今天我们来说一下关于JDBC的相关知识,关于JDBC我想大家都不陌生了,而且我记得早就开始使用它了,记得那是大二的时候做课程设计,但是那时候是为了完成任务,所以遇到问题就google,那时候也没有时间去整理,所以这次就来详细说一下关于JDBC的知识
摘要:
JDBC(Java Data Base Connectivity,java数据库连接),由一些接口和类构成的API。
J2SE的一部分,由java.sql,javax.sql包组成。
应用程序、JDBC API、数据库驱动及数据库之间的关系
![]()
JDBC的使用步骤
1.注册驱动 (只做一次)
方式一:Class.forName(“com.mysql.jdbc.Driver”);
推荐这种方式,不会对具体的驱动类产生依赖。
方式二:DriverManager.registerDriver(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver);
会造成DriverManager中产生两个一样的驱动,并会对具体的驱动类产生依赖。
方式三:System.setProperty(“jdbc.drivers”, “driver1:driver2”);
虽然不会对具体的驱动类产生依赖;但注册不太方便,所以很少使用。
驱动类型(四种类型)
2.建立连接(Connection)
-
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
url格式:
JDBC:子协议:子名称//主机名:端口/数据库名?属性名=属性值&…
User,password可以用“属性名=属性值”方式告诉数据库;
其他参数如:useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=GBK。
3.创建执行SQL的语句(Statement)
-
Statement
-
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
-
st.executeQuery(sql);
-
PreparedStatement
-
String sql = “select * from table_name where col_name=?”;
-
PreparedStatement ps = conn.preparedStatement(sql);
-
ps.setString(1, “col_value”);
-
ps.executeQuery();
4.处理执行结果(ResultSet)
-
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(sql);
-
While(rs.next()){
-
rs.getString(“col_name”);
-
rs.getInt(“col_name”);
-
-
}
5.释放资源
释放ResultSet, Statement,Connection.
数据库连接(Connection)是非常稀有的资源,用完后必须马上释放,如果Connection不能及时正确的关闭将导致系统宕机。Connection的使用原则是尽量晚创建,尽量早的释放。
下面来看一下完整的Demo:
工具类:JdbcUtils
-
package com.weijia.firstdemo;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.DriverManager;
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
import java.sql.Statement;
-
-
import javax.sql.DataSource;
-
-
public class JdbcUtils {
-
-
private static String user = "root";
-
private static String password = "123456";
-
private static String dbName = "test";
-
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/"+dbName+"?user="+user+"&password="+password+"&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=gb2312";
-
-
private static DataSource dataSource = null;
-
-
-
-
-
static{
-
try{
-
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
System.out.println("Exception:"+e.getMessage()+"");
-
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
-
}
-
}
-
-
private JdbcUtils(){
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException{
-
return DriverManager.getConnection(url);
-
}
-
-
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
-
return dataSource;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static void free(ResultSet rs,Statement st,Connection conn){
-
try{
-
if(rs != null){
-
rs.close();
-
}
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
try{
-
if(st != null){
-
st.close();
-
}
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
try{
-
if(conn != null){
-
conn.close();
-
}
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
}
测试类:
-
package com.weijia.firstdemo;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.DriverManager;
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
import java.sql.Statement;
-
-
public class Demo {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
-
test();
-
-
template();
-
}
-
-
-
public static void template(){
-
Connection conn = null;
-
Statement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try {
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
st = conn.createStatement();
-
-
rs = st.executeQuery("select * from user");
-
-
while(rs.next()){
-
System.out.println(rs.getObject(1) + "\t" + rs.getObject(2) + "\t" + rs.getObject(3) + "\t");
-
}
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
-
DriverManager.registerDriver(new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver());
-
-
System.setProperty("jdbc.drivers","");
-
-
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
-
-
-
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306";
-
String userName = "root";
-
String password = "";
-
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url,userName,password);
-
-
-
Statement st = conn.createStatement();
-
-
-
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from user");
-
-
-
while(rs.next()){
-
System.out.println(rs.getObject(1) + "\t" + rs.getObject(2) + "\t" + rs.getObject(3) + "\t");
-
}
-
-
-
rs.close();
-
st.close();
-
conn.close();
-
}
-
-
}
注意:这里还要记住引入额外的jar.这个网上很多的,这里使用的是MySql,搜一下MySql驱动的jar就行了。这里我们将一些操作都放到一个工具类中,这种方式是很优雅的。
使用JDBC来实现CRUD的操作
我们这里就采用分层操作:Dao层,Service层
首先看一下domain域中的User实体
-
package com.weijia.domain;
-
-
import java.util.Date;
-
-
public class User {
-
-
private int id;
-
private String name;
-
private Date birthday;
-
private float money;
-
-
public User(){
-
-
}
-
-
public User(int id,String name,Date birthday,float money){
-
this.id = id;
-
this.name = name;
-
this.birthday = birthday;
-
this.money = money;
-
}
-
-
public int getId() {
-
return id;
-
}
-
public void setId(int id) {
-
this.id = id;
-
}
-
public String getName() {
-
return name;
-
}
-
public void setName(String name) {
-
this.name = name;
-
}
-
public Date getBirthday() {
-
return birthday;
-
}
-
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
-
this.birthday = birthday;
-
}
-
public float getMoney() {
-
return money;
-
}
-
public void setMoney(float money) {
-
this.money = money;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public String toString(){
-
return "[id="+id+",name="+name+",birthday="+birthday+",money="+money+"]";
-
}
-
}
再来看一下Dao层结构:
接口:
-
package com.weijia.domain;
-
-
public interface UserDao {
-
-
-
public void addUser(User user);
-
-
public User getUserById(int userId);
-
-
public int update(User user);
-
-
public int delete(User user);
-
-
}
实现类:
-
package com.weijia.domain;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.Date;
-
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
-
import com.weijia.firstdemo.JdbcUtils;
-
-
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
-
-
-
-
-
public void addUser(User user) {
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "insert into user(id,name,birthday,money) values(?,?,?,?)";
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
st.setInt(1,user.getId());
-
st.setString(2,user.getName());
-
-
st.setDate(3,new Date(user.getBirthday().getTime()));
-
st.setFloat(4, user.getMoney());
-
int count = st.executeUpdate();
-
System.out.println("添加记录条数:"+count);
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new DaoException(e.getMessage(),e);
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
public int delete(User user) {
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "delete from user where id=?";
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
st.setInt(1,user.getId());
-
int count = -1;
-
count = st.executeUpdate();
-
System.out.println("删除记录条数:"+count);
-
return count;
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new DaoException(e.getMessage(),e);
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
public User getUserById(int userId) {
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "select * from user where id=?";
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
st.setInt(1,userId);
-
rs = st.executeQuery();
-
if(rs.next()){
-
User user = new User();
-
user.setId(userId);
-
user.setName(rs.getString("name"));
-
user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
-
user.setMoney(rs.getFloat("money"));
-
return user;
-
}
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new DaoException(e.getMessage(),e);
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn);
-
}
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
public int update(User user){
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "update user set name=?,birthday=?,money=? where id=?";
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
st.setString(1,user.getName());
-
st.setDate(2,new Date(user.getBirthday().getTime()));
-
st.setFloat(3,user.getMoney());
-
st.setInt(3,user.getId());
-
int count = 0;
-
count = st.executeUpdate();
-
System.out.println("更新的记录数:"+count);
-
return count;
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new DaoException(e.getMessage(),e);
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
然后是Servic层:
-
package com.weijia.domain;
-
-
public class UserService {
-
-
private UserDao userDao;
-
-
public UserService(){
-
-
userDao = DaoFactory.getInstance().createUserDao();
-
System.out.println("userDao:"+userDao);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
public void regist(User user){
-
if(user == null){
-
System.out.println("注册信息无效!!");
-
}else{
-
userDao.addUser(user);
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public User query(int userId){
-
User user = userDao.getUserById(userId);
-
if(user == null){
-
System.out.println("查询结果为空!!");
-
}else{
-
System.out.println(user.getId()+"\t"+user.getName()+"\t"+user.getBirthday()+"\t"+user.getMoney());
-
}
-
return userDao.getUserById(userId);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
public void update(User user){
-
if(user.getId()<=0){
-
System.out.println("用户id无效,无法更新");
-
}else{
-
userDao.update(user);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
public void delete(User user){
-
if(user.getId()<=0){
-
System.out.println("用户id无效,无法删除!!");
-
}else{
-
userDao.delete(user);
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
这里我们还需要额外的两个类:
一个是异常类,因为我们需要自定义我们自己的一个异常,这样方便进行捕获:
-
package com.weijia.domain;
-
-
public class DaoException extends RuntimeException{
-
-
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
-
-
public DaoException(){
-
-
}
-
-
public DaoException(Exception e){
-
super(e);
-
}
-
-
public DaoException(String msg){
-
super(msg);
-
}
-
-
public DaoException(String msg,Exception e){
-
super(msg,e);
-
}
-
-
}
同时,我们这里面采用工厂模式进行实例化UserDao对象:
-
package com.weijia.domain;
-
-
import java.io.FileInputStream;
-
import java.util.Properties;
-
-
public class DaoFactory {
-
-
-
-
private static UserDao userDao = null;
-
private static DaoFactory instance = new DaoFactory();
-
-
private DaoFactory(){
-
-
-
-
Properties prop = new Properties();
-
try{
-
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("src/com/weijia/domain/daoconfig.properties");
-
prop.load(fis);
-
String className = prop.getProperty("userDaoClass");
-
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
-
userDao = (UserDao)clazz.newInstance();
-
fis.close();
-
}catch(Throwable e){
-
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
-
}
-
}
-
-
public static DaoFactory getInstance(){
-
return instance;
-
}
-
-
public UserDao createUserDao(){
-
return userDao;
-
}
-
-
}
这里面是读取properties文件,然后去读取类名进行加载,这种方式是很灵活的
测试:
-
package com.weijia.domain;
-
-
import java.util.Date;
-
-
public class TestDemo {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
UserService userService = new UserService();
-
System.out.println("添加用户:");
-
userService.regist(new User(1,"jiangwei",new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()),300));
-
}
-
-
}
这里我们看到其实这些操作真的很简单,就是按照那样的几个步骤来操作即可,同时我们还需要将结构进行分层,以便管理,我们这里面测试的时候,撇开了创建数据库的一个环节,至于那个环节,也是不难的,可以从网上搜索一下即可。
Statement中的sql依赖注入的问题
接着来看一下关于我们上面的例子中使用了Statement进行操作的,其实这里面是存在一个问题的,就是会有sql注入的问题,我们先来看一下这个问题:
查询学生信息:
-
-
-
-
-
-
static void read(String name) throws SQLException{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
Statement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try {
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
st = conn.createStatement();
-
-
String sql = "select id,name from user where name='"+name+"'";
-
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
-
-
while(rs.next()){
-
System.out.println(rs.getObject("id") + "\t" + rs.getObject("name") + "\t");
-
}
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
我们使用代码测试一下:
我们运行会发现,将查询出所有的学生的记录,这个是什么原因呢?我们不妨将sql打印一下会发现:
-
select id,name from user where name=''or 1 or''
擦,因为sql语句中把1认为是true,又因为是或的关系,所以将所有的学生的信息查询出来了,这个就是sql注入,因为Statement会把传递进来的参数进行一下转化操作,用引号包含一下,所以会出现这个问题,那么我们该怎么解决呢?有的同学说我们可以添加一句过滤的代码,将传递的参数取出单引号,这个方法是可行的的,但是这个只能解决那些使用单引号的数据库,可能有的数据库使用的是双引号包含内容,那就不行了,所以应该想一个全套的方法,那么这里我们就是用一个叫做:PreparedStatement类,这个类是Statement类的子类,关于这两个类的区别可以查看我的另外一片文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/jiangwei0910410003/article/details/26143977
我们这里只看这个sql注入的问题:
我们将上面读取用户信息的代码改写成PreparedStatement:
-
-
-
-
-
-
static void readPrepared(String name) throws SQLException{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
String sql = "select id,name from user where name=?";
-
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
st.setString(1, name);
-
rs = st.executeQuery();
-
-
while(rs.next()){
-
System.out.println(rs.getObject("id") + "\t" + rs.getObject("name") + "\t");
-
}
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
-
}
-
}
之后我们在执行:
-
readPrepared("'or 1 or'");
就不会全部查出来了,只会查询空结果,因为表中没有一个学生的名字叫做 'or 1 or'。
JDBC中特殊数据类型的操作问题
第一个是日期问题:
我们在操作日期问题的时候会发现,使用PreparedStatement进行参数赋值的时候,有一个方法是:setDate(...),但是这个方法接收的参数是sql中的Date类,而不是我们平常使用的util中的Date类,所以我们要做一次转化,通常我们是这样做的,就是在定义实体类的时候将其日期型的属性定义成util中的Date类型,在进行数据库操作的时候.
进行一次转换:setDate(x,new Date(birthday.getTime());,这里birthday就是一个util.Date类型的一个属性,而new Date是sql.Date类型的,这样转化就可以了,同样我们在读取数据的时候将转化操作反过来即可。
第二个问题就是大文本数据的问题
因为有时候我们会存入一些文本内容,因为varchar的大小在mysql中也是有上线的,所以我们这里要使用blob类型了,我们这里来看一下实例:
-
-
-
-
static void insert(){
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement ps = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "insert into clob_test(bit_text) values(?)";
-
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
File file = new File("src/com/weijia/type/ClubDemo.java");
-
Reader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(file));
-
-
ps.setCharacterStream(1, reader, (int)file.length());
-
ps.executeUpdate();
-
reader.close();
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs,ps,conn);
-
}
-
}
我们将一个Java代码文件插入到数据库中
我们查询一下clob_test表:
![]()
我们看到文件内容存入到库中了。同样我们也可以从表中读取一段文本出来,使用
-
Clob clob = rs.getClob(1);
-
InputStream is = clob.getAsciiStream();
或者读取一个Reader也是可以的,这里的InputStream和Reader是针对不同流,一个字节流,这个不需要关心编码问题的,Reader是字符流需要关心编码问题。
JDBC中事务的概念
我们当初在学习数据库的时候就了解事务的概念了,事务在数据库中的地位是很重要的。在JDBC中默认情况事务是自动提交的,所以我们在进行CRUD操作的时候不需要关心开启事务,提交事务,事务回滚的一些操作,那么下面我们就来看一下怎么手动的操作一些事务:
下载我们假定这样的一个场景:
有来两个用户1和2,现在
将用户1中的账户的钱减少10
查询用户2中的账户的钱,如果钱少于300,就增加10,否则抛出异常
看一下代码:
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
Statement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
-
st = conn.createStatement();
-
-
String sql = "update user set money=money-10 where id=1";
-
st.executeUpdate(sql);
-
-
sql = "select money from user where id=2";
-
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
-
float money = 0.0f;
-
if(rs.next()){
-
money = rs.getFloat("money");
-
}
-
if(money>300){
-
throw new RuntimeException("已经超过最大值");
-
}
-
sql = "update user set money=money+10 where id=2";
-
st.executeUpdate(sql);
-
conn.commit();
-
-
}catch(RuntimeException e){
-
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
我们运行测试一下,因为我们这里想让它抛出异常,所以我们将用户2中的钱改成大于300的,运行一下,结果抛出异常了,但是我们发现了用户1中的钱少了10,但是由于抛出异常,所以后面的代码不执行了,用户2中的钱没有变化,那么这样的操作明显不对的,所以我们这时候要解决这个问题,使用事务的回滚操作,在捕获到异常的时候需要做回滚操作:
-
if(conn != null){
-
conn.rollback();
-
}
这样即使抛出了异常,这些操作也会进行回滚的,那么用户1中的钱就不会少10了。
同时上面我们看到,我们是在开始的时候手动的关闭事务的自动提交,然后再手动的提交事务,下面再来看一下事务的保存点的问题。
场景:在上面的基础上,我们添加一个用户3,同时对用户1和用户3中的钱进行减少10,用户2的操作不变,但是当抛出异常的时候,我们希望用户1的操作还是有效的,用户3的操作还原,这时候我们需要将事务回滚到用户3的那个点就可以了,这就是事务的保存点的概念,看一下代码:
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
Statement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
Savepoint sp = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
-
st = conn.createStatement();
-
-
String sql = "update user set money=money-10 where id=1";
-
st.executeUpdate(sql);
-
sp = conn.setSavepoint();
-
-
sql = "update user set money=money-10 where id=3";
-
st.executeUpdate(sql);
-
-
sql = "select money from user where id=2";
-
rs = st.executeQuery(sql);
-
float money = 0.0f;
-
if(rs.next()){
-
money = rs.getFloat("money");
-
}
-
System.out.println("money:"+money);
-
if(money>300){
-
throw new RuntimeException("已经超过最大值");
-
}
-
sql = "update user set money=money+10 where id=2";
-
st.executeUpdate(sql);
-
conn.commit();
-
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
if(conn != null && sp != null){
-
conn.rollback(sp);
-
conn.commit();
-
}
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
我们在用户1之后设置一个保存点,在异常中只需要回滚到保存点就可以了。
下面再来看一下事务的隔离级别,因为这部分的内容比较重要和繁琐,请看另外一篇文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/jiangwei0910410003/article/details/24960785
JDBC中调用存储过程
关于MySql中的存储过程的知识请看这两篇文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/jiangwei0910410003/article/details/24964331
http://blog.csdn.net/jiangwei0910410003/article/details/24965087
当我们会创建存储过程的时候,我们在到JDBC中去调用这个存储过程,
下面看一下实例:
我们现在想在插入一条数据的时候能够得到主键id的值(因为我们一般把主键id的值设置成自增长的形式),首先来创建一个存储过程:
-
delimiter $$
-
drop procedure if exists addUser $$
-
create procedure addUser(in name varchar(45),in birthday date,in money float,out pid int)
-
begin
-
insert into user(name,birthday,money) values(anme,birthday,money);
-
select last_insert_id() into pid;
-
end $$
-
delimiter ;
这里name,birthday,money都是输入值是:in
pid是输出值:out
然后我们在代码中进行执行这个存储过程:
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
CallableStatement cs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
-
String sql = "{ call addUser(?,?,?,?)}";
-
cs = conn.prepareCall(sql);
-
cs.registerOutParameter(4, Types.INTEGER);
-
cs.setString(1,"jiangwei");
-
cs.setDate(2,new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
-
cs.setFloat(3,300);
-
cs.executeUpdate();
-
-
int id = cs.getInt(4);
-
System.out.println("id:"+id);
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
这样我们就得到了插入一条记录的时候得到他的主键id的值
其实这种调用存储结构的方法,在早起的时候是很实用的,因为那时候没有分层架构的思想,所以会将业务逻辑层的实现放到存储过程中去做了,在调用存储过程的时候,会发现一个问题就是这样去获取主键id的值的方式,是不通用的,因为不同的数据库可能存储过程的编写是不一样的,所以做不到一致性,而且现在有了三成架构的思想,我们慢慢的就将这种方式给淘汰了,而是直接使用JDBC给我们提供的一套api来获取主键key的值:直接上代码吧:
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
java.sql.Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement ps = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "insert into user(name,birthday,money) values('jiangwei','1987-01-01',400)";
-
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
-
ps.executeUpdate();
-
-
rs = ps.getGeneratedKeys();
-
int id = 0;
-
if(rs.next()){
-
id = rs.getInt(1);
-
}
-
System.out.println("id:"+id);
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs,ps,conn);
-
}
-
}
我们只要设置一个参数Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS就可以得到一个主键集合了,这里要注意的是,因为有的表结构中会出现组合主键的情况,所以返回的是一个主键集合。这种方式就和底层数据库摆脱了关系,做到一致性了。
JDBC来实现批处理功能
我们在前面的例子中会发现,每次都是执行一条语句,然后关闭连接,这样效率可能会很低,如果我们想一次插入几千条数据的话,这时候可以使用批处理的功能,所谓批处理就是将多个执行语句进行捆绑然后去执行,但是效率上并非就一定高,因为我们知道这个数据库连接是tcp的,所以在将多个语句捆绑在一起的时候,在传输的过程中也是会进行分包发送的,这个包的大小也不是固定的,这个大小很难掌控的,我们之后经过多次测试之后,才能得到一次批量处理的适宜数量。下面来看一下实例吧:
首先是普通的插入一条数据:
-
static void create() throws Exception{
-
-
-
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement ps = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "insert user(name,birthday,money) values(?,?,?)";
-
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
-
ps.setString(1,"jiangwei");
-
ps.setDate(2,new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
-
ps.setFloat(3,400);
-
ps.executeUpdate();
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn);
-
}
-
}
然后是批处理插入100条数据:
-
static void createBatch() throws Exception{
-
-
-
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement ps = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
String sql = "insert user(name,birthday,money) values(?,?,?)";
-
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
-
-
-
-
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
-
ps.setString(1,"jiangwei");
-
ps.setDate(2,new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()));
-
ps.setFloat(3,400);
-
-
ps.addBatch();
-
}
-
ps.executeBatch();
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs, ps, conn);
-
}
-
}
测试代码:
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
-
for(int i=0;i<100;i++){
-
create();
-
}
-
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
-
System.out.println("For Waste Time:"+(endTime-startTime));
-
createBatch();
-
System.out.println("Batch Waste Time:"+(System.currentTimeMillis()-endTime));
-
}
我们在控制台中看到他们分别消耗的时间:
![]()
我们可以看到这个批处理消耗的时间明显很少。。当然我们在开始的时候也说过了,这个批处理的最适宜的大小要掌控好。
JDBC中的滚动结果集和分页技术
我们在前面的例子中可以看到,在处理结果集的时候,我们都是一条一条向后处理的,但是有时候我们需要人为的控制结果集的滚动,比如我们想往前滚动,想直接定位到哪个结果集记录等操作,当然JDBC也是提供了一套Api让我们来操作的
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
Statement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
st = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
-
rs = st.executeQuery("select id,name,money,birthday from user");
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
rs.absolute(2);
-
System.out.println("id="+rs.getInt("id")+"\tname="+rs.getString("name")+"\tbirthday="+rs.getDate("birthday")+"\tmoney="+rs.getFloat("money"));
-
-
-
rs.beforeFirst();
-
-
-
rs.afterLast();
-
-
rs.isFirst();
-
rs.isLast();
-
rs.isAfterLast();
-
rs.isBeforeFirst();
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs,st,conn);
-
}
-
}
我们看到结果集:rs有很多方法的,我们一次来看一下:
next():这个很常用的,就是将结果集向后滚动
previous():这个方法和next是相反的,将结果集向前滚动
absolute(int index):这个方法是将结果集直接定位到指定的记录上,这个参数是从1开始的,不是0,如果不在指定的范围内的话,会报告异常的
beforeFirst():这个方法是将结果集直接滚动到第一条记录的前面的位置(默认情况是这样的,所以我们每次在取出数据的时候,需要使用next方法,将结果集滚动到第一条记录上)
afterLast():这个方法是将结果集直接滚动到最后一条记录的后面的位置
isFirst():判断是不是在第一行记录
isLast():判断是不是在最后一行记录
isAfterLast():判断是不是第一行前面的位置
isBeforeFirst():判断是不是最后一行的后面的位置
当然我们要向实现可滚动的结果集,还要设置一下参数:
-
st = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE,ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY);
参数的含义:
ResultSet.RTYPE_FORWORD_ONLY:这是缺省值,只可向前滚动;
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_INSENSITIVE:双向滚动,但不及时更新,就是如果数据库里的数据修改过,并不在ResultSet中反应出来。
ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE:双向滚动,并及时跟踪数据库的更新,以便更改ResultSet中的数据。
ResultSet.CONCUR_READ_ONLY:这是缺省值,指定不可以更新 ResultSet
ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE:指定可以更新 ResultSet(这个后面会说到)
同时在这里我们只需要使用absolute方法就可以实现分页的功能,因为他可以随便的定位到指定的记录集中,但是这个是在全部将结果集查询处理的基础上来实现的,就是首先将所有符合条件的结果集查询出来放到内存中,然后再就行分页操作,那么这种分页的效率就很低了,所以我们强烈建议在数据库查询数据的时候就进行分页操作,比如MySql中使用limit关键字进行操作,MSSQL中使用top关键字,Oracle中使用number关键字,但是有的数据库中不支持分页查询操作,所以这时候我们只能使用上面的形式来进行分页了。
JDBC中的可更新以及对更新敏感的结果集操作
我们有时候可能有这样的需求,就是在查询出结果集的时候,想对指定的记录进行更新操作,说白了,就是将查询和更新操作放到一起进行,来看一下代码:
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
Statement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
-
st = conn.createStatement(ResultSet.TYPE_SCROLL_SENSITIVE, ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE);
-
rs = st.executeQuery("select * from user");
-
-
while(rs.next()){
-
-
-
-
String name = rs.getString("name");
-
if("jiangwei".equals(name)){
-
rs.updateFloat("money",170);
-
rs.updateRow();
-
}
-
}
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs,st,conn);
-
}
-
}
我们看到在循环处理结果集的时候,我们将name是jiangwei的记录的钱修改成170,并且反映到数据库中
这里一定要记得设置参数:ResultSet.CONCUR_UPDATABLE,不然会报异常的,这个参数的功能就是将更新的操作同步到数据库中的
这里我们是不建议这种做法的,因为将查询和更新的操作放到一起来操作的话,维护是很差的,我们一定要将CRUD操作进行分开处理,这里只是介绍一下相关知识,不推荐使用的。
下面来看一下通过反射技术,来实现将结果集填充到指定的实体类中,其实这部分的内容很简单的,直接上代码:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
static <T> T test(String sql,Class<T> clazz) throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement ps = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
rs = ps.executeQuery();
-
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
-
int count = rsmd.getColumnCount();
-
String[] colNames = new String[count];
-
for(int i=1;i<=count;i++){
-
colNames[i-1] = rsmd.getColumnLabel(i);
-
}
-
-
T user = clazz.newInstance();
-
-
if(rs.next()){
-
Method[] ms = user.getClass().getMethods();
-
for(int i=0;i<colNames.length;i++){
-
String colName = colNames[i];
-
String methodName = "set" + colName;
-
for(Method method:ms){
-
-
-
-
if(methodName.equalsIgnoreCase(method.getName())){
-
method.invoke(user, rs.getObject(colNames[i]));
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
return user;
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs,ps,conn);
-
}
-
return null;
-
}
测试代码:
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
-
-
User user = test("select id as Id,name as Name,birthday as Birthday,money as Money from user",User.class);
-
System.out.println(user);
-
}
其实就是使用反射技术将得到实体类中所有属性的set方法,然后通过set方法进行属性值的填充,这里唯一要注意的问题就是返回的结果集中的字段名称必须要和实体类中的属性名称相同,要做到这一点我们又两种方式:
一种是直接将表中的字段名称和实体类中的属性名称相同
一种是使用别名的方式来操作,将别名设置的和实体类中的属性名称相同
其实我们会发现,后面说到的Hibernate框架就是采用这种机制的
元数据的相关知识
我们知道元数据信息就是标示数据本身的一些数据信息
1.数据库的元数据信息
就是数据库的相关信息,如数据库的版本号,驱动名称,是否支持事务操作等信息,JDBC提供了接口让我们可以获取这些信息的:
-
static void test() throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
-
DatabaseMetaData metaData = conn.getMetaData();
-
System.out.println("databaseName:"+metaData.getDatabaseProductName());
-
System.out.println("driverName:"+metaData.getDriverName());
-
System.out.println("isSupportBatch:"+metaData.supportsBatchUpdates());
-
System.out.println("isSupportTransaction:"+metaData.supportsTransactions());
-
}
这些信息对于我们使用人员来说可能没有太大的用处,但是对于开发框架的人来说用处很大的,比如Hibernate框架,他要做到兼容所有的数据库特性的话,必须要将不同特性统一起来,所以他肯定要获取数据库的元数据信息的,后面会说到Hibernate中有一个配置叫做:方言,这个就是用来设置数据库名称的。
2.查询参数的元数据信息
当我们在使用PreparedStatement来进行参数填充的时候,我们想知道参数的一些信息,直接上代码:
-
static void test(String sql,Object[] params) throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
-
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
-
-
ParameterMetaData pMetaData= ps.getParameterMetaData();
-
int count = pMetaData.getParameterCount();
-
for(int i=1;i<=count;i++){
-
-
System.out.println(pMetaData.getParameterClassName(i));
-
System.out.println(pMetaData.getParameterType(i));
-
System.out.println(pMetaData.getParameterTypeName(i));
-
-
ps.setObject(i,params[i-1]);
-
}
-
ps.executeQuery();
-
}
测试代码:
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
String sql = "select name,birthday,money from user where name=?";
-
Object[] params = new Object[]{"jiangwei"};
-
test(sql,params);
-
}
我们知道Statement是不支持参数填充的,所以不可能获取到参数的元数据信息的
我们运行测试代码,会看到如下异常信息:
![]()
这时候我们就要注意了,如果想获取到元数据信息的话,我们还需要在连接数据的url后面添加一个参数:
generateSimpleParameterMetadata=true
添加完之后,我们运行结果如下:
![]()
我们看到可以获取参数在Java中的类型,12代表的是sql包中的类型:java.sql.Types.VARCHAR,这个字段是个整型值,值就是12,他对应到数据库中varchar类型的
这里要注意一点:有时候我们会发现这里获取到数据库中的类型是错误的,比如这里我们如果将数据库中的name字段的类型修改成char类型的,这里获取到的还是varchar,这一点想一想也是对的,你想想这个是获取查询参数的信息,我们还没有进行查询操作的,系统不可能那么智能的获取到数据库中准确的字段的类型的,所以他这里就做了一个大致的对应关系,将Java中的类型和数据库中的类型对应起来的,因为数据库中char和varchar都是字符串的。所以我们不能相信这里得到的数据库中字段的类型的,需要通过结果集中的元数据类型。
3.结果集中元数据信息
就是查询结果的一般信息,比如字段的相关信息
我们在上面看到要想获取数据库中字段的真实类型的话,只有先进行查询操作才可以,在这里我们就可以获取到正确的类型了,上代码:
-
static void test(String sql) throws Exception{
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement ps = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
rs = ps.executeQuery();
-
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
-
int count = rsmd.getColumnCount();
-
String[] colNames = new String[count];
-
for(int i=1;i<=count;i++){
-
-
System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnClassName(i));
-
System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnName(i));
-
System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnType(i));
-
System.out.println(rsmd.getColumnLabel(i));
-
colNames[i-1] = rsmd.getColumnName(i);
-
}
-
-
Map<String,Object> data = null;
-
-
if(rs.next()){
-
data = new HashMap<String,Object>();
-
for(int i=0;i<colNames.length;i++){
-
data.put(colNames[i], rs.getObject(colNames[i]));
-
}
-
}
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(rs,ps,conn);
-
}
-
}
我们这里可以获取到结果集中字段的总数count,以及字段的类型,名称,别名等信息,同时我们这里还穿插了一段代码,就是将结果集封装成一个HashMap结构,字段名做key,字段值做value
JDBC中的数据源
首先我们要知道什么是数据源,为什么要有数据源,我们从上面的例子看到,我们每次执行操作的时候,都是打开连接,关闭连接,这个连接的建立和关闭是很好资源和时间的,所以我们就在想一个策略怎么才能优化呢?所以数据源的概念就出来的,数据源就是用来管理连接的一个池子,使用高效的算法进行调度,这样在执行操作的时候是很方便的,为了容易理解数据源的相关概念,我们自己编写一个数据源:
-
package com.weijia.datasource;
-
-
import java.io.PrintWriter;
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.DriverManager;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
import java.util.LinkedList;
-
-
import javax.sql.DataSource;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource{
-
-
private static String user = "root";
-
private static String password = "123456";
-
private static String dbName = "test";
-
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/"+dbName+"?user="+user+"&password="+password+"&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=gb2312";
-
-
private static int initCount = 5;
-
private static int maxCount = 10;
-
private static int currentCount = 0;
-
-
private LinkedList<Connection> connectionsPool = new LinkedList<Connection>();
-
-
public MyDataSource(){
-
try{
-
for(int i=0;i<initCount;i++){
-
this.connectionsPool.addLast(createConnection());
-
currentCount++;
-
}
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
-
}
-
}
-
-
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException{
-
-
synchronized(connectionsPool){
-
if(connectionsPool.size() > 0){
-
return this.connectionsPool.removeFirst();
-
}
-
if(currentCount < maxCount){
-
currentCount++;
-
return createConnection();
-
}
-
-
-
throw new SQLException("已经没有连接了");
-
-
-
-
}
-
}
-
-
public void free(Connection conn) throws SQLException{
-
this.connectionsPool.addLast(conn);
-
}
-
-
private Connection createConnection() throws SQLException{
-
return DriverManager.getConnection(url);
-
}
-
-
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password)throws SQLException {
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
-
return 0;
-
}
-
-
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter arg0) throws SQLException {
-
-
}
-
-
public void setLoginTimeout(int arg0) throws SQLException {
-
-
}
-
-
}
然后修改一下JdbcUtils中的代码:
-
package com.weijia.firstdemo;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
import java.sql.Statement;
-
-
import javax.sql.DataSource;
-
-
import com.weijia.datasource.MyDataSource;
-
-
public class JdbcUtils {
-
-
private static String user = "root";
-
private static String password = "123456";
-
private static String dbName = "test";
-
private static String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/"+dbName+"?user="+user+"&password="+password+"&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=gb2312&generateSimpleParameterMetadata=true";
-
-
private static MyDataSource dataSource = null;
-
-
-
-
-
static{
-
try{
-
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
-
dataSource = new MyDataSource();
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
System.out.println("Exception:"+e.getMessage()+"");
-
throw new ExceptionInInitializerError(e);
-
}
-
}
-
-
private JdbcUtils(){
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException{
-
return dataSource.getConnection();
-
}
-
-
public static DataSource getDataSource(){
-
return dataSource;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public static void free(ResultSet rs,Statement st,Connection conn){
-
try{
-
if(rs != null){
-
rs.close();
-
}
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
try{
-
if(st != null){
-
st.close();
-
}
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}finally{
-
try{
-
dataSource.free(conn);
-
}catch(SQLException e){
-
e.printStackTrace();
-
}
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
}
我们看到,在我们自定义的数据源中,主要有这么几个变量:
初始化连接数,最大连接数,当前的连接数,连接池(因为我们可能需要频繁的添加连接和删除连接所以使用LinkedList,因为这个list是链表结构的,增加和删除效率高)
主要流程是:初始化数据源的时候,初始化一定量的连接放到池子中,当用户使用getConnection()方法取出连接的时候,我们会判断这个连接池中还有没有连接了,有就直接取出第一个连接返回,没有的话,我们在判断当前的连接数有没有超过最大连接数,超过的话,就抛出一个异常(其实这里还可以选择等待其他连接的释放,这个具体实现是很麻烦的),没有超过的话,就创建连接,并且将其放入池子中。
我们自定义的数据源是实现了JDBC中的DataSource接口的,这个接口很重要的,后面我们会说到apache的数据源都是要实现这个接口的,这个接口统一了数据源的标准,这个接口中有很多实现的,所以看到我们的数据源类中有很多没必要的方法,但是那个方法都是要实现的,最重要的就是要实现getConnection方法,其他的实现都只需要调用super.XXX就可以了。
在JdbcUtils类中我们也是需要修改的,首先我们要在静态代码块中初始化我们的数据源,在getConnection方法中调用数据源的getConnection方法,在free方法中调用数据源的free方法即可。
看一下测试类:
-
package com.weijia.datasource;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
-
import com.weijia.firstdemo.JdbcUtils;
-
-
public class Test {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
-
Connection conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
System.out.println(conn);
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, null, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
运行结果:
![]()
我们可以看到,我们在测试代码中申请了10个连接,从结果上可以看出前五个是不同的连接,后五个连接和前五个是一样的,这是因为我们在释放连接的时候就是free方法中,是将连接重新放到池子中的,上面显示的是五个,是因为我们初始化的连接数是5个,当第一个连接释放的时候这个连接其实已经放到了池子的第六个位置,以此类推。
下面我们继续来看下个问题,我们在上面的数据源中可以看到,我们定义了一个free方法来释放连接的,然后在JdbcUtils中调用这个方法即可,但是这个貌似不太符合我们的使用习惯,因为之前我们看到我们释放连接的时候都是使用close方法的,所以这里面我们在修改一下,至于怎么修改呢?
首先我们知道那个close方法是JDBC中的Connection接口中的,所有自定义的连接都是需要实现这个接口的,那么我们如果我们想让我们free中的逻辑放到close中的话,就需要实现这个接口了,我们可以看到
-
DriverManager.getConnection(url)
通过这种方式获取到的Connection也是mysql中实现了Connection的接口的,那么现在我们可能需要自定一个我们自己的连接,然后实现Connection接口,将free方法中的逻辑搬到close方法中,同时我们还要在连接类中保持一个mysql中的连接对象,这里面的逻辑有点不好理解,先看代码:
-
package com.weijia.datasource;
-
-
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.DatabaseMetaData;
-
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
import java.sql.SQLWarning;
-
import java.sql.Savepoint;
-
import java.sql.Statement;
-
import java.util.Map;
-
-
public class MyConnection implements Connection{
-
-
-
private Connection realConnection;
-
private MyDataSource2 dataSource;
-
-
private int maxUseCount = 5;
-
private int currentUseCount = 0;
-
-
public MyConnection(Connection conn,MyDataSource2 dataSource){
-
this.realConnection = conn;
-
this.dataSource = dataSource;
-
}
-
-
public void close() throws SQLException {
-
this.currentUseCount++;
-
if(this.currentUseCount < this.maxUseCount){
-
this.dataSource.free(this);
-
}else{
-
dataSource.currentCount--;
-
this.realConnection.close();
-
}
-
}
-
-
public void clearWarnings() throws SQLException {
-
this.realConnection.clearWarnings();
-
}
-
-
public void commit() throws SQLException {
-
this.realConnection.commit();
-
}
-
-
public Statement createStatement() throws SQLException {
-
return this.realConnection.createStatement();
-
}
-
-
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType, int resultSetConcurrency)throws SQLException {
-
return this.realConnection.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency);
-
}
-
-
public Statement createStatement(int resultSetType,int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)throws SQLException {
-
return this.realConnection.createStatement(resultSetType, resultSetConcurrency, resultSetHoldability);
-
}
-
-
public boolean getAutoCommit() throws SQLException {
-
return this.realConnection.getAutoCommit();
-
}
-
-
public String getCatalog() throws SQLException {
-
return this.realConnection.getCatalog();
-
}
-
-
public int getHoldability() throws SQLException {
-
return this.realConnection.getHoldability();
-
}
-
-
public DatabaseMetaData getMetaData() throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public int getTransactionIsolation() throws SQLException {
-
-
return 0;
-
}
-
-
public Map<String, Class<?>> getTypeMap() throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public SQLWarning getWarnings() throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public boolean isClosed() throws SQLException {
-
-
return false;
-
}
-
-
public boolean isReadOnly() throws SQLException {
-
-
return false;
-
}
-
-
public String nativeSQL(String sql) throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql) throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,
-
int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public CallableStatement prepareCall(String sql, int resultSetType,
-
int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)
-
throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql) throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int autoGeneratedKeys)
-
throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int[] columnIndexes)
-
throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, String[] columnNames)
-
throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType,
-
int resultSetConcurrency) throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public PreparedStatement prepareStatement(String sql, int resultSetType,
-
int resultSetConcurrency, int resultSetHoldability)
-
throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public void releaseSavepoint(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public void rollback(Savepoint savepoint) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public void setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public void setCatalog(String catalog) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public void setHoldability(int holdability) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public void setReadOnly(boolean readOnly) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public Savepoint setSavepoint() throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public Savepoint setSavepoint(String name) throws SQLException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
public void setTransactionIsolation(int level) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
public void setTypeMap(Map<String, Class<?>> map) throws SQLException {
-
-
-
}
-
-
}
首先看到了这个类中有很多恶心的代码,那些方法都是Connection接口中的,我们这里只需要实现close方法就可以了,其他的方法中可以添加:
-
return this.realConnection.XXX
我们看到会在类中保留一个Connection对象,这个对象就是真实的连接对象,即我们使用
-
DriverManager.getConnection(url)
这种方法获取到的,因为我们要在close方法中使用到这个真实的连接
我们看一下close方法吧:
-
public void close() throws SQLException {
-
this.currentUseCount++;
-
if(this.currentUseCount < this.maxUseCount){
-
this.dataSource.free(this);
-
}else{
-
dataSource.currentCount--;
-
this.realConnection.close();
-
}
-
}
首先看到我们定义了一个类变量:currentUseCount用来表示当前连接的使用次数,同时还有一个类变量就是maxUseCount表示当前连接的最大使用次数,我们看一下close方法的逻辑:
首先当用户调用close方法的时候当前连接的使用数就加一,这里有些同学可能不能理解,我们想想上面还记得我们释放连接的时候是怎么做的,是将这个连接重新放到池子中,所以这个连接又被用了一次,所以这里面是加一,当这个连接的当前使用次数没有超过他的最大使用次数的话,就还把他放到池子中(就是数据源中的free方法,这个方法中传递的参数是我们自定义的连接对象,因为我们不是真的需要关闭这个连接的),如果使用次数超过了最大使用次数的话,我们就将这个连接真正的释放关闭了,同时需要将数据源中当前的连接数减去一,这里我们是调用真实连接的关闭方法的,所以我们需要在我们自定义的连接中保持一个真实连接的对象,其实我们采用的是组合的方法,在一个要想调用另外类中的方法,我们需要在本类中维持一个他的对象,然后进行调用他特定的方法,这种方式也是一种设计模式叫做:静态代理,相当于我们本类是另外一个类的代理。
同时我们需要在构造函数中传递一个数据源对象进来的,当然我们这时候需要在之前的数据源中修改一下,这里修改很简单的,只需要修改数据源中的createConnection方法就可以了:
-
private Connection createConnection() throws SQLException{
-
Connection realConn = DriverManager.getConnection(url);
-
MyConnection myConnection = new MyConnection(realConn,this);
-
return myConnection;
-
}
我们返回的其实是我们自己的定义的连接,这个连接其实也是真实连接的一个代理对象。这样我们在JdbcUtils中的free方法中直接调用:
而不需要调用:
这样的释放方式就和我们之前普通连接的释放方式是一样的。其实我们上面做的这么多的操作就是为了这个,想让用户能够还是直接调用conn.close方法就可以释放连接,我们还是运行一下之前的测试类:
-
package com.weijia.datasource;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
-
import com.weijia.firstdemo.JdbcUtils;
-
-
public class Test {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
-
Connection conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
System.out.println(conn);
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, null, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
}
运行结果如下:
![]()
我们看到前五个用的是同一个连接对象,这个原因就是我们在我们自定义的连接MyConnection类中使用了当前连接的最大使用次数是5次
我们看到在定义我们自己的连接类的时候,需要实现Connection接口,这个接口中需要实现的方法很多,其实我们只需要一个close方法就可以了,这时候我们还可以将我们的代码在修改一下,下面是我们修改之后的自定义连接类:
-
package com.weijia.datasource;
-
-
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
-
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
-
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
-
public class MyConnectionHandler implements InvocationHandler{
-
-
private Connection realConnection = null;
-
private Connection warpedConnection = null;
-
private MyDataSource2 dataSource = null;
-
-
-
private int maxUseCount = 5;
-
private int currentUseCount = 0;
-
-
public MyConnectionHandler(MyDataSource2 dataSource){
-
this.dataSource = dataSource;
-
}
-
-
public Connection bind(Connection conn){
-
this.realConnection = conn;
-
warpedConnection = (Connection)Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Connection.class},this);
-
return warpedConnection;
-
}
-
-
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args)throws Throwable {
-
if("close".equals(method.getName())){
-
this.currentUseCount++;
-
if(this.currentUseCount < this.maxUseCount){
-
this.dataSource.free(warpedConnection);
-
}else{
-
dataSource.currentCount--;
-
this.realConnection.close();
-
}
-
}
-
return method.invoke(this.realConnection, args);
-
}
-
-
}
这里我们看到了并没有实现Connection接口了,而且代码也是很简洁的,其实这个就是动态代理的模式,我们通过bind方法传递进来一个真实的连接对象,然后使用Proxy类实例化一个代理对象,newProxyInstance方法的参数说明:
第一个:需要代理对象的类加载器
第二个:需要代理对象实现的接口
第三个:InvocationHandler回调接口,我们主要的工具都是实现这个接口中的invoke方法
然后我们在invoke方法中拦截close方法即可,将之前的close方法中的逻辑搬到这里就可以了。我们使用上面的测试代码运行如下:
![]()
这里我们就看到了使用动态代理很简单的,但是有一个限制,就是代理对象必须要实现一个接口,这里正好是Connection接口,他比静态代理优雅了很多的,后面我们在说到Spring的时候还会说到这个动态代理模式的
好了,上面我们就可以看到我们自己定义了一个数据源,连接,这样对我们后面的操作优化了很多。
下面我们在来看一下apache的数据源DataSource,其实这个数据源大体上和我们上面设计的以一样的,只是他做了更优化,更好。
首先我们导入需要的jar包:
![]()
然后我们定义一个dbcpconfig.properties文件,用于配置数据源的相关信息:
-
#连接设置
-
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
-
url=jdbc:mysql:
-
username=root
-
password=123456
-
-
#<!-- 初始化连接 -->
-
initialSize=10
-
-
#最大连接数量
-
maxActive=50
-
-
#<!-- 最大空闲连接 -->
-
maxIdle=20
-
-
#<!-- 最小空闲连接 -->
-
minIdle=5
-
-
#<!-- 超时等待时间以毫秒为单位 6000毫秒/1000等于60秒 -->
-
maxWait=60000
-
-
-
#JDBC驱动建立连接时附带的连接属性属性的格式必须为这样:[属性名=property;]
-
#注意:"user" 与 "password" 两个属性会被明确地传递,因此这里不需要包含他们。
-
connectionProperties=useUnicode=true;characterEncoding=gbk;generateSimpleParameterMetadata=true
-
-
#指定由连接池所创建的连接的自动提交(auto-commit)状态。
-
defaultAutoCommit=true
-
-
#driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的只读(read-only)状态。
-
#如果没有设置该值,则“setReadOnly”方法将不被调用。(某些驱动并不支持只读模式,如:Informix)
-
defaultReadOnly=
-
-
#driver default 指定由连接池所创建的连接的事务级别(TransactionIsolation)。
-
#可用值为下列之一:(详情可见javadoc。)NONE,READ_UNCOMMITTED, READ_COMMITTED, REPEATABLE_READ, SERIALIZABLE
-
defaultTransactionIsolation=READ_UNCOMMITTED
-
-
从这些配置上我们可以看到前面的几个参数的含义就是我们自定义数据源中的使用到的,这里还有一个参数是maxWait是超时,这个就是我们在获取连接的时候,当连接数超过最大连接数的时候,需要等待的时间,在前面我们自己定义的数据源中我们是采用抛出异常的问题来解决的,这里我们看到apache是采用线程等待的方式来解决的。
-
我们在代码里面修改的东西也是很少的,在JdbcUtils中的静态代码块中使用apache的数据源即可:
-
-
Properties prop = new Properties();
-
prop.load(JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("dbcpconfig.properties"));
-
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(prop);
apache中的连接也是经过改装的,我们直接调用conn.close方法即可,和我们上面实现的是一样的。
JDBC中CRUD的模板模式
我们从前面的例子中可以看到,我们在操作CRUD的时候,返现有很多重复的代码,比如现在一个UserDao来操作查询操作,写了一段查询代码,然后有一个ProductDao也来操作查询操作,也写了一段查询代码,其实我们会发现这两个查询代码中有很多是重复的,这时候我们就想了,能不能够进行代码的优化,我们想到了模板模式,就是将相同的代码提取出来放到父类中做,不同的代码放到各自的子类中去做,这样重复的代码只会出现一次了,下面来看一下实例,首先我们看一下抽象出来的Dao代码:
-
package com.weijia.template;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
-
import com.weijia.domain.DaoException;
-
import com.weijia.firstdemo.JdbcUtils;
-
-
public abstract class AbstractDao {
-
-
-
-
-
protected int update(String sql,Object[] args) {
-
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
-
st.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
-
}
-
int count = 0;
-
count = st.executeUpdate();
-
System.out.println("更新的记录数:"+count);
-
return count;
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new DaoException(e.getMessage(),e);
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
protected Object find(String sql,Object[] args){
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
-
st.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
-
}
-
rs = st.executeQuery();
-
Object obj = null;
-
while(rs.next()){
-
-
obj = rowMapper(rs);
-
}
-
return obj;
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new DaoException(e.getMessage(),e);
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
-
-
-
protected abstract Object rowMapper(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException;
-
-
}
看一下UserDaoImpl类:
-
package com.weijia.template;
-
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
-
import com.weijia.domain.User;
-
-
public class UserDaoImpl extends AbstractDao{
-
-
-
-
-
public int update(User user) {
-
String sql = "udpate user set name=?,birthday=?,money=?,where id=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{user.getName(),user.getBirthday(),user.getMoney(),user.getId()};
-
return super.update(sql, args);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
public void delete(User user){
-
String sql = "delete from user where id=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{user.getId()};
-
super.update(sql, args);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public User findUser(String loginName){
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{loginName};
-
return (User)super.find(sql, args);
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
protected Object rowMapper(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException{
-
User user = new User();
-
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
-
user.setName(rs.getString("name"));
-
user.setMoney(rs.getFloat("money"));
-
user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
-
return user;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
}
ProductDaoImpl类:
-
package com.weijia.template;
-
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
-
public class ProductDaoImpl extends AbstractDao{
-
-
public int update(){
-
String sql = "update product set pname=?,price=? where pid=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{"drug",11,1};
-
return super.update(sql, args);
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
protected Object rowMapper(ResultSet rs) {
-
return null;
-
}
-
-
}
看到了,这样来实现的话,代码就很简洁了,这里的ProductDaoImpl类中没有写完,就是大概是那个意思。这里体现出了一个设计模式就是:模板模式
接着看,现在有一个问题,就是查询,其实update的方式很简单的,完全可以统一化的,因为查询需要处理查询之后的结果集,所以很纠结的,上面的例子中我们看到,我们查询的是一个User对象,假如现在我只是想查询一个用户的name,那么我们只能在写一个findUserName方法了,同时还需要在AbstractDao父类中添加一个抽象方法的行映射器,这种方式就很纠结了,假如我们还有其他的查询需要的话,重复的代码又开始多了,这里我们将采用策略模式进行解决,我们只需要定义行映射器的接口:
-
package com.weijia.strategy;
-
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
-
public interface RowMapper {
-
-
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException;
-
-
}
在父类中只需要修改一下查询的方法:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
protected Object find(String sql,Object[] args,RowMapper rowMapper){
-
Connection conn = null;
-
PreparedStatement st = null;
-
ResultSet rs = null;
-
try{
-
conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
-
st = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
-
for(int i=0;i<args.length;i++){
-
st.setObject(i+1, args[i]);
-
}
-
rs = st.executeQuery();
-
Object obj = null;
-
while(rs.next()){
-
obj = rowMapper.mapRow(rs);
-
}
-
return obj;
-
}catch(Exception e){
-
throw new DaoException(e.getMessage(),e);
-
}finally{
-
JdbcUtils.free(null, st, conn);
-
}
-
}
添加了一个RowMapper接口变量
然后在子类中实现这个接口即可:
-
-
-
-
-
-
public String findUserName(int id){
-
String sql = "select name from user where id=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{id};
-
Object user = super.find(sql, args,new RowMapper(){
-
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
-
return rs.getObject("name");
-
}
-
});
-
return ((User)user).getName();
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public User findUser(String loginName){
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{loginName};
-
return (User)super.find(sql, args,new RowMapper(){
-
-
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
-
User user = new User();
-
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
-
user.setName(rs.getString("name"));
-
user.setMoney(rs.getFloat("money"));
-
user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
-
return user;
-
}
-
-
});
-
}
我们可以看到这两个查询的方法就很优雅了,这样做了之后,我们只需要在指定的子类中添加指定的方法即可,其实策略模式很简单的,就是相当于回调机制,就是想执行指定的方法,但是Java中没有函数指针,C++中其实可以的,所以只能通过回调来实现了。
通过上面的CRUD优化之后,我们在进行操作的时候,代码编写是很方便和简洁的
Spring框架中的JdbcTemplate
说完了上面的我们自定义的CRUD模板,下面我来看一下Spring框架给我们提供的CRUD模板(JdbcTemplate),其实他的实现原理和我们上面是一样的,只是他的功能会更强。
下面来看一下实例代码:
-
package com.weijia.springtemplate;
-
-
import java.sql.Connection;
-
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
-
import java.sql.ResultSet;
-
import java.sql.SQLException;
-
import java.sql.Statement;
-
import java.util.List;
-
import java.util.Map;
-
-
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.ConnectionCallback;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
-
-
import com.weijia.domain.User;
-
import com.weijia.firstdemo.JdbcUtils;
-
-
public class JdbcTemplateTest {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args){
-
User user = new User();
-
user.setMoney(20);
-
user.setId(1);
-
update(user);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
static void update(User user){
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
String sql = "update user set money=? where id=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{user.getMoney(),user.getId()};
-
jdbc.update(sql, args);
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
static User findUser(String name){
-
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{name};
-
-
Object user = jdbc.queryForObject(sql,args,new RowMapper(){
-
public Object mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
-
User user = new User();
-
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
-
user.setName(rs.getString("name"));
-
user.setMoney(rs.getFloat("money"));
-
user.setBirthday(rs.getDate("birthday"));
-
return user;
-
}});
-
return (User)user;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
static User findUsers(String name){
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{name};
-
-
-
-
Object user = jdbc.queryForObject(sql,args,new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class){});
-
return (User)user;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
static List findUser1(int id){
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where id<?";
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{id};
-
List users = jdbc.query(sql,args,new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class){});
-
return users;
-
}
-
-
-
-
static int getUserCount(){
-
String sql = "select count(*) from user";
-
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
return jdbc.queryForInt(sql);
-
}
-
-
static String getUserName(int id){
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
String sql = "select name from user where id="+id;
-
Object name = jdbc.queryForObject(sql, String.class);
-
return (String)name;
-
}
-
-
static Map getUser(int id){
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
String sql = "select id,name,birthday from user where id=?";
-
return jdbc.queryForMap(sql,new Object[]{id});
-
}
-
-
-
static User addUser(final User user){
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
-
-
jdbc.execute(new ConnectionCallback(){
-
public Object doInConnection(Connection conn) throws SQLException,DataAccessException {
-
String sql = "insert into user(name,birtdhday,birthday) values('jiangwei','1987-01-01',400)";
-
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql, Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
-
ps.executeUpdate();
-
-
ResultSet rs = ps.getGeneratedKeys();
-
if(rs.next()){
-
user.setId(rs.getInt(1));
-
}
-
return null;
-
}});
-
return user;
-
}
-
-
}
下面来看一下,JdbcTemplate的相关使用方法:
首先看一下,我们开始使用一个数据源来初始化一个JdbcTemplate模板
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
然后只需要直接执行其相关的方法即可:
update(String sql,Object[] args):第一个参数是sql语句,第二参数是需要填充的更新参数
queryForObject(String sql,Object[] args, RowMapper rowMapper):第一参数是sql语句,第二参数是需要填充的查询参数,第三个参数是行映射器(和前面我们设计的一样),这个方法只适用查询结果是一个的情况,如果查询结果是多个的话,这个方法会报异常的,同时这个方法第三个参数我们也可以传递一个:new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class){}对象,这个就可以将查询结果填充到User实体类中了,当然这里有一个限制就是要求查询出来的结果集中的字段名和实体类中的属性名一样,其实这内部使用的是反射技术来实现的,我们之前写过这样的方法的。
query(String sql,Object[]args,RowMapper rowMapper):这个方法和上面的那个方法不同的就是返回的结果,这个方法返回的是一个List,针对于查询结果是多个的情况
queryForInt(String sql,Object[] args):这个方法是针对查询结果是一个整型的,比如我们需要查询出用户的总数
queryForLong(String sql,Object[] args):这个方法是查询出long类型的
queryForObject(String sql, Class requiredType):这个方法是对于那些没有特定查询类型的方法同一使用这个方法,比如现在想查询一个用户的名称是String类型的,或者想查询用户的money,是float类型的,这里我们只需要在第二个参数中指定类型即可
queryForMap(String sql,Object[] args):查询返回的是一个Map集合
queryForList(String sql,Object[] args):查询返回的是一个List集合
上面的方法我们就足够了
下面再来看一个需求,如果我们想得到插入一条记录之后的主键的操作,这里改如何操作呢?
在之前我们操作的是需要将PreparedStatement中设置一个参数,不然会报错的,我们通过上面的方法可以知道其内部都是使用PreparedStatement实现的,因为有占位符,需要设置查询参数的。但是他并没有提供一个方法能够设置这个PreparedStatement的一些参数,但是如果我们想获取到主键值的话,必须要设置PreparedStatement的第二参数为:Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS,那么这时候,JdbcTemplate还给我们提供了一个方法:
-
jdbc.execute(new ConnectionCallback(){
-
public Object doInConnection(Connection con) throws SQLException,DataAccessException {
-
-
return null;
-
}
-
});
execute方法中传递一个Connection的回调类,然后实现一个方法,在方法中我们可以获取到当前的连接,当我们拿到了这个连接的话,就可以进行操作了。
这样一来,上面提到的JdbcTemplate中的方法就可以满足我们的日常需求了
加强版的JdbcTemplate
1.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate
这个模板其实我们见名知意,他的最大的作用应该是参数名称的功能,我们在上面的模板中可以看到,我们每次传递的参数数组中的参数顺序必须和查询语句中的占位符的顺序要相同,但是这个模板给我们提供了一个便捷的好处就是,不需要关心参数的顺序:
-
static User findUsers(User user){
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=:n and money>:m and id<:id";
-
-
-
-
-
Map<String,Object> params = new HashMap<String,Object>();
-
params.put("n", user.getName());
-
params.put("m", user.getMoney());
-
params.put("id", user.getId());
-
Object users = named.queryForObject(sql, params, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class));
-
return (User)users;
-
}
这里要注意的是查询语句sql中不在使用占位符了,而是使用参数变量的形式:
:参数名
这个参数名,我们会在下面的HashMap中当做key来进行参数的填充,然后将这个HashMap变量传递到queryForObject方法中,而不是在使用数组的方式了,这种方式其实就是将数组类型的参数传递变成了Map类型的参数传递,其实方法的功能都是没有改变的,只是相对应的方法中的参数不再是Object[]数组了,而是Map集合类型的
同样的假如是JavaBean类型的怎么填充参数呢?这里也提供了一个方法:
-
SqlParameterSource ps = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(user);
这样直接进行参数的填充,但是这里有一个限制就是sql中的参数名称必须要和JavaBean中的属性名称一样(内部使用反射技术实现的)
最后我们获取主键的值的方式也变化了:
-
SqlParameterSource ps = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(user);
-
-
KeyHolder keyHolder = new GeneratedKeyHolder();
-
named.update(sql, ps, keyHolder);
-
-
Map map = keyHolder.getKeys();
-
int id = keyHolder.getKey().intValue();
这样比JdbcTemplate中的方法更简单了。
下面看一下完整的实例代码:
-
package com.weijia.springtemplate;
-
-
import java.util.Date;
-
import java.util.HashMap;
-
import java.util.Map;
-
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.BeanPropertySqlParameterSource;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.SqlParameterSource;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.GeneratedKeyHolder;
-
import org.springframework.jdbc.support.KeyHolder;
-
-
import com.weijia.domain.User;
-
import com.weijia.firstdemo.JdbcUtils;
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
public class NamedJdbcTemplate {
-
-
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
-
System.out.println("add id:"+addUser(new User(1,"jiangwei",new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()),100)));
-
}
-
-
-
public static NamedParameterJdbcTemplate named = new NamedParameterJdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
-
static User findUser(User user){
-
JdbcTemplate jdbc = new JdbcTemplate(JdbcUtils.getDataSource());
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=? and money>? and id<?";
-
-
Object[] args = new Object[]{user.getName(),user.getMoney(),user.getId()};
-
-
Object users = jdbc.queryForObject(sql,args,new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class){});
-
return (User)users;
-
}
-
-
static User findUsers(User user){
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=:n and money>:m and id<:id";
-
-
-
-
-
-
Map<String,Object> params = new HashMap<String,Object>();
-
params.put("n", user.getName());
-
params.put("m", user.getMoney());
-
params.put("id", user.getId());
-
Object users = named.queryForObject(sql, params, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class));
-
return (User)users;
-
}
-
-
static User findUser1(User user){
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where name=:name and money>:money and id<:id";
-
-
SqlParameterSource ps = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(user);
-
Object users = named.queryForObject(sql, ps, new BeanPropertyRowMapper(User.class));
-
return (User)users;
-
}
-
-
static int addUser(User user){
-
String sql = "insert into user(name,birthday,money) values(:name,:birthday,:money)";
-
-
SqlParameterSource ps = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(user);
-
-
KeyHolder keyHolder = new GeneratedKeyHolder();
-
named.update(sql, ps, keyHolder);
-
-
Map map = keyHolder.getKeys();
-
int id = keyHolder.getKey().intValue();
-
return keyHolder.getKey().intValue();
-
}
-
-
}
2.SimpleJdbcTemplate
见名知意,这个模板会操作变得更简单的,他的主要变化就是两点:
第一、实现可变参数了
第二、查询出来的对象无须进行类型转换了
-
-
static User findUser(int id,String name,Class<User> clazz){
-
String sql = "select id,name,money,birthday from user where id=? and name=?";
-
-
-
-
-
return simple.queryForObject(sql, ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(clazz),id,name);
-
}
我们看到queryForObject方法中第二个参数是ParameterizedBeanPropertyRowMapper.newInstance(Class clazz),传递进去的是查询出来的实体类的类型class,这样我们在返回的时候,就不需要进行类型转化了
最后一个参数其实是可变参数,可以传递多个值的,但是这个传递的值的顺序必须要和上面sql中占位符的顺序一致,下面是测试代码:
-
System.out.println(findUser(1505,"jiangwei",User.class));
总结:
至此我们就将JDBC的相关知识都介绍完毕了,因为JDBC本身的内容是很多的,我们也只有遇到问题的时候采取解决,上面的只是对于开发来说应该没有多大的问题了,可能会有一些细节上的问题,这个只能在后续进行完善了。上面说到的内容,可能有些不全,我将整个讲解的项目功能放到了网上,下载地址:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/jiangwei0910410003/7373133
这个需要注意的是一定记得连接上正确的数据库,这个可以查看连接数据库的那段代码。。
如果发现有问题,请及时提醒,我做修改,希望能够和大家一起做到百分百的成功。。
/**
*
* __ (__`\
* (__`\ \\`\
* `\\`\ \\ \
* `\\`\ \\ \
* `\\`\#\\ \#
* \_ ##\_ |##
* (___)(___)##
* (0) (0)`\##
* |~ ~ , \##
* | | \##
* | /\ \## __..---'''''-.._.._
* | | \ `\## _.--' _ `.
* Y | \ `##' \`\ \
* / | \ | `\ \
* /_...___| \ | `\\
* / `. | / ##
* | | | / ####
* | | | / ####
* | () () | \ | | _.-' ##
* `. .' `._. |______..| |-'|
* `------' | | | | | || |
* | | | | | || |
* | | | | | || |
* | | | | | || |
* _____ | | | |____| || |
* / `` |-`/ ` |` |
* \________\__\_______\__\
* """"""""" """""""'"""
* Don't be a fucking stupid donkey! No, this is a fucking mule!
*/

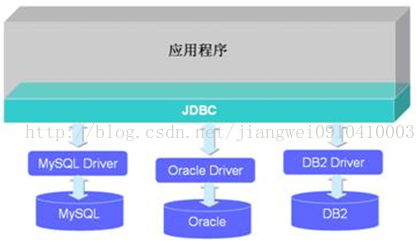
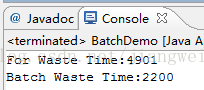
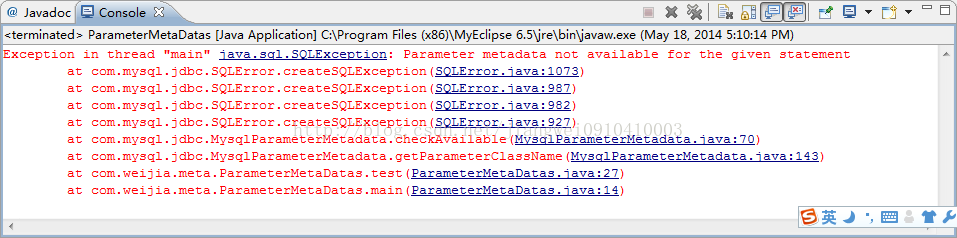
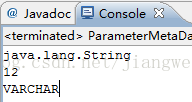
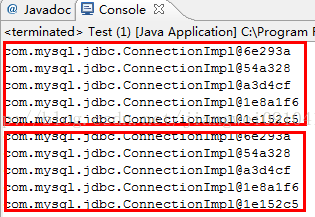
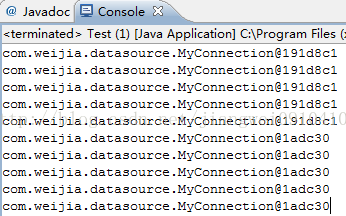
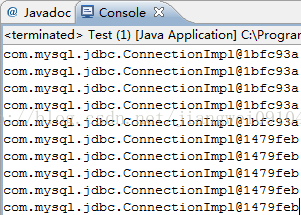

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号