集合与数组
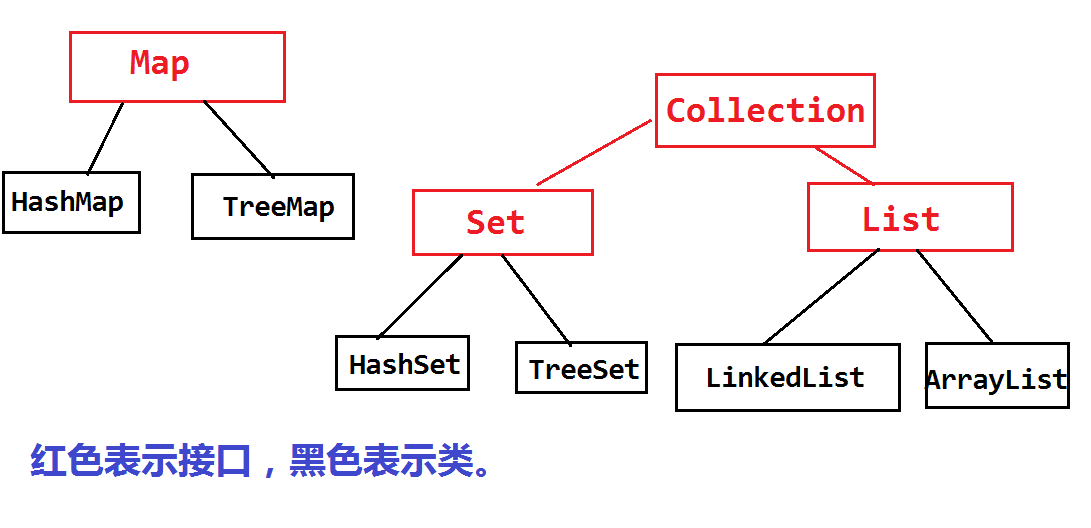
01集合:
集合框架图
单列集合
List:有索引,有顺序,能重复的
Set:无索引,无数序,不能重复的
Hashset:
查看源码,发现Hashset底层是个Hashmap,只不过value都是空的object
Map是不允许key相同的,所以Hashset中的值是唯一的
TreeSet:
底层也是Map,value也是空的object,同样能保证值的唯一性
问题1:怎样保证HashSet中存储的自定义对象的唯一性
注:如果对象的属性都相同,则这里看成是同一个对象
HashSet实际上是HashMap的key,保证唯一就是要让jvm将属性相同的对象当作同一个key
那么jvm是怎么确定同一个key的呢?
查看源码,HashMap的put方法中用到了对象的hash值,和对象的equals方法
可以理解成如果对象的hash值不同,就不能存在Map中,而每一个对象的hash值肯定是不一样的(hash值是通过对象的地址值根据一种算法算出来的),
所以肯定是可以存的,显然这里不能用Object类中原始的获得hash值的方法
所以要重写hash方法和equals方法,保证对象如果属性是一致的,则hash值一样,这样在Map.put的时候调用自身的hash方法和equals方法,如果属性一致的话就当作
同一个对象,就不会存在Map的key中,这样保证元素的唯一性
重写hash方法和equals方法:可以使用快捷键
问题2:TreeSet是怎样自定义排序的
TreeSet底层使用了二叉树算法
两种方式如下:
1 public class Stu implements Comparable<Stu>{//自定义对象的排序方法:第一种
2 private String name;
3 private int age;
4 public Stu() {
5 super();
6 }
7 public Stu(String name, int age) {
8 super();
9 this.name = name;
10 this.age = age;
11 }
12 public String getName() {
13 return name;
14 }
15 public void setName(String name) {
16 this.name = name;
17 }
18 public int getAge() {
19 return age;
20 }
21 public void setAge(int age) {
22 this.age = age;
23 }
24 //自定义类判断对象是否一样,为什么要重写h和e方法
25 @Override
26 public int hashCode() {
27 final int prime = 31;
28 int result = 1;
29 result = prime * result + age;
30 result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
31 return result;
32 }
33 @Override
34 public boolean equals(Object obj) {
35 if (this == obj)
36 return true;
37 if (obj == null)
38 return false;
39 if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
40 return false;
41 Stu other = (Stu) obj;
42 if (age != other.age)
43 return false;
44 if (name == null) {
45 if (other.name != null)
46 return false;
47 } else if (!name.equals(other.name))
48 return false;
49 return true;
50 }
51 //按照年龄来排序
52 //这种方式一般不用,比较的时候直接在定义TreeSet的时候写比较器,这样不会对其它地方产生影响
53 @Override
54 public int compareTo(Stu o) {
55 return (this.age -o.age);
56 }
57 }
1 TreeSet<Stu> ts = new TreeSet<>(//自定义对象的排序方法:第二种
2 //比较器
3 new Comparator<Stu>() {
4 @Override
5 public int compare(Stu o1, Stu o2) {
6 // TODO Auto-generated method stub
7 int num = o1.getAge()-o2.getAge();
8 return num == 0 ? 1 : num;
9 }
10 }
11 );
问题3:TreeMap怎样实现自定义对象的key排序
看源码发现TreeMap的put方法里面定义了比较器
实现排序的方法如下:
TreeMap<Student, String> tm = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
int num = s1.getName().compareTo(s2.getName());
return num == 0 ? s1.getAge() - s2.getAge() : num;
}
});


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号