SpringBoot启动原理解析
一.前言
SpringBoot项目的启动, 都需要如下的启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootDemo3Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo3Application.class, args);
}
}分析启动类, 可以看出核心是:
- 注解@SpringBootApplication
- 方法SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo3Application.class, args)
分析SpringBoot的启动原理, 就需要从以上两处开始
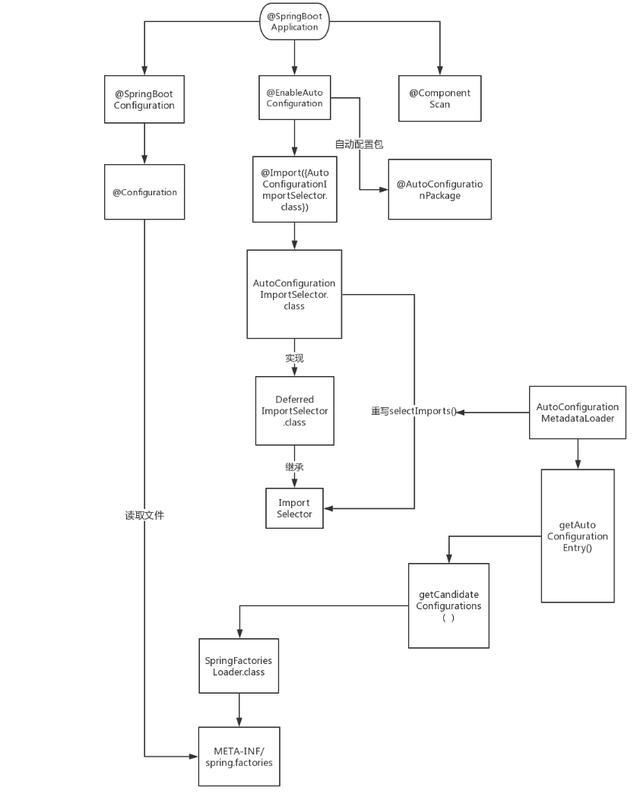
二.注解@SpringBootApplication
点开注解, 源码如下
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(
excludeFilters = {@Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {TypeExcludeFilter.class}
), @Filter(
type = FilterType.CUSTOM,
classes = {AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class}
)}
)
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
}@SpringBootApplication是由三个注解组合而成( 原生JDK注解忽略 ), 分别是:
- @SpringBootConfiguration
- @EnableAutoConfiguration
- @ComponentScan
即以上三个注解可以替代@SpringBootApplication
2.1 注解@SpringBootConfiguration
首先查看该注解源码
@Configuration
@Indexed
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Configuration.class
)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}该注解包含:
- @configuration : 该注解是Spring原生注解, 标注该类是Spring配置类, 可以在该类中向IOC容器添加Bean
- @Indexed : 标识项目在编译打包的时候会在项目中自动生成
META-INT/spring.components文件, 当SpringContext在执行ComponentScan扫描时,META-INT/spring.components将会被CandidateComponentsIndexLoader读取并加载,转换为CandidateComponentsIndex对象,这样的话@ComponentScan不在扫描指定的package,而是读取CandidateComponentsIndex对象,从而达到提升性能的目的 - proxyBeanMethods() default true : 外部无论对配置类中的这个组件注册方法调用多少次获取的都是之前注册容器中的单实例对象
2.2 注解@ComponentScan
作用 : @ComponentScan的功能其实就是自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件(比如@Component和@Repository等)或者bean定义,最终将这些bean定义加载到IoC容器中
2.3 注解@EnableAutoConfiguration
作用 : 该注解是SpringBoot的核心注解, 借助@Import的帮助,将所有符合自动配置条件的bean定义加载到IoC容器
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
String[] excludeName() default {};
}该注解包含
- @AutoConfigurationPackage
- @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
2.3.1 注解@AutoConfigurationPackage
查看源码, 该注解中包含@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Register.class) , 通过@Import注解将Register导入到ioc容器中, 然后通过Register向IOC容器中导入一系列组件
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
/**
* Base packages that should be registered with {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}.
* <p>
* Use {@link #basePackageClasses} for a type-safe alternative to String-based package
* names.
* @return the back package names
* @since 2.3.0
*/
String[] basePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #basePackages} for specifying the packages to be
* registered with {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* @return the base package classes
* @since 2.3.0
*/
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImports(metadata));
}
}- AnnotationMetadata metadata : 启动类

- new packageImports(metadata).getPackageNames : 获得启动类的包名
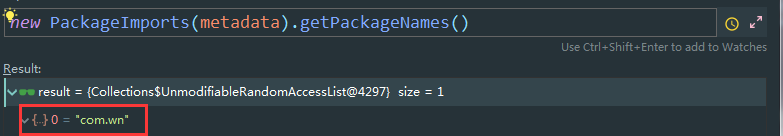
- BeanDefinitionRegistry registry

- register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0])); : 将启动类的包( 包含子包 )所有标注了@Component相关注解的组件导入到IOC容器
2.3.2 @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class})
将AutoConfigurationImportSelector
- 利用getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}- 调用List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes)获取到所有需要导入到容器中的配置类
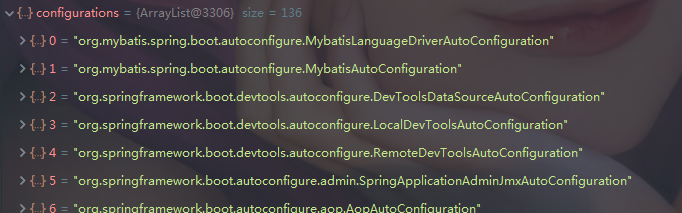
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}- 利用工厂加载 Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories( ClassLoader classLoader);得到所有的组件
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}- 从META-INF/spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。 默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有META-INF/spring.factories位置的文件 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories

2.4 注解小结
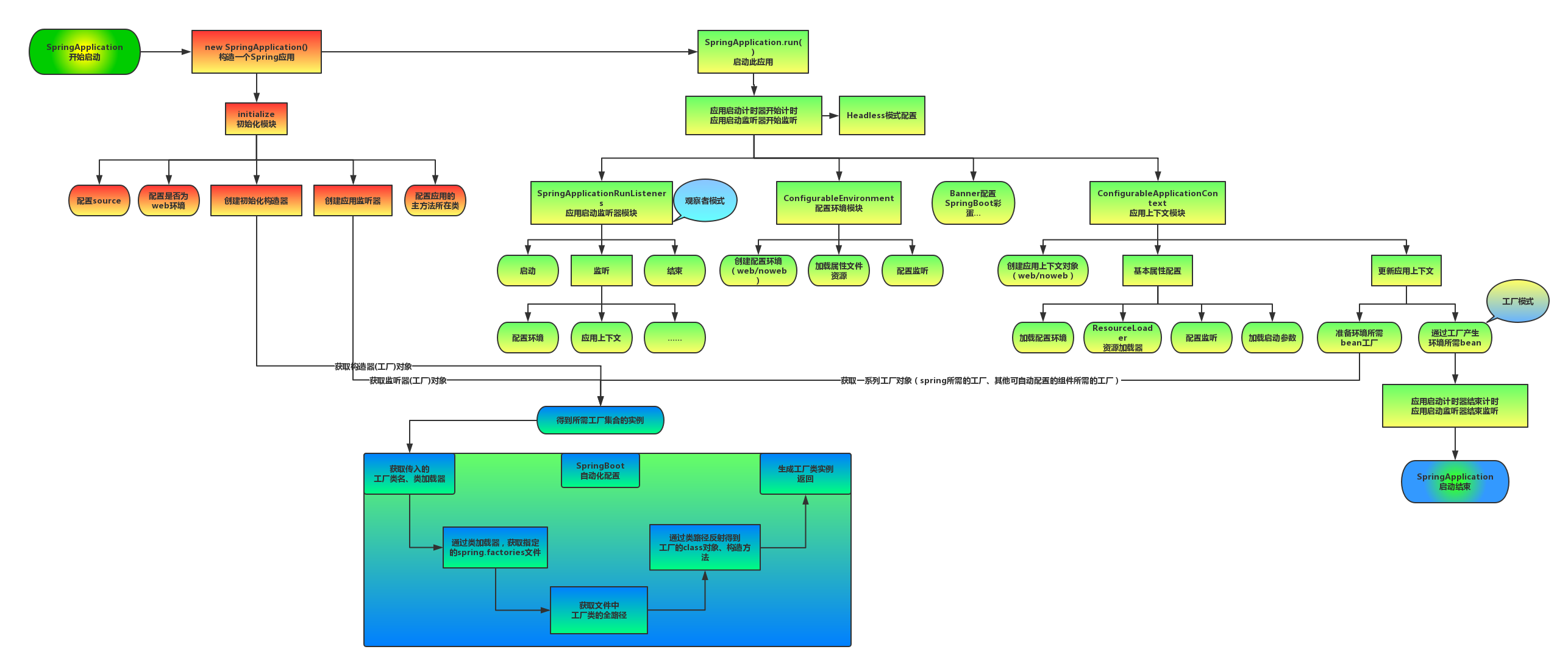
三.方法SpringApplication.run(SpringBootDemo3Application.class, args)
点进run方法, 源码如下
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
//继续点进下一层run方法
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}- 首先new了一个SpringApplication对象
- 然后调用SpringApplication对象的run方法
3.1 实例化SpringApplication对象
调用SpringApplication的1个参数的构造方法, 将启动类信息传入
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
继续调用2个参数的构造方法, 传入2个参数
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
//断言有主配置类, 否则抛出异常
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
//保存主配置类信息
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
//根据加载的处理器确定web应用的类型
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
//获取所有的初始化器, 从spring.factories寻找
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
//获取所有的应用监听器, 从spring.factories寻找
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}- 当前web应用类型
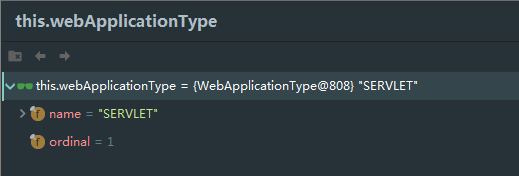
- 所有的初始化器

- 所有的应用监听器
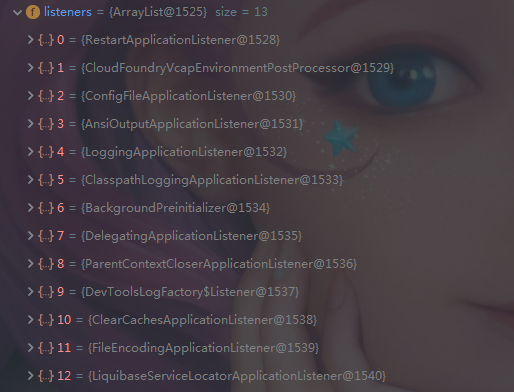
在项目依赖的spring.factories文件中可以找到以上初始化器和监听器
#路径springframework\boot\spring-boot\2.3.4.RELEASE\spring-boot-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar!\META-INF\spring.factories
# PropertySource Loaders
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=\
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertiesPropertySourceLoader,\
org.springframework.boot.env.YamlPropertySourceLoader
# Run Listeners
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=\
org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
# Error Reporters
org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzers
# Application Context Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.rsocket.context.RSocketPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.web.context.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.ClearCachesApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.context.logging.LoggingApplicationListener,\
org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.cloud.CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.env.SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor,\
org.springframework.boot.reactor.DebugAgentEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Failure Analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.context.properties.NotConstructorBoundInjectionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanCurrentlyInCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanDefinitionOverrideFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BeanNotOfRequiredTypeFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.BindValidationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.UnboundConfigurationPropertyFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ConnectorStartFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchMethodFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.PortInUseFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.ValidationExceptionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyNameFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.analyzer.InvalidConfigurationPropertyValueFailureAnalyzer
# FailureAnalysisReporters
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalysisReporter=\
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.LoggingFailureAnalysisReporter3.2 调用SpringApplication对象的run方法
将main方法中的args参数传入, 分析源码
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
//实例化1个程序停止运行监听器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
//记录启动时间
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
//让当前应用进入headless模式(自力更生模式)。java.awt.headless
configureHeadlessProperty();
//获取所有的运行监听器
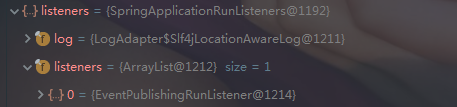
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
//遍历 SpringApplicationRunListener 调用 starting 方法;相当于通知所有感兴趣系统正在启动过程的人,项目正在 starting
listeners.starting();
try {
//保存命令行参数(args)
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
//准备环境, 返回或者创建基础环境信息对象 : StandardServletEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
//根据环境配置需要忽略的bean信息
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建IOC容器(createApplicationContext())
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
//准备IOC容器的基本信息
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新IOC容器。refreshContext ---> 创建容器中的所有组件(Spring注解)
refreshContext(context);
//容器刷新完成后 ---> 目前无内容, 预留
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
//停止运行监听器停止运行, 记录容器启动完成花费的时间
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
//所有监听器调用 listeners.started(context); 通知所有的监听器容器已创建完成
listeners.started(context);
//调用所有runners, 遍历执行runner的run方法
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
//通知所有的监听器, 项目进入运行状态
listeners.running(context);
}catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}- 获取所有RunListener (运行监听器) [为 了方便所有Listener进行事件感知] ---> getSpringFactoriesInstances 去spring.factories找SpringApplicationRunListener
https://www.yuque.com/atguigu/springboot/tmvr0e