falco如何使用eBPF探针感知事件
Falco是一个开源的云原生安全工具,使用C++编写,主要用于监控、检测和响应运行中的容器环境中的安全事件。官方GitHub仓库(https://github.com/falcosecurity/falco). Falco可以检测和警告涉及Linux系统调用的任何行为。Falco的原理如下图所示,Falco警报是基于特定的system calls, arguments, and properties of the calling process触发的。Falco在用户空间和内核空间运行。系统调用由Falco内核模块解释。然后使用用户空间中的库分析系统调用。然后使用配置Falco规则的规则引擎对事件进行筛选。然后,可疑事件被警告到配置为Syslog、文件、标准输出和其他的输出。
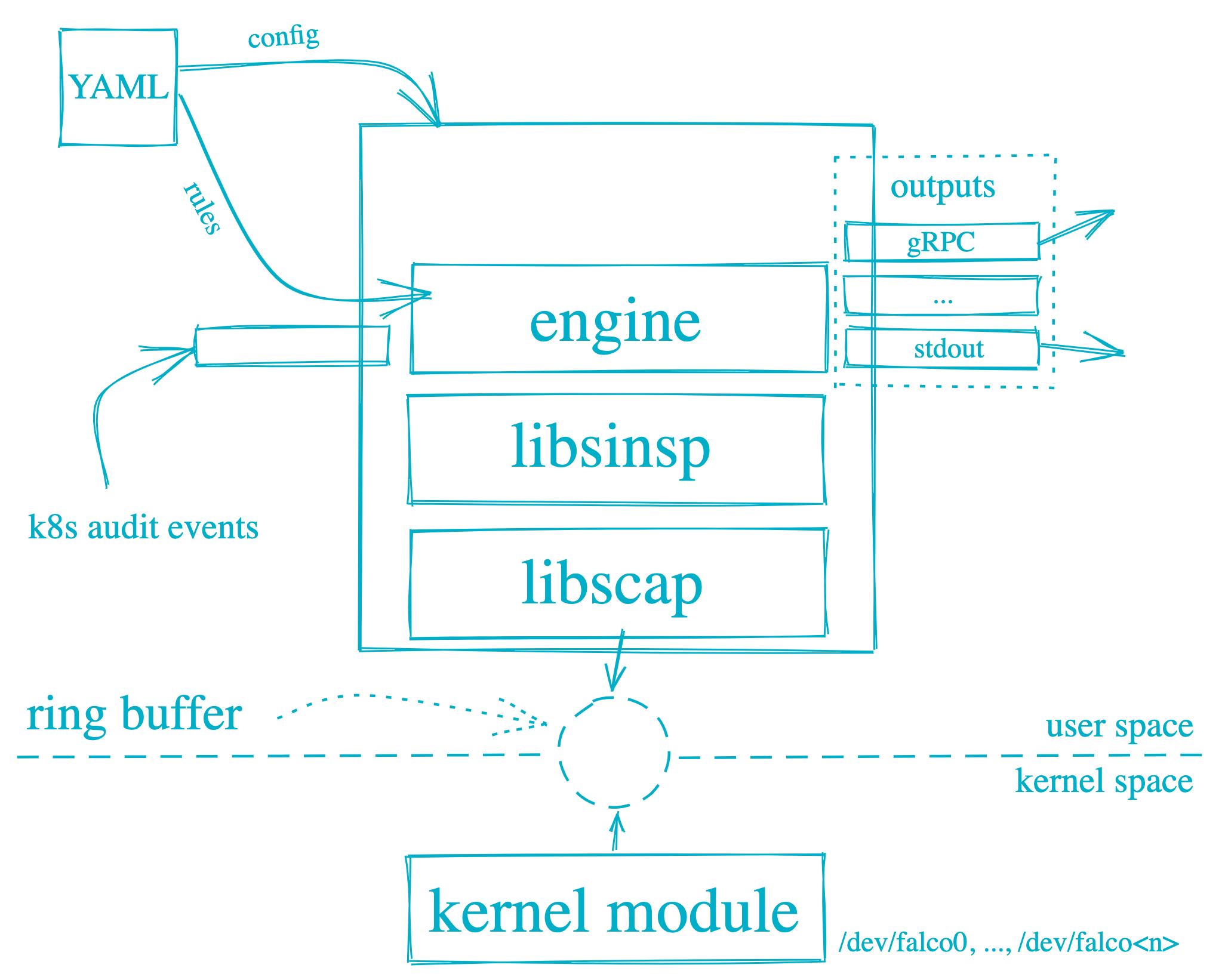
Falco的底层依赖sysdig开发的探针模块,架构图如下
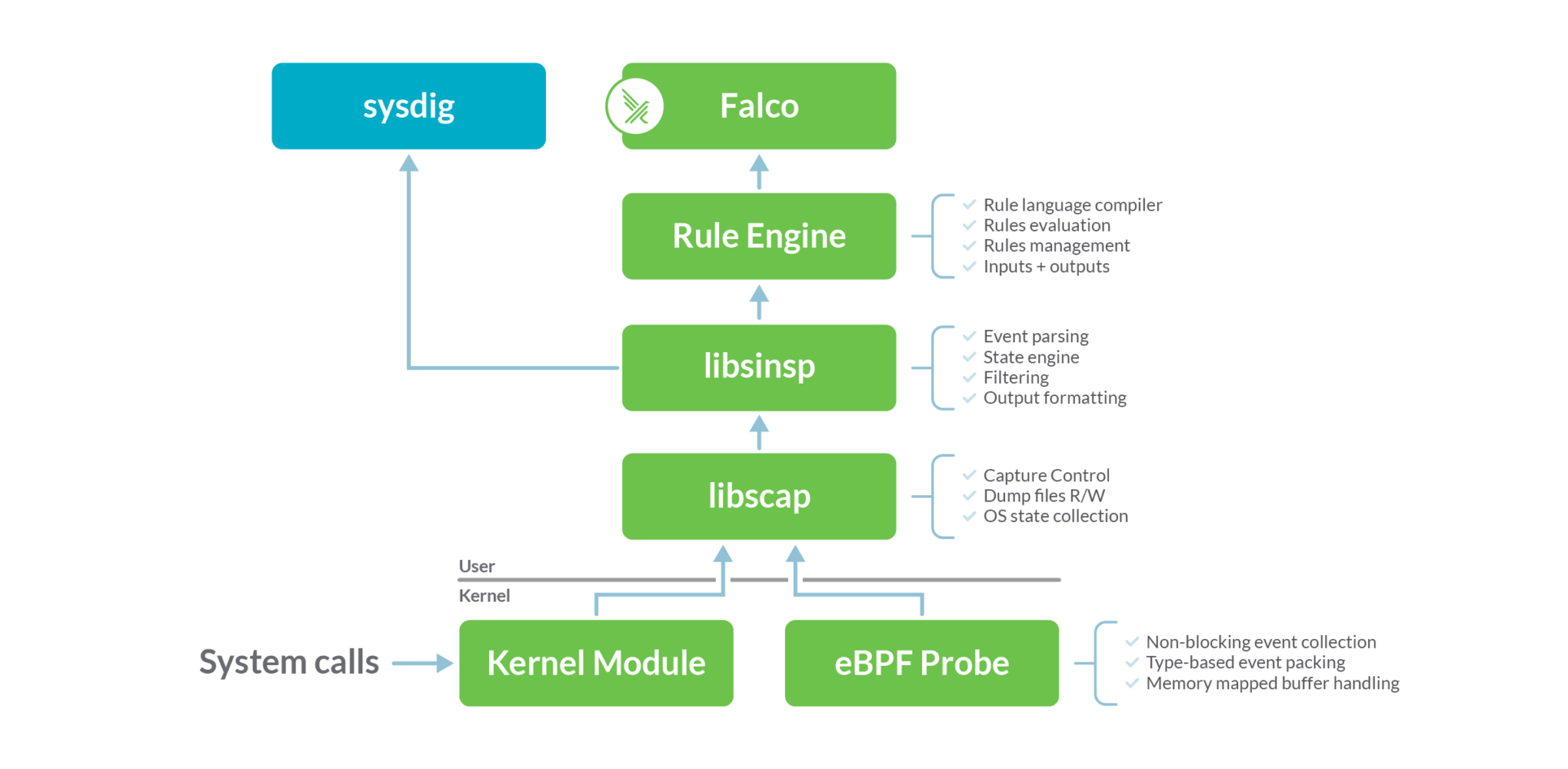
Falco和sysdig在相同的数据源上运行:系统调用。该数据源是使用内核模块或eBPF探针收集的。这两种方法在功能上是等效的,但是内核模块的效率稍微高一些,而eBPF方法更安全、更现代。Falco默认使用内核模块来收集系统调用,如果需要用eBPF探针则使用命令 falco --modern-bpf来运行进程
安装二进制falco
falco安装 falco的驱动有kernel module, ebpf 和 Modern eBPF. 我尝试的是kmod驱动,这种方式不要求很高的内核,支持的内核版本可以通过 https://download.falco.org/?prefix=driver/5.0.1%2Bdriver/x86_64/ 来查看,其中5.0.1是falco driver版本号,对应falco 0.35.1. 列表中的以.ko结尾的是kmod驱动,以.o结尾的是ebpf驱动。其中ebpf驱动要求的内核版本centos至少是4.18,ubuntu至少是4.15.
1. curl -L -O https://download.falco.org/packages/bin/x86_64/falco-0.34.1-x86_64.tar.gz
curl -L -O https://download.falco.org/?prefix=packages/bin/aarch64/falco-0.34.1-x86_64.tar.gz
2. tar -xvf falco-0.34.1-x86_64.tar.gz
cp -R falco-0.34.1-x86_64/* /
3. apt update -y
apt install -y dkms make linux-headers-$(uname -r)
# If you use the falco-driver-loader to build the BPF probe locally you need also clang toolchain
apt install -y clang llvm
4. # If you want to install the kernel module
falco-driver-loader module
# If you want to install the eBPF probe
falco-driver-loader bpf
以上命令成功后,系统会自动创建/dev/falco0 1 2...等文件,这些文件是驱动创建的设备文件,就是一个内核系统调用事件数据发送到用户空间的通道。程序启动后会去这里找这些文件,如果没有回报错。
5. # Kernel module (default driver)
falco
# eBPF probe
FALCO_BPF_PROBE="" falco
// modern eBPF probe
falco --modern-bpf
// For more info see all available options
falco --help
还可以以Daemonset的形式部署:https://github.com/falcosecurity/deploy-kubernetes/tree/main/kubernetes/falco/templates, 在已有集群中apply 这6个文件即可。这些YAML文件中有挂载本地文件的动作但是这些POD不依赖本地文件,但是,我目前运行起来后并不能实时告警(通过kubectl logs查看)过好久才有log. 关于falco daemonset 的配置说明可参考https://falco.org/docs/reference/daemon/config-options/
规则rule
关于容器创建的rule定义如下:
点击查看代码
- macro: container
condition: (container.id != host)
- macro: container_started
condition: >
((evt.type = container or
(spawned_process and proc.vpid=1)) and
container.image.repository != incomplete)
- macro: spawned_process
condition: evt.type = execve and evt.dir = <
Condition语法
支持的syscall event
Condition支持的字段和输出
从以上定义可以看出是事件的类型是容器或者创建进程并且该进程的vpid为1,并且要满足容器的镜像仓库地址完整。其中evt.type可以通过事件的属性https://falco.org/docs/reference/rules/supported-fields/ (或者通过二进制文件falco --list=syscall查询)意思是该事件的名称是container,很显然这个事件名称并不是像open这样的原始事件名称,我们后续再探究。下一个spawned_process是一个宏:事件名是execve并且是出方向,并且vpid属性(the id of the process generating the event as seen from its current PID namespace)是1.
falco的eBPF探针
以falco-0.34.1为例,探针代码在falco-0.34.1-x86_64/usr/src/falco-4.0.0+driver/bpf下面的probe.c中定义,有以下几种类型:
BPF_PROBE("raw_syscalls/", sys_enter, sys_enter_args)
BPF_PROBE("raw_syscalls/", sys_exit, sys_exit_args)
BPF_PROBE("sched/", sched_process_exit, sched_process_exit_args)
BPF_PROBE("sched/", sched_switch, sched_switch_args)
BPF_PROBE("exceptions/", page_fault_user, page_fault_args)
BPF_PROBE("exceptions/", page_fault_kernel, page_fault_args)
BPF_PROBE("signal/", signal_deliver, signal_deliver_args)
BPF_PROBE("sched/", sched_process_exec, sched_process_exec_args)
Falco 利用这些挂载的有限个数的基础事件来触发监控,然后通过在事件处理程序中执行 eBPF 程序,对更多的事件进行监控。Falco 的规则引擎和 eBPF 程序可以配合使用,通过条件匹配等方式,对各种事件进行筛选和处理。
下面以tracepoint:syscalls:sys_enter为例分析下,Falco是如何利用eBPF来采集系统调用的详细信息的。
点击查看代码
- sys_enter 表示 raw_syscalls分类下的 sys_enter_xxx 事件: tracepoint:raw_syscalls:sys_enter - sys_exit 表示 raw_syscalls分类下的 sys_exit_xxx 事件:tracepoint:raw_syscalls:sys_enter. 也就是说可以用 sys_enter 和 sys_exit 事件来监控所有系统调用事件 - sched_process_exit 表示sched分类下的进程退出事件 - sched_process_exec Tracepoint called after a exec-family syscall - sched_switch 进程或者线程切换? - page_fault_user 用户空间的缺页异常 - page_fault_kernel 内核空间的缺页异常 - signal_deliver 信号传递BPF_PROBE("raw_syscalls/", sys_enter, sys_enter_args)
{
...
// 获取系统调用的系统调用相关信息
id =bpf_syscall_get_nr(ctx);
sc_evt =get_syscall_info(id);
evttype = sc_evt->enter_event_type;
...
// 调用具体系统调用的信息采集方法
#ifdef BPF_SUPPORTS_RAW_TRACEPOINTS
call_filler(ctx, ctx, evt_type, settings, drop_flags);
#else
/* Duplicated here to avoid verifier madness */
structsys_enter_args stack_ctx;
memcpy(stack_ctx.args, ctx->args,sizeof(ctx->args));
if(stash_args(stack_ctx.args))
return0;
call_filler(ctx,&stack_ctx, evt_type, settings, drop_flags);#endif
return0;
}
点击查看代码
static __always_inline void call_filler(void *ctx,
void *stack_ctx,
enum ppm_event_typeevt_type,
struct sysdig_bpf_settings *settings,
enum syscall_flags drop_flags)
{
...
bpf_tail_call(ctx,&tail_map, filler_info->filler_id);
bpf_printk("Can't tail call fillerevt=%d, filler=%d\n",
state->tail_ctx.evt_type,
filler_info->filler_id);
...}
点击查看代码
struct bpf_map_def __bpf_section("maps") tail_map ={
.type = BPF_MAP_TYPE_PROG_ARRAY,
.key_size =sizeof(u32),
.value_size =sizeof(u32),
.max_entries = PPM_FILLER_MAX,
};
点击查看代码
#define FILLER(x,is_syscall) \
static__always_inline int__bpf_##x(struct filler_data *data); \
\
__bpf_section(TP_NAME "filler/" #x) \
static__always_inline int bpf_##x(void*ctx) \
{ \
struct filler_data data; \
intres; \
\
res=init_filler_data(ctx,&data,is_syscall); \
if(res==PPM_SUCCESS){ \
if(!data.state->tail_ctx.len) \
write_evt_hdr(&data); \
res=__bpf_##x(&data); \
} \
\
if(res==PPM_SUCCESS) \
res=push_evt_frame(ctx,&data); \
\
if(data.state) \
data.state->tail_ctx.prev_res=res; \
\
bpf_tail_call(ctx,&tail_map,PPM_FILLER_terminate_filler);\
bpf_printk("Can't tail call terminate filler\n"); \
return 0; \
} \
\
static__always_inline int __bpf_##x(struct filler_data *data) \
FILLER(sys_open_x,true)
{
...
// 调用参数采集
res = bpf_val_to_ring(data, dev);
return res;
}
FILLER(sys_empty,true)
...
点击查看代码
static __always_inline int __bpf_sys_open_x(struct filler_data *data);
__bpf_section(TP_NAME "filler/" sys_open_x)
static __always_inline int bpf_sys_open_x(void *ctx)
{
...
// 调用实际的信息获取的方法,采集系统调用信息
res = __bpf_sys_open_x(&data);
...
if(res == PPM_SUCCESS)
// 将采集的数据发送给用户态程序
res = push_evt_frame(ctx,&data);
...
}
static __always_inline int __bpf_sys_open_x(struct filler_data *data)
{
...
// 调用参数采集,并将结果填充到data结构体中
if(retval <0||!bpf_get_fd_dev_ino(retval,&dev,&ino))
dev =0;
res = bpf_val_to_ring(data, dev);
return res;
}
static __always_inline int push_evt_frame(void *ctx,
struct filler_data *data)
{
...
#ifdef BPF_FORBIDS_ZERO_ACCESS
int res = bpf_perf_event_output(ctx,
&perf_map,
BPF_F_CURRENT_CPU,
data->buf,
((data->state->tail_ctx.len -1)& SCRATCH_SIZE_MAX)+1);
#else
int res = bpf_perf_event_output(ctx,
&perf_map,
BPF_F_CURRENT_CPU,
data->buf,
data->state->tail_ctx.len & SCRATCH_SIZE_MAX);
#endif
点击查看代码
struct bpf_map_def __bpf_section("maps") perf_map ={
.type = BPF_MAP_TYPE_PERF_EVENT_ARRAY,
.key_size =sizeof(u32),
.value_size =sizeof(u32),// 只能是 sizeof(u32) ,代表的是 perf_event 的文件描述符
.max_entries =0,//是perf_event 的文件描述符数量。
};
在这时用户态程序就可以从perf 缓冲区中获取到记录数据,传入Falco的规则引擎中进行匹配分析。
另外需要说明的问题,在Falco的eBPF模块中falco-0.34.1-x86_64/usr/src/falco-4.0.0+driver/main.c,没有明显的main函数,因为内核模块的初始化通常由模块初始化函数,在驱动程序中,模块的初始化函数通常由module_init宏来标记,它告诉内核在加载模块时调用哪个函数而不是一个传统的main函数。
falco用户空间实现
falco/userspace/falco/falco.cpp 中的main函数,然后调用app/app.cpp中的falco::app::run函数,这个函数列出了所有要被调用到的方法,详情如下
点击查看代码
bool falco::app::run(falco::app::state& s, bool& restart, std::string& errstr)
{
// The order here is the order in which the methods will be
// called. Before changing the order, ensure that all
// dependencies are honored (e.g. don't process events before
// loading plugins, opening inspector, etc.).
std::list<app_action> run_steps = {
falco::app::actions::load_config,
falco::app::actions::print_help,
falco::app::actions::print_version,
falco::app::actions::print_page_size,
falco::app::actions::print_generated_gvisor_config,
falco::app::actions::print_ignored_events,
falco::app::actions::print_syscall_events,
falco::app::actions::require_config_file,
falco::app::actions::print_plugin_info,
falco::app::actions::list_plugins,
falco::app::actions::load_plugins,
falco::app::actions::init_inspectors,
falco::app::actions::init_falco_engine,
falco::app::actions::list_fields,
falco::app::actions::select_event_sources,
falco::app::actions::validate_rules_files,
falco::app::actions::load_rules_files,
falco::app::actions::print_support,
falco::app::actions::init_outputs,
falco::app::actions::create_signal_handlers,
falco::app::actions::create_requested_paths,
falco::app::actions::pidfile,
falco::app::actions::init_clients,
falco::app::actions::configure_interesting_sets,
falco::app::actions::configure_syscall_buffer_size,
falco::app::actions::configure_syscall_buffer_num,
falco::app::actions::start_grpc_server,
falco::app::actions::start_webserver,
falco::app::actions::process_events,
};
std::list<app_action> teardown_steps = {
falco::app::actions::unregister_signal_handlers,
falco::app::actions::stop_grpc_server,
falco::app::actions::stop_webserver,
};
...
falcosecurity/libs/tree/master/userspace/libsinsp/sinsp.cpp 中的函数 open_bpf(),然后该函数调用open_common(),open_common调用scap_alloc()函数。就到了libscap库中了。open_common又调用scap_init()函数,scap_init又调用scap_init_live_int().
另外可以关注几个关键函数:handle_event()用于输出函数,
libscap加载
falcosecurity-libs/userspace/libscap/engine/bpf/scap_bpf.c init()开始,该函数调用scap_bpf_load(). scap_bpf_load又下调用load_bpf_file()和load_all_progs()随即用ioctl(pmu_fd, PERF_EVENT_IOC_ENABLE, 0)使能event,
参考文献
[1]. http://blog.nsfocus.net/falco-ebpf/
[2]. https://lwn.net/Articles/645169/
[3]. https://www.ebpf.top/post/bpf_ring_buffer




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】
· [AI/GPT/综述] AI Agent的设计模式综述