num_reader = new LineNumberReader(reader); long lineNu = 0; while (line_num_reader.readLine() != null) lineNu++; return lineNu; }} |
Golang 代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 | package mainimport ( "bufio" _ "container/list" "fmt" "io" "os" "strings" "time")func main() { file_path := "ONL_STLM_JNL_410_20190625.dat" new_file_path := file_path + ".result" t1 := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1e3 // lines := read_file(file_path) mapList := read_file(file_path) t2 := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1e3 write_file(mapList, new_file_path) t3 := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1e3 fmt.Printf("t1=%v, t2=%v, 读取耗时=%v, 写入耗时=%v, 合计耗时=%v\n", t1, t2, (t2-t1)/1e3, (t3-t2)/1e3, (t3-t1)/1e3)}// 逐行读取文件func read_file(fp string) map[string][]string { file, err := os.Open(fp) if err != nil { fmt.Printf("读取文件错误: %s\n", err) return nil } defer file.Close() br := bufio.NewReader(file) //声明一个切片 // var file_list []string //声明一个 map mapList := make(map[string][]string) for { b_line, _, err := br.ReadLine() if err == io.EOF { break } // 向 list 中追加元素 // file_list.PushBack(string(line)) // file_list = append(file_list, string(line)+"\n") line := string(b_line) // 使用map items := strings.Split(line, "|@|") type_name := items[1] if mapValue, has_key := mapList[type_name]; has_key { mapValue := append(mapValue, line) mapList[type_name] = mapValue } else { //创建一个临时切片 tmp_slice := []string{line} mapList[type_name] = tmp_slice } } // 输出 list 长度 // fmt.Println(file_list) return mapList}func line2map(lines []string) map[string][]string { /* _, err := os.Stat(new_file_path) if err == nil { //文件存在,删除重建 } */ //类别 mapList := make(map[string][]string) //第一次循环,查找分类 for _, value := range lines { item := strings.Split(value, "|@|") //类别名称,作为map主键 key := item[1] if mapValue, has_key := mapList[key]; has_key { //包含该类别, map的value继续添加 mapValue := append(mapValue, value) mapList[key] = mapValue } else { //不包含该类别, 新增一个key lines := []string{value} mapList[key] = lines } /* //判断类型是否在切片中 _, found := in_array(classes, item[1]) if !found { classes = append(classes, item[1]) } */ } //找到的类别 共12个类别 fmt.Printf("找到的%d类别:\n", len(mapList)) return mapList}/*Find获取一个切片并在其中查找元素。如果找到它,它将返回它的密钥,否则它将返回-1和一个错误的bool*///从切片中查找func in_array(slice []string, val string) (int, bool) { for i, item := range slice { if item == val { return i, true } } return -1, false}// 写入文件func write_file(mapList map[string][]string, new_file_path string) { file_handle, err := os.OpenFile(new_file_path, os.O_CREATE|os.O_RDWR, 0666) buf := bufio.NewWriter(file_handle) if err != nil { fmt.Println("打开新文件错误:", err) return } defer file_handle.Close() //遍历map for key, value := range mapList { fmt.Printf("--%s %v\n", key, len(value)) for nu := range value { // fmt.Print(value[nu]) //行末带有换行符 buf.WriteString(value[nu]) } } //缓存写入文件 /* fmt.Println(item) fmt.Printf("%v | %v", key, string(value)) */ err = buf.Flush() if err != nil { fmt.Printf("写入磁盘错误: ", err) }} |




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· 用 C# 插值字符串处理器写一个 sscanf
· Java 中堆内存和栈内存上的数据分布和特点
· 开发中对象命名的一点思考
· .NET Core内存结构体系(Windows环境)底层原理浅谈
· 为什么说在企业级应用开发中,后端往往是效率杀手?
· DeepSeek 解答了困扰我五年的技术问题。时代确实变了!
· 本地部署DeepSeek后,没有好看的交互界面怎么行!
· 趁着过年的时候手搓了一个低代码框架
· 推荐一个DeepSeek 大模型的免费 API 项目!兼容OpenAI接口!