http://www.cnblogs.com/springyangwc/archive/2011/10/12/2208991.html
概述
AutoResetEvent 允许线程通过发信号互相通信。 通常,当线程需要独占访问资源时使用该类。
线程通过调用 AutoResetEvent 上的 WaitOne 来等待信号。 如果 AutoResetEvent 为非终止状态,则线程会被阻止,并等待当前控制资源的线程通过调用 Set 来通知资源可用。
调用 Set 向 AutoResetEvent 发信号以释放等待线程。 AutoResetEvent 将保持终止状态,直到一个正在等待的线程被释放,然后自动返回非终止状态。 如果没有任何线程在等待,则状态将无限期地保持为终止状态。
如果当 AutoResetEvent 为终止状态时线程调用 WaitOne,则线程不会被阻止。 AutoResetEvent 将立即释放线程并返回到非终止状态。
ManualResetEvent 允许线程通过发信号互相通信。 通常,此通信涉及一个线程在其他线程进行之前必须完成的任务。
当一个线程开始一个活动(此活动必须完成后,其他线程才能开始)时,它调用 Reset 以将 ManualResetEvent 置于非终止状态。 此线程可被视为控制 ManualResetEvent。 调用 ManualResetEvent 上的 WaitOne 的线程将阻止,并等待信号。 当控制线程完成活动时,它调用Set 以发出等待线程可以继续进行的信号。 并释放所有等待线程。
一旦它被终止,ManualResetEvent 将保持终止状态,直到它被手动重置。 即对 WaitOne 的调用将立即返回。
可以通过将布尔值传递给构造函数来控制 ManualResetEvent 的初始状态,如果初始状态处于终止状态,为 true;否则为 false。
ManualResetEvent 也可以同 staticWaitAll 和 WaitAny 方法一起使用。
生活中的例子
AutoResetEvent :在上海坐地铁,检票口有个刷卡的通道,一次只能一个人刷卡后通过,而我过后,它又是关闭的,另一个人又得再刷卡.一次操作,只有一个事件,这时就是非终止状态,一般是用来同步访问资源.
ManualResetEvent :公司园区的大门很大,一次可以多人通过。
ManualResetEvent和AutoResetEvent 比较
ManualResetEvent和AutoResetEvent都继承自EventWaitHandler,它们的唯一区别就在于父类 EventWaitHandler的构造函数参数EventResetMode不同,这样我们只要弄清了参数EventResetMode值不同 时,EventWaitHandler类控制线程同步的行为有什么不同,两个子类也就清楚了。
共同点:
A、Set方法将事件状态设置为终止状态,允许一个或多个等待线程继续;Reset方法将事件状态设置为非终止状态,导致线程阻止;WaitOne阻止当前线程,直到当前线程的WaitHandler收到事件信号。
B、可以通过构造函数的参数值来决定其初始状态,若为true则事件为终止状态从而使线程为非阻塞状态,为false则线程为阻塞状态。
C、如果某个线程调用WaitOne方法,则当事件状态为终止状态时,该线程会得到信号,继续向下执行。
不同点:
A、AutoResetEvent.WaitOne()每次只允许一个线程进入,当某个线程 得到信号后,AutoResetEvent会自动又将信号置为不发送状态,则其他调用WaitOne的线程只有继续等待,也就是说 AutoResetEvent一次只唤醒一个线程;
B、ManualResetEvent则可以唤醒多个线程,因为当某个线程调用了ManualResetEvent.Set()方法后,其他调用WaitOne的线程获得信号得以继续执行,而ManualResetEvent不会自动将信号置为不发送。
C、也就是说,除非手工调用了ManualResetEvent.Reset()方法,则ManualResetEvent将一直保持有信号状态,ManualResetEvent也就可以同时唤醒多个线程继续执行。
先看下AutoResetEvent 的代码
01 |
namespace System.Threading { |
04 |
using System.Security.Permissions; |
05 |
using System.Runtime.InteropServices; |
07 |
[HostProtection(Synchronization=true, ExternalThreading=true)] |
08 |
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)] |
09 |
public sealed class AutoResetEvent : EventWaitHandle |
11 |
public AutoResetEvent(bool initialState) : base(initialState,EventResetMode.AutoReset){ } |
再来看下EventWaitHandle的代码
001 |
namespace System.Threading |
004 |
using System.Threading; |
005 |
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices; |
006 |
using System.Security.Permissions; |
008 |
using Microsoft.Win32; |
009 |
using Microsoft.Win32.SafeHandles; |
010 |
using System.Runtime.InteropServices; |
011 |
using System.Runtime.Versioning; |
013 |
using System.Security.AccessControl; |
016 |
[HostProtection(Synchronization=true, ExternalThreading=true)] |
017 |
[ComVisibleAttribute(true)] |
018 |
public class EventWaitHandle : WaitHandle |
020 |
[ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.None)] |
021 |
[ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine, ResourceScope.Machine)] |
022 |
public EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode) : this(initialState,mode,null) { } |
024 |
[SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] |
025 |
[ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
026 |
[ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
027 |
public EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode, string name) |
029 |
if(null != name && System.IO.Path.MAX_PATH < name.Length) |
031 |
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_WaitHandleNameTooLong",name)); |
034 |
SafeWaitHandle _handle = null; |
037 |
case EventResetMode.ManualReset: |
038 |
_handle = Win32Native.CreateEvent(null, true, initialState, name); |
040 |
case EventResetMode.AutoReset: |
041 |
_handle = Win32Native.CreateEvent(null, false, initialState, name); |
045 |
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_InvalidFlag",name)); |
048 |
if (_handle.IsInvalid) |
050 |
int errorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error(); |
052 |
_handle.SetHandleAsInvalid(); |
053 |
if(null != name && 0 != name.Length && Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE == errorCode) |
054 |
throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(Environment.GetResourceString("Threading.WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException_InvalidHandle",name)); |
056 |
__Error.WinIOError(errorCode, ""); |
058 |
SetHandleInternal(_handle); |
061 |
[SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] |
062 |
[ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
063 |
[ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
064 |
public EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode, string name, out bool createdNew) |
066 |
: this(initialState, mode, name, out createdNew, null) |
070 |
[SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] |
071 |
[ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
072 |
[ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
073 |
public unsafe EventWaitHandle(bool initialState, EventResetMode mode, string name, out bool createdNew, EventWaitHandleSecurity eventSecurity) |
076 |
if(null != name && System.IO.Path.MAX_PATH < name.Length) |
078 |
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_WaitHandleNameTooLong",name)); |
080 |
Win32Native.SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES secAttrs = null; |
083 |
if (eventSecurity != null) { |
084 |
secAttrs = new Win32Native.SECURITY_ATTRIBUTES(); |
085 |
secAttrs.nLength = (int)Marshal.SizeOf(secAttrs); |
087 |
byte[] sd = eventSecurity.GetSecurityDescriptorBinaryForm(); |
088 |
byte* pSecDescriptor = stackalloc byte[sd.Length]; |
089 |
Buffer.memcpy(sd, 0, pSecDescriptor, 0, sd.Length); |
090 |
secAttrs.pSecurityDescriptor = pSecDescriptor; |
094 |
SafeWaitHandle _handle = null; |
095 |
Boolean isManualReset; |
098 |
case EventResetMode.ManualReset: |
099 |
isManualReset = true; |
101 |
case EventResetMode.AutoReset: |
102 |
isManualReset = false; |
106 |
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_InvalidFlag",name)); |
109 |
_handle = Win32Native.CreateEvent(secAttrs, isManualReset, initialState, name); |
110 |
int errorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error(); |
112 |
if (_handle.IsInvalid) |
115 |
_handle.SetHandleAsInvalid(); |
116 |
if(null != name && 0 != name.Length && Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE == errorCode) |
117 |
throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(Environment.GetResourceString("Threading.WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException_InvalidHandle",name)); |
119 |
__Error.WinIOError(errorCode, name); |
121 |
createdNew = errorCode != Win32Native.ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS; |
122 |
SetHandleInternal(_handle); |
125 |
private EventWaitHandle(SafeWaitHandle handle) |
127 |
SetHandleInternal(handle); |
130 |
[SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] |
131 |
[ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
132 |
[ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
133 |
public static EventWaitHandle OpenExisting(string name) |
136 |
return OpenExisting(name, EventWaitHandleRights.Modify | EventWaitHandleRights.Synchronize); |
139 |
[SecurityPermissionAttribute(SecurityAction.LinkDemand,Flags=SecurityPermissionFlag.UnmanagedCode)] |
140 |
[ResourceExposure(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
141 |
[ResourceConsumption(ResourceScope.Machine)] |
142 |
public static EventWaitHandle OpenExisting(string name, EventWaitHandleRights rights) |
144 |
#endif // !FEATURE_PAL |
147 |
throw new ArgumentNullException("name", Environment.GetResourceString("ArgumentNull_WithParamName")); |
152 |
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_EmptyName"), "name"); |
155 |
if(null != name && System.IO.Path.MAX_PATH < name.Length) |
157 |
throw new ArgumentException(Environment.GetResourceString("Argument_WaitHandleNameTooLong",name)); |
162 |
SafeWaitHandle myHandle = Win32Native.OpenEvent(Win32Native.EVENT_MODIFY_STATE | Win32Native.SYNCHRONIZE, false, name); |
164 |
SafeWaitHandle myHandle = Win32Native.OpenEvent((int) rights, false, name); |
167 |
if (myHandle.IsInvalid) |
169 |
int errorCode = Marshal.GetLastWin32Error(); |
171 |
if(Win32Native.ERROR_FILE_NOT_FOUND == errorCode || Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_NAME == errorCode) |
172 |
throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(); |
173 |
if(null != name && 0 != name.Length && Win32Native.ERROR_INVALID_HANDLE == errorCode) |
174 |
throw new WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException(Environment.GetResourceString("Threading.WaitHandleCannotBeOpenedException_InvalidHandle",name)); |
176 |
__Error.WinIOError(errorCode,""); |
178 |
return new EventWaitHandle(myHandle); |
182 |
bool res = Win32Native.ResetEvent(safeWaitHandle); |
184 |
__Error.WinIOError(); |
189 |
bool res = Win32Native.SetEvent(safeWaitHandle); |
192 |
__Error.WinIOError(); |
198 |
public EventWaitHandleSecurity GetAccessControl() |
200 |
return new EventWaitHandleSecurity(safeWaitHandle, AccessControlSections.Access | AccessControlSections.Owner | AccessControlSections.Group); |
203 |
public void SetAccessControl(EventWaitHandleSecurity eventSecurity) |
205 |
if (eventSecurity == null) |
206 |
throw new ArgumentNullException("eventSecurity"); |
208 |
eventSecurity.Persist(safeWaitHandle); |
再来看下ManualResetEvent的代码
01 |
namespace System.Threading { |
04 |
using System.Security.Permissions; |
05 |
using System.Runtime.InteropServices; |
07 |
[HostProtection(Synchronization=true, ExternalThreading=true)] |
08 |
[System.Runtime.InteropServices.ComVisible(true)] |
09 |
public sealed class ManualResetEvent : EventWaitHandle |
11 |
public ManualResetEvent(bool initialState) : base(initialState,EventResetMode.ManualReset){} |
其实这两个的差别就是AutoResetEvent是base(initialState,EventResetMode.AutoReset)而 ManualResetEvent是base(initialState,EventResetMode.ManualReset).
AutoResetEvent是操作单个线程的,而ManualResetEvent可以操作多个线程.
AutoResetEvent开发示例
在主线程运行后,新开一个新线程,由新线程来控制主线程的等待和执行.
类关系图
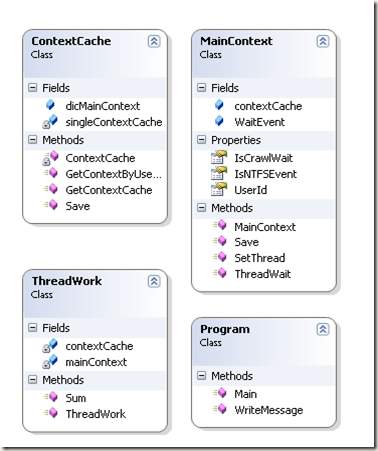
代码实现
005 |
namespace TestMultipleThread |
008 |
using System.Collections.Generic; |
009 |
using System.Threading; |
010 |
public class ThreadWork |
012 |
private MainContext mainContext; |
013 |
private ContextCache contextCache; |
017 |
contextCache = ContextCache.GetContextCache(); |
018 |
mainContext = contextCache.GetContextByUserId("001"); |
023 |
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("this is thread ID {0} execute", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId)); |
024 |
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) |
028 |
if (mainContext != null && mainContext.IsCrawlWait == false) |
030 |
mainContext.IsNTFSEvent = true; |
031 |
while (mainContext.IsCrawlWait) |
036 |
Console.WriteLine("main thread is wait"); |
038 |
Console.WriteLine("main thread is start"); |
039 |
mainContext.IsNTFSEvent = false; |
040 |
mainContext.SetThread(); |
048 |
public static void Main() |
050 |
MainContext mainContext = new MainContext("001"); |
054 |
ThreadWork threadWork = new ThreadWork(); |
055 |
ThreadStart myThreadDelegate = new ThreadStart(threadWork.Sum); |
056 |
Thread myThread = new Thread(myThreadDelegate); |
059 |
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) |
061 |
if (mainContext.IsNTFSEvent) |
062 |
mainContext.ThreadWait(); |
066 |
Console.WriteLine("main Thread continue"); |
067 |
Thread.Sleep(100000); |
072 |
public void WriteMessage() |
074 |
Console.WriteLine("Stop the main thread."); |
078 |
public class MainContext |
080 |
public string UserId { get; set; } |
082 |
public AutoResetEvent WaitEvent; |
084 |
public ContextCache contextCache; |
087 |
public void ThreadWait() |
089 |
if (WaitEvent == null) WaitEvent = new AutoResetEvent(false); |
098 |
public MainContext(string userID) |
103 |
contextCache = ContextCache.GetContextCache(); |
108 |
contextCache.Save(UserId, this); |
111 |
public void SetThread() |
114 |
if (!IsNTFSEvent && IsCrawlWait) |
121 |
public bool IsCrawlWait { get; set; } |
123 |
public bool IsNTFSEvent { get; set; } |
128 |
public class ContextCache |
130 |
public Dictionary<string, MainContext> dicMainContext = new Dictionary<string, MainContext>(); |
132 |
public void Save(string userId, MainContext mainContext) |
134 |
dicMainContext.Add(userId, mainContext); |
137 |
private static ContextCache singleContextCache; |
139 |
public MainContext GetContextByUserId(string userId) |
142 |
dicMainContext.TryGetValue(userId, out context); |
146 |
private ContextCache() |
150 |
public static ContextCache GetContextCache() |
152 |
if (singleContextCache == null) |
154 |
singleContextCache = new ContextCache(); |
156 |
return singleContextCache; |
运行结果

参考资料:
1、MSDN
2、C#多线程:深入了解线程同步lock,Monitor,Mutex,同步事件和等待句柄(中) 地址: http://dongguojun.iteye.com/blog/960586
欢迎各位参与讨论,如果觉得对你有帮助,请点击 推荐下,万分谢谢.
推荐下,万分谢谢.
作者:spring yang
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/springyangwc/
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。
 推荐下,万分谢谢.
推荐下,万分谢谢.





