Dubbo之Cluster路由
dubbo版本
- dubbo版本2.6.7
路由
-
服务目录(Directory)在刷新 Invoker 列表的过程中,会通过 Router 进行服务路由,筛选出符合路由规则的服务提供者。服务路由包含一条路由规则,路由规则决定了服务消费者的调用目标,即规定了服务消费者可调用哪些服务提供者
-
Dubbo提供了几种服务路由
- 条件路由 ConditionRouter:使用Dubbo定义的语法规则写路由规则
- 脚本路由 ScriptRouter:JDK自身的脚本引擎今夕路由规则脚本,默认是JavaScript
- 文件路由:需要提交一个文件,文件内容为对应的路由规则
- 标签路由 TagRouter(2.7.x)
-
UML图
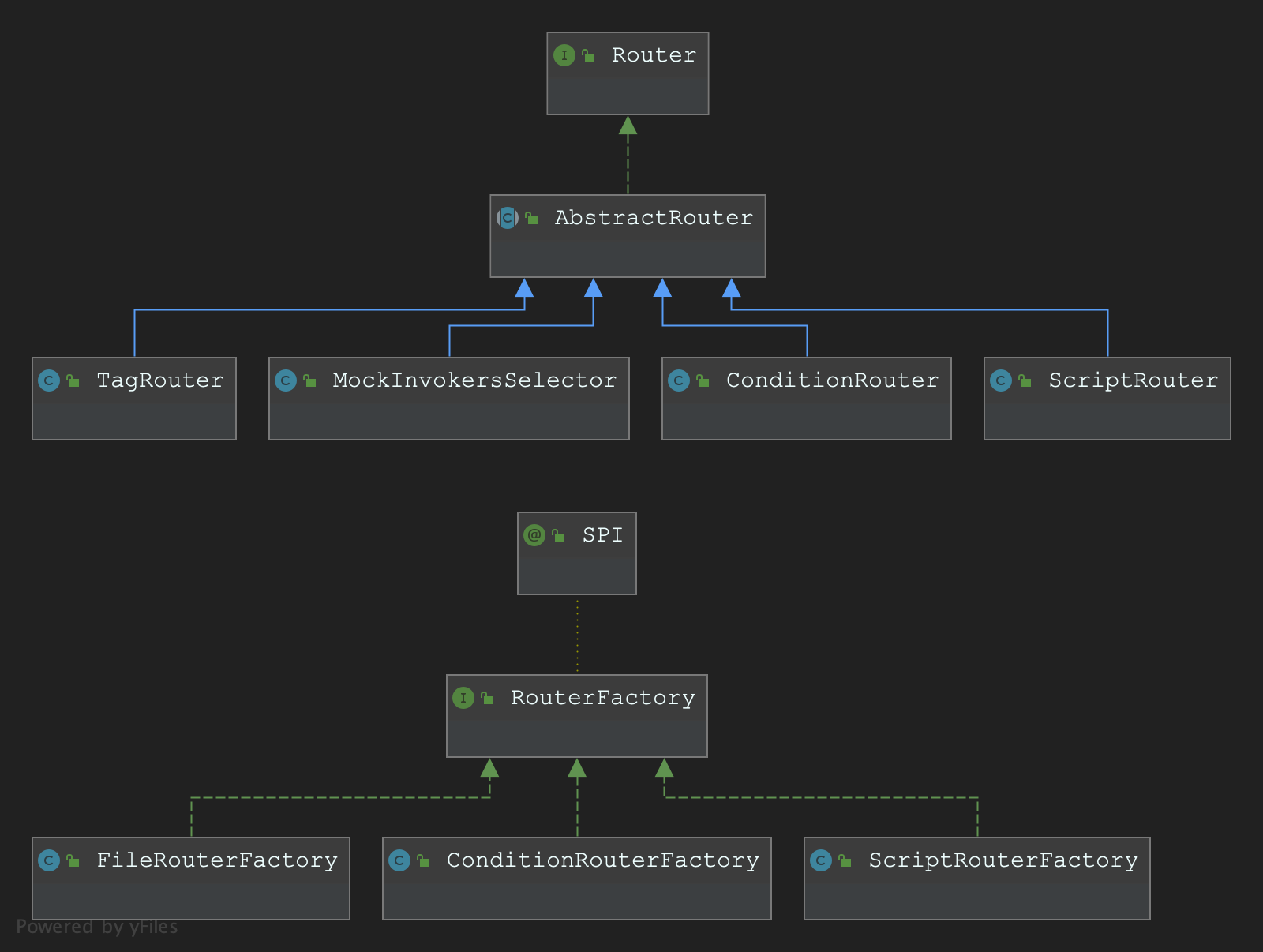
-
SPI配置文件的内容
file=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.router.file.FileRouterFactory script=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.router.script.ScriptRouterFactory condition=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.cluster.router.condition.ConditionRouterFactory -
所有的路由实现都需要实现Route接口,RouterFactory也是SPI扩展
public interface Router extends Comparable<Router>{ //路由的URL URL getUrl(); //核心方法,用于筛选出符合路由规则的Invoker列表 <T> List<Invoker<T>> route(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException; //优先级,排序使用 int getPriority(); } @SPI public interface RouterFactory { @Adaptive("protocol") Router getRouter(URL url); }
条件路由
-
条件路由规则由两个条件组成:[服务消费者匹配条件] => [服务提供者匹配条件]
-
新建一个测试用例,用于Debug源码,参考官方的测试用例ConditionRouterTest
@Test public void testRule() { String rule = "host = 172.16.117.33 => host = 2.2.2.2 & host != 1.1.1.1 & method = sayHello,sayHi"; Router router1 = new ConditionRouterFactory().getRouter(getRouteUrl(rule)); List<Invoker<String>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<String>>(); Invoker<String> invoker1 = new MockInvoker<String>(URL.valueOf( "dubbo://2.2.2.2:20880/cn.jannal.dubbo.facade.DemoService?default.serialization=fastjson")); invokers.add(invoker1); List<Invoker<String>> filterInvoker = router1.route(invokers, URL.valueOf("consumer://172.16.117.33/com.foo.BarService"), new RpcInvocation()); System.out.println(filterInvoker); Assert.assertEquals(1, filterInvoker.size()); }
规则解析
-
条件路由规则解析是在ConditionRouter的构造方法中完成的。主要逻辑是,通过
=>分隔出【左侧条件】和【右侧条件】,然后通过parseRule分别解析出左侧和右侧规则条件,并封装成一个Map<String, MatchPair>public class ConditionRouter extends AbstractRouter { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ConditionRouter.class); //路由器优先级,多个路由排序用,优先级越大越靠前执行 private static final int DEFAULT_PRIORITY = 2; private static Pattern ROUTE_PATTERN = Pattern.compile("([&!=,]*)\\s*([^&!=,\\s]+)"); // 是否强制执行路由规则,哪怕没有合适的invoker private final boolean force; //存放consumer路由规则,【=> 左边的内容】 private final Map<String, MatchPair> whenCondition; //存放provider路由规则 【=> 右边的内容】 private final Map<String, MatchPair> thenCondition; public ConditionRouter(URL url) { this.url = url; this.priority = url.getParameter(Constants.PRIORITY_KEY, DEFAULT_PRIORITY); this.force = url.getParameter(Constants.FORCE_KEY, false); try { //获取路由规则,以host = 172.16.117.33 => host = 2.2.2.2 & host != 1.1.1.1 & method = sayHello,sayHi为例 String rule = url.getParameterAndDecoded(Constants.RULE_KEY); if (rule == null || rule.trim().length() == 0) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal route rule!"); } //替换掉字符串里的"consumer." "provider." rule = rule.replace("consumer.", "").replace("provider.", ""); // 定位 => 分隔符 int i = rule.indexOf("=>"); //左侧和右侧的表达式 //左侧:host = 172.16.117.33 String whenRule = i < 0 ? null : rule.substring(0, i).trim(); //右侧host = 2.2.2.2 & host != 1.1.1.1 & method = sayHello,sayHi String thenRule = i < 0 ? rule.trim() : rule.substring(i + 2).trim(); /** * 解析服务消费者匹配规则。左侧如果为【空或者true】表示全匹配 * 最终的when表达式对象类似于 * { * "host":{ * "matches":["172.16.117.33"], * "mismatches":[] * } * } */ Map<String, MatchPair> when = StringUtils.isBlank(whenRule) || "true".equals(whenRule) ? new HashMap<String, MatchPair>() : parseRule(whenRule); /** * 解析服务提供者匹配规则。右侧如果为【空或者false】表示全匹配 * 最终的then为 * { * "host":{ * "matches":["2.2.2.2"], * "mismatches":["1.1.1.1"] * }, * "method":{ * "matches":["sayHello","sayHi'], * "mismatches":[] * } * } */ Map<String, MatchPair> then = StringUtils.isBlank(thenRule) || "false".equals(thenRule) ? null : parseRule(thenRule); // NOTE: It should be determined on the business level whether the `When condition` can be empty or not. // When条件是允许为空的,外部业务来保证类似的约束条件,解析构造的规则放在condition变量里 this.whenCondition = when; this.thenCondition = then; } catch (ParseException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } } ...省略.... } -
ConditionRouter#parseRule是解析规则的核心方法,解析规则会存放到Map<String, MatchPair>中,用于后续循环匹配规则。支持的规则分隔符有A=B、A&B、A!=B、A=C,D这4种形式private static Map<String, MatchPair> parseRule(String rule) throws ParseException { Map<String, MatchPair> condition = new HashMap<String, MatchPair>(); if (StringUtils.isBlank(rule)) { return condition; } // Key-Value pair, stores both match and mismatch conditions MatchPair pair = null; // Multiple values Set<String> values = null; // 通过正则表达式匹配路由规则,ROUTE_PATTERN = "([&!=,]*)\\s*([^&!=,\\s]+)" //1. 第一个括号,匹配& ! = , //2. 第二个括号,匹配英文字母,数字等字符,即非& ! = 字符 final Matcher matcher = ROUTE_PATTERN.matcher(rule); /** * 循环匹配host = 2.2.2.2 & host != 1.1.1.1 & method = sayHello * group(0) group(1) * "" host => MathPair * = 172.16.117.33 * & host => MathPair * !- 1.1.1.1 * & method => MathPair * = sayHello * , sayHi * 具体逻辑为 * 1. 如果分隔符是空或者&,则表示group(2)是一个条件K(这里host和method都属于) * 分隔符为空表示是起始处 * 2. 如果分隔符是, =和!=,则表示group(2)是一个条件的V值(这里2.2.2.2、1.1.1.1、sayHi、sayHello) */ while (matcher.find()) { // Try to match one by one // 获取括号一内的匹配结果 String separator = matcher.group(1); // 获取括号二内的匹配结果 String content = matcher.group(2); // Start part of the condition expression. // 分隔符为空,表示匹配的是表达式的开始部分 if (separator == null || separator.length() == 0) { pair = new MatchPair(); condition.put(content, pair); } // The KV part of the condition expression //分割符是&,表示也是一个条件 else if ("&".equals(separator)) { //如果获取不到MatchPair,则重新创建一个 if (condition.get(content) == null) { pair = new MatchPair(); condition.put(content, pair); } else { pair = condition.get(content); } } // The Value in the KV part. else if ("=".equals(separator)) { if (pair == null) throw new ParseException("Illegal route rule \"" + rule + "\", The error char '" + separator + "' at index " + matcher.start() + " before \"" + content + "\".", matcher.start()); values = pair.matches; // 将 content 存入到 MatchPair 的 matches 集合中 values.add(content); } // The Value in the KV part. else if ("!=".equals(separator)) { if (pair == null) throw new ParseException("Illegal route rule \"" + rule + "\", The error char '" + separator + "' at index " + matcher.start() + " before \"" + content + "\".", matcher.start()); values = pair.mismatches; values.add(content); } // The Value in the KV part, if Value have more than one items. else if (",".equals(separator)) { // Should be seperateed by ',' if (values == null || values.isEmpty()) throw new ParseException("Illegal route rule \"" + rule + "\", The error char '" + separator + "' at index " + matcher.start() + " before \"" + content + "\".", matcher.start()); //直接添加到上次的values中(上次是=或者!=null),matches或者mismatches values.add(content); } else { throw new ParseException("Illegal route rule \"" + rule + "\", The error char '" + separator + "' at index " + matcher.start() + " before \"" + content + "\".", matcher.start()); } } return condition; } -
MatchPair是私有的内部类
private static final class MatchPair { //匹配列表(对应=),内部用Set集合类型,防止重复。 MatchPai final Set<String> matches = new HashSet<String>(); //不匹配列表(对应!=) final Set<String> mismatches = new HashSet<String>(); //执行匹配规则的方法 private boolean isMatch(String value, URL param) { if (!matches.isEmpty() && mismatches.isEmpty()) { //只有允许项目 for (String match : matches) { if (UrlUtils.isMatchGlobPattern(match, value, param)) { return true; } } return false; } // 只匹配 mismatches if (!mismatches.isEmpty() && matches.isEmpty()) { for (String mismatch : mismatches) { if (UrlUtils.isMatchGlobPattern(mismatch, value, param)) { return false; } } return true; } // 匹配 matches和mismatches if (!matches.isEmpty() && !mismatches.isEmpty()) { //when both mismatches and matches contain the same value, then using mismatches first for (String mismatch : mismatches) { if (UrlUtils.isMatchGlobPattern(mismatch, value, param)) { return false; } } for (String match : matches) { if (UrlUtils.isMatchGlobPattern(match, value, param)) { return true; } } return false; } return false; } }
条件路由
-
route是路由的核心方法,用于筛选出符合路由规则的Invoker列表。
@Override public <T> List<Invoker<T>> route(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException { if (invokers == null || invokers.isEmpty()) { return invokers; } try { //consumer不在限制之内(比如when为空),全部放行,url是consumer。 if (!matchWhen(url, invocation)) { return invokers; } List<Invoker<T>> result = new ArrayList<Invoker<T>>(); //thenCondition为null表示拒绝一切请求 if (thenCondition == null) { logger.warn("The current consumer in the service blacklist. consumer: " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + ", service: " + url.getServiceKey()); return result; } for (Invoker<T> invoker : invokers) { //服务提供者,只要符合路由才能提供服务 if (matchThen(invoker.getUrl(), url)) { result.add(invoker); } } if (!result.isEmpty()) { return result; } else if (force) { //force强制执行路由。result即使是空的,也返回。如果为false,相当于不执行路由 logger.warn("The route result is empty and force execute. consumer: " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + ", service: " + url.getServiceKey() + ", router: " + url.getParameterAndDecoded(Constants.RULE_KEY)); return result; } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error("Failed to execute condition router rule: " + getUrl() + ", invokers: " + invokers + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } return invokers; } //匹配when boolean matchWhen(URL url, Invocation invocation) { return whenCondition == null || whenCondition.isEmpty() || matchCondition(whenCondition, url, null, invocation); } //匹配then private boolean matchThen(URL url, URL param) { return !(thenCondition == null || thenCondition.isEmpty()) && matchCondition(thenCondition, url, param, null); } -
matchCondition是匹配的核心方法
private boolean matchCondition(Map<String, MatchPair> condition, URL url, URL param, Invocation invocation) { //将服务提供者或消费者 url 转成 Map,即获取URL中变量 Map<String, String> sample = url.toMap(); boolean result = false; // 遍历 condition中所有的key(条件的K) for (Map.Entry<String, MatchPair> matchPair : condition.entrySet()) { // 获取匹配项key,比如 host、method 等 String key = matchPair.getKey(); String sampleValue; //get real invoked method name from invocation // 如果 invocation 不为空,且 key 为 mehtod或者methods,表示进行方法匹配 if (invocation != null && (Constants.METHOD_KEY.equals(key) || Constants.METHODS_KEY.equals(key))) { //获取被调用方法的名称 sampleValue = invocation.getMethodName(); } else { //从服务提供者或消费者 url 中获取指定字段值,比如 host、application 等 sampleValue = sample.get(key); if (sampleValue == null) { //如果不存在,则尝试获取default.值 sampleValue = sample.get(Constants.DEFAULT_KEY_PREFIX + key); } } if (sampleValue != null) { //如果获取的值不为空,则调用isMatch方法进行匹配 if (!matchPair.getValue().isMatch(sampleValue, param)) { // 只要有一个规则匹配失败,立即返回 false 结束方法逻辑 return false; } else { result = true; } } else { //not pass the condition // sampleValue 为空,表明服务提供者或消费者 url 中不包含相关字段。此时如果 // MatchPair 的 matches 不为空,表示匹配失败,返回 false。 if (!matchPair.getValue().matches.isEmpty()) { return false; } else { result = true; } } } return result; }
分类:
Dubbo2.6.x源码解析
标签:
Dubbo2.6.x源码分析




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· 分享 3 个 .NET 开源的文件压缩处理库,助力快速实现文件压缩解压功能!
· Ollama——大语言模型本地部署的极速利器
· DeepSeek如何颠覆传统软件测试?测试工程师会被淘汰吗?
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端