AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS源码解读)
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer继承自AbstractOwnableSynchronizer。
双向链表
head->A->B->C->D
tail->D->C->B->A
参数及代码块
// 获取Unsafe类的实例,用于对内存进行操作(CAS操作)
private static final Unsafe unsafe = Unsafe.getUnsafe();
// 在内存中的偏移量
private static final long stateOffset;
private static final long headOffset;
private static final long tailOffset;
private static final long waitStatusOffset;
private static final long nextOffset;
static {
try {
// 获取偏移量
stateOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("state"));
headOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("head"));
tailOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.class.getDeclaredField("tail"));
waitStatusOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("waitStatus"));
nextOffset = unsafe.objectFieldOffset
(Node.class.getDeclaredField("next"));
} catch (Exception ex) { throw new Error(ex); }
}
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node
Node为内部类,数据结构为双向链表。
compareAndSetState
如果期望值和更新值不一样,则返回false。
/**
* 比较并且设置状态
* @param expect 期望值
* @param update 更新值
*/
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) {
// 通过unsafe中的原子方法来设置
return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update);
}
unsafe.compareAndSwap**方法是基于JNI的原子操作
acquire
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// 如果当前线程未获取到锁(即被其他线程占有),把当前线程加到队列
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
tryAcquire
子类必须重写tryAcquire方法,不然会抛出异常。
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
addWaiter
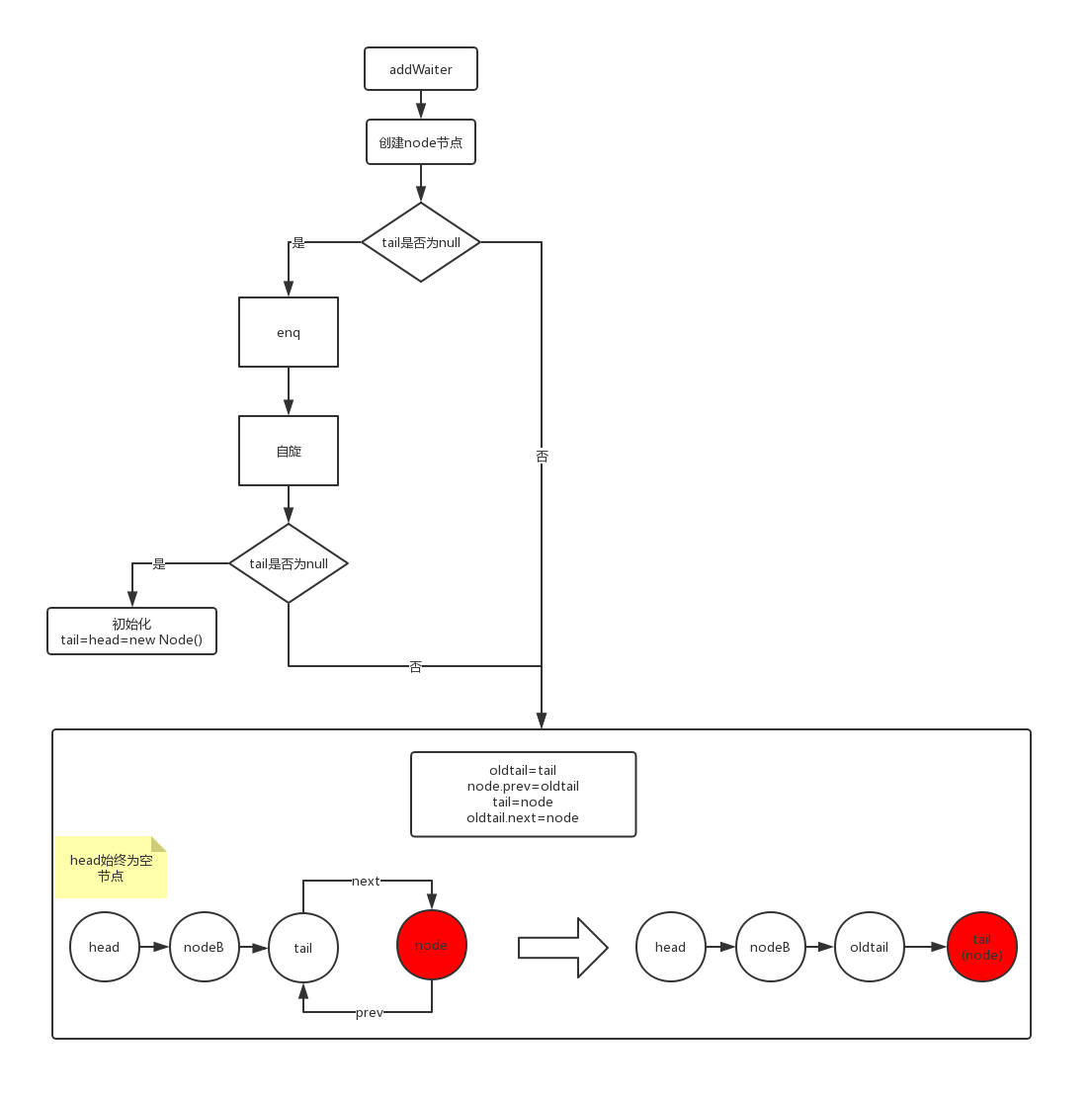
放入尾节点
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 创建node节点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// tail(尾节点)
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
// 如果尾节点设置成功,直接返回创建的node节点
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
enq
private Node enq(final Node node) {
// 一直循环去获取,直到尾节点设置成功才返回
for (;;) {
// 双向链表的知识
Node t = tail;
// 尾节点为空时,默认初始化头节点=尾节点=空节点
if (t == null) {
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// node的前驱节点指向为当前的尾节点
node.prev = t;
// 将尾节点设置成node节点(新的尾节点)
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
// 当前尾节点的后继节点指向为node节点
t.next = node;
// 返回旧的尾节点
return t;
}
}
}
}
acquireQueued

这里有三种状态
- pred.waitStatus => 0, 返回 interrupted => false
- pred.waitStatus => -1, 返回 interrupted => false
- pred.waitStatus => -1, 线程一直被挂起, 直到锁被释放(release), 返回 interrupted => true
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 是否中断
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// node的前驱节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 当p为头节点,并且获取到锁 【FIFO】先进先出
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 设置头节点为node
setHead(node);
// 删除p后继节点的引用
p.next = null;
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 线程一直被挂起,直到上面的if成立
// 下面分析
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
// 已中断
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
// 一旦发生异常,则会进入
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
第一次会进入else,将waitStatus设置为Node.SIGNAL即-1,返回false,不会执行parkAndCheckInterrupt,
第二次及之后进入直接返回true,就会执行parkAndCheckInterrupt。
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 默认为0
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
parkAndCheckInterrupt
为什么要返回当前线程的中断标识呢?因为LockSupport.park()会响应线程中断。
即,当线程中断时,无论是LockSupport.unpark()还是Thread.interrupt(),都会马上执行下面的return Thread.interrupted()。
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 阻塞线程
LockSupport.park(this);
// 返回当前线程中断标识
return Thread.interrupted();
}
LockSupport
park
public static void park(Object blocker) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
setBlocker(t, blocker);
// 设置线程无限阻塞
UNSAFE.park(false, 0L);
// 阻塞时不会执行
setBlocker(t, null);
}
setBlocker
设置t线程的parkBlocker属性,记录线程是被谁阻塞的。
private static void setBlocker(Thread t, Object arg) {
// Even though volatile, hotspot doesn't need a write barrier here.
UNSAFE.putObject(t, parkBlockerOffset, arg);
}
一个LockSupport的demo
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
public class LockSupportDemo {
public static Object o = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new MyThread1();
t.start();
Thread.sleep(4000);
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
static class MyThread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("等待挂起");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("已挂起");
System.out.println("等待唤醒");
LockSupport.park(o);
System.out.println("已唤醒");
}
}
}
输出为
等待挂起
已挂起
等待唤醒
已唤醒
思考?
LockSupport.park()和Object.wait()的区别?
....下次补充
Thread.interrupted()和Thread.isInterrupted()的区别?
....下次补充
cancelAcquire
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
// 删除挂载的线程
node.thread = null;
Node pred = node.prev;
// 把node的前驱节点指向挂载到没有被CANCELLED的节点上
// 为什么不判断pred不为null呢?因为在enq()方法里将节点插入到队列的时候就已经初始化过了
/**
* private Node enq(final Node node) {
* for (;;) {
* Node t = tail;
* if (t == null) { // 如果为null就初始化
* if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
* tail = head;
* } else {
* node.prev = t;
* if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
* t.next = node;
* return t;
* }
* }
* }
* }
*/
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
Node predNext = pred.next;
// 将node节点的状态设置为CANCELLED
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// 如果node是尾节点,将尾节点设置为node的前驱节点
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
// 将node前驱节点的后继节点指向设置为null,目的是为了切断与node节点的联系
// pred.next设置为null
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
int ws;
// node的前驱节点不是头节点
// 将node的前驱节点的状态设置为Node.SIGNAL,如果已经是Node.SIGNAL则不需要设置
// pred.thread != null 这个是干啥的,疑问??
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
// node的后继节点不为null,状态不为CANCELLED
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
// 将node的前驱节点的后继节点指向设置为node的后继节点
// 断开node节点的前后联系
// APrev - ANext - NodePrev - NodeNext - CPrev - CNext
// ||
// APrev - ANext - CPrev - CNext
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
// node的前驱节点是头节点,唤醒该节点线程
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
// node的后继节点指向设置为node
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
selfInterrupt
线程在等待的过程中被中断,不响应,需要补上中断。
static void selfInterrupt() {
// 中断当前线程
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
release
- waitStatus ===>>> 0 默认值
- waitStatus ===>>> 1 Node.CANCELLED
- waitStatus ===>>> -1 Node.SIGNAL
- waitStatus ===>>> -2 Node.CONDITION
- waitStatus ===>>> -3 Node.PROPAGATE
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 尝试释放锁,返回true则表示已经释放
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 头节点
Node h = head;
// 头节点不为null 并且waitStatus不为0
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryRelease
子类必须重写tryRelease方法,不然会抛出异常。
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
unparkSuccessor
唤醒队列中的头节点线程
/**
* node的前驱节点是头节点,唤醒该节点线程
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
int ws = node.waitStatus;
// 状态不为CANCELLED
if (ws < 0)
// 将waitStatus设置为0
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
// node的后继节点
Node s = node.next;
// 后继节点为空 或者 状态是CANCELLED
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
// 找到一个有效节点
// 尾节点!=头节点,从尾节点找到头节点的下一个未被CANCELLED的节点
// 疑问?为什么从尾节点往前遍历,而不从头节点往后遍历??
// HeadPrev - HeadNext - APrev - ANext - (TailPrev - TailNext) => s=TailNode => t=t.prev=ANode
// || t
// HeadPrev - HeadNext - (APrev - ANext) => s=ANode => t=t.prev=HeadNode
// || t
// ------------------------退出循环---------------------
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
// s就是找到的有效节点(头节点之后的第一个有效节点,因为头节点是空节点)
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
思考?
为什么从尾节点往前遍历,而不从头节点往后遍历?
因为head.next可能被设置为null??在哪里设置为null的呢
LockSupport
unpark
解除线程阻塞
public static void unpark(Thread thread) {
if (thread != null)
UNSAFE.unpark(thread);
}
有三个字送给你,
一是“诚”,
二是“勤”,
三是“专”。
当你无比地想做成一件事,
愿意为它倾尽无数心血和努力时,
结果总不会太差。
一是“诚”,
二是“勤”,
三是“专”。
当你无比地想做成一件事,
愿意为它倾尽无数心血和努力时,
结果总不会太差。






