Hadoop序列化
数据在虚拟机内外交换的方式简称为序列化
*序列化(Serialization)是指把结构化对象转化为字节流。(写出去,以内存中得对象为基础或参照物)
*反序列化(Deserialization)是序列化的逆过程。即把字节流转回结构化对象。(读进来,以内存中得对象为基础或参照物)
Java序列化(java.io.Serializable),接口,只需要实现该接口即可,Serializable已经提供了java序列化的实现
1.hadoop序列化源碼
在hadoop中,可以使用ctrl+shift+t打开open type,键入hadoop序列化的类型writable即可查看
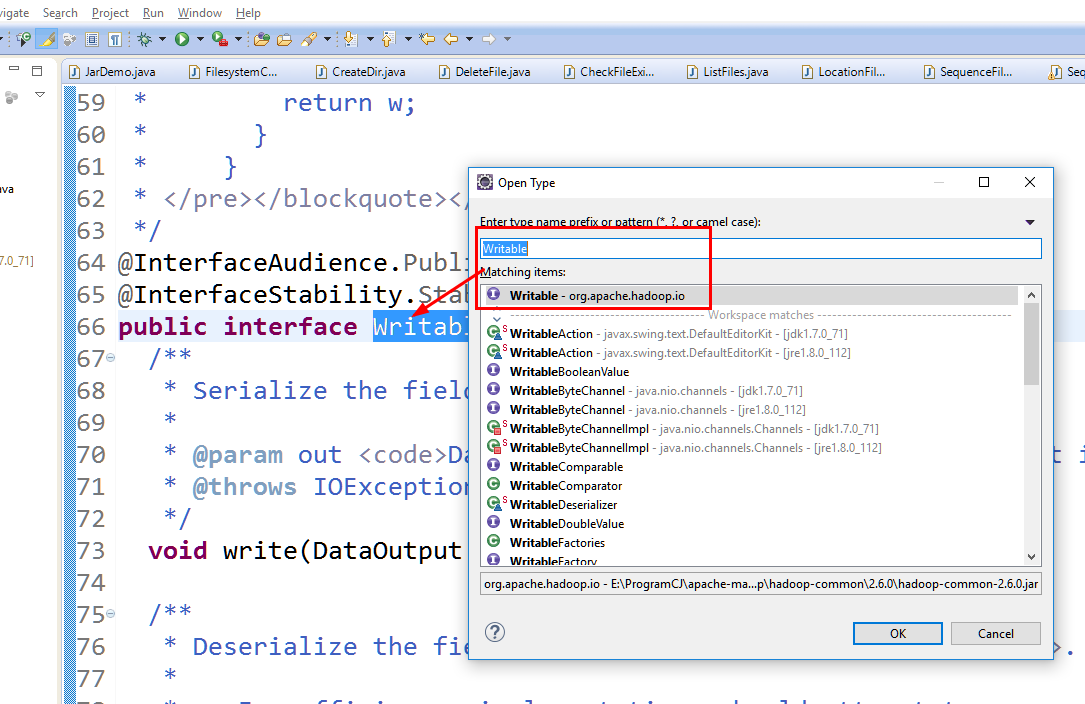
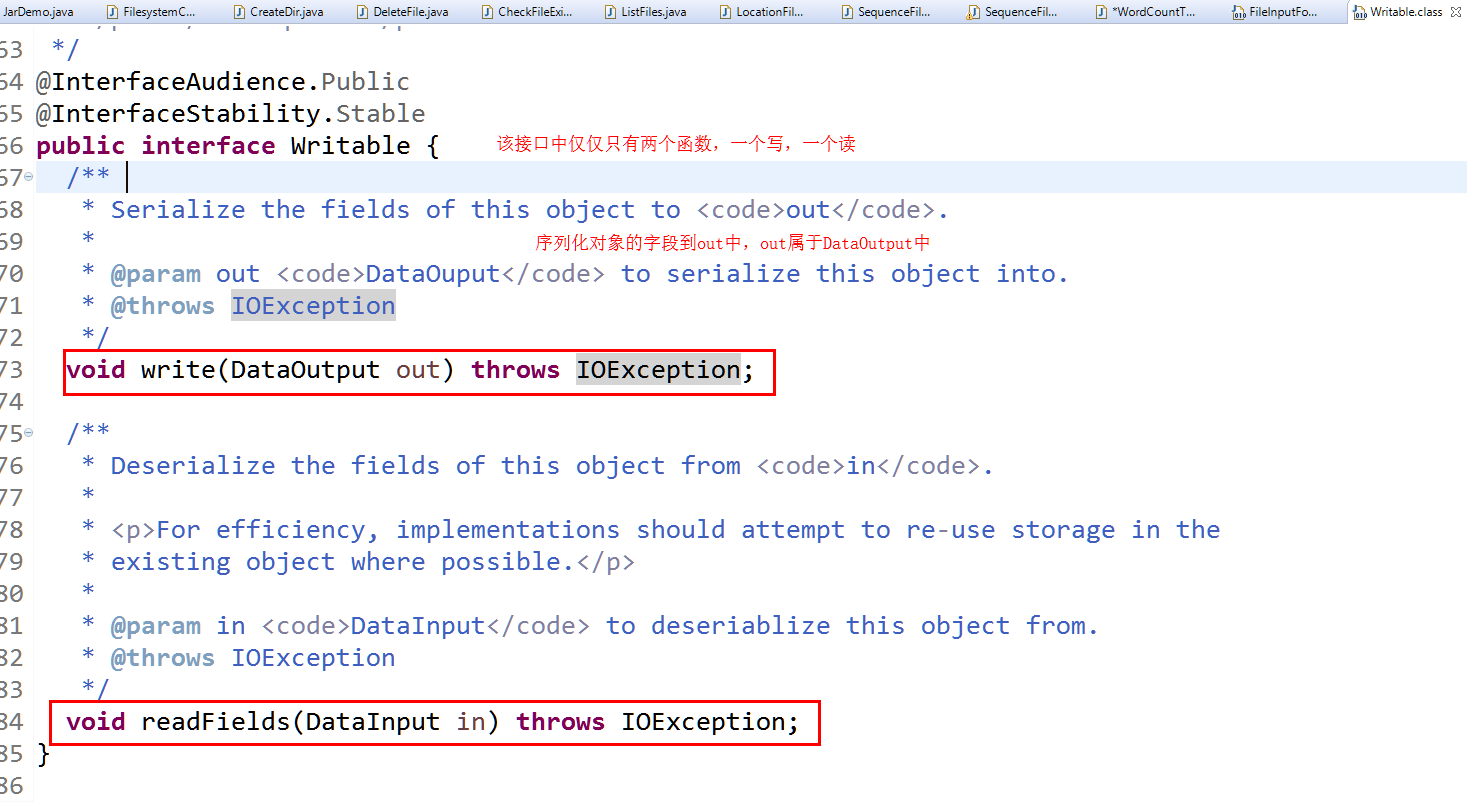
注意:这里的序列化方法需要自己在程序中实现,而java提供了默认的实现。
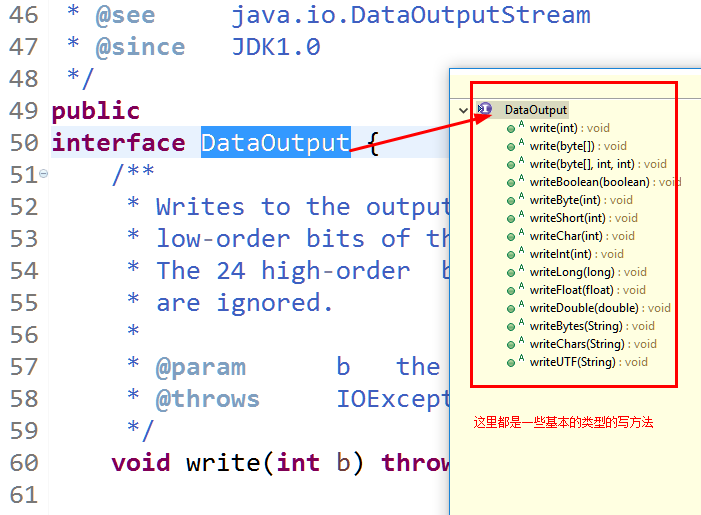
(2)LongWritable类源码
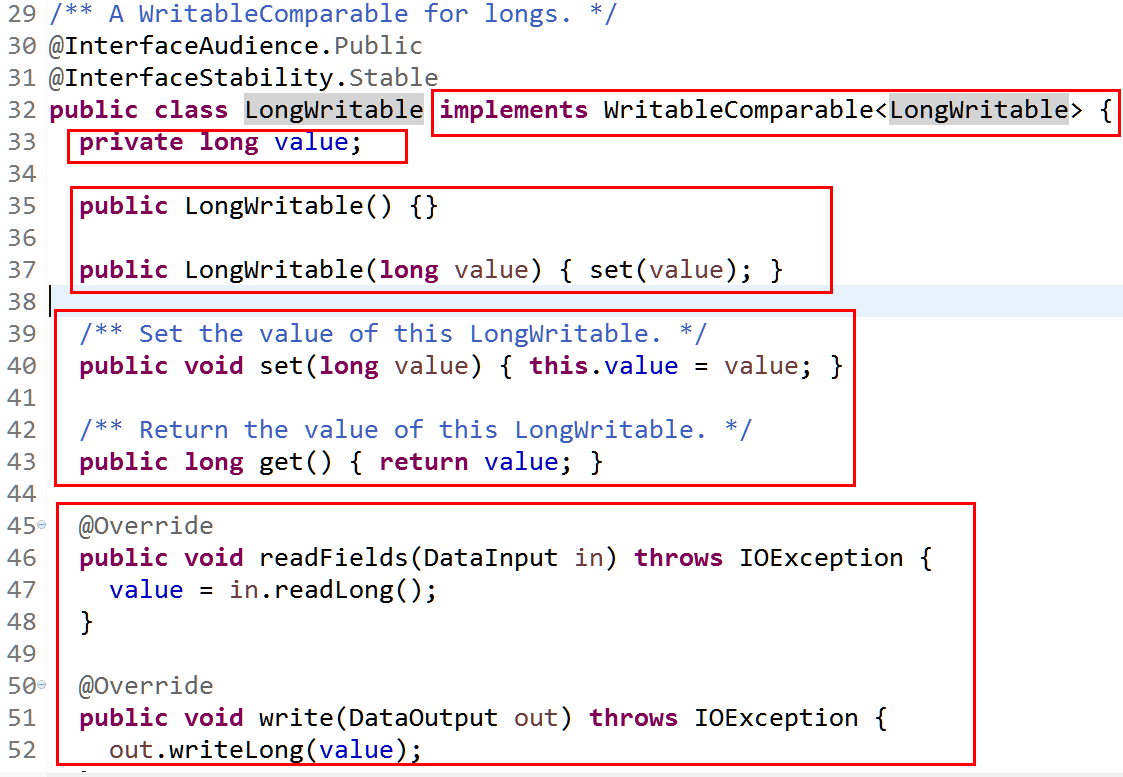
crtl+鼠标点击WritableComparable可看到,这个接口最终集成了Writable和Comparable两个接口

(3)同理:可以查看Text的源码,如下
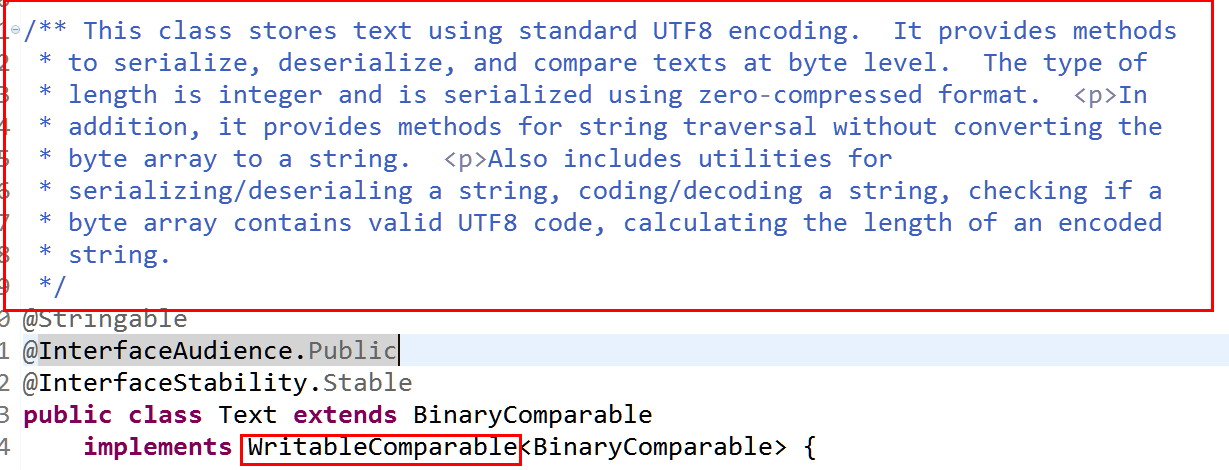
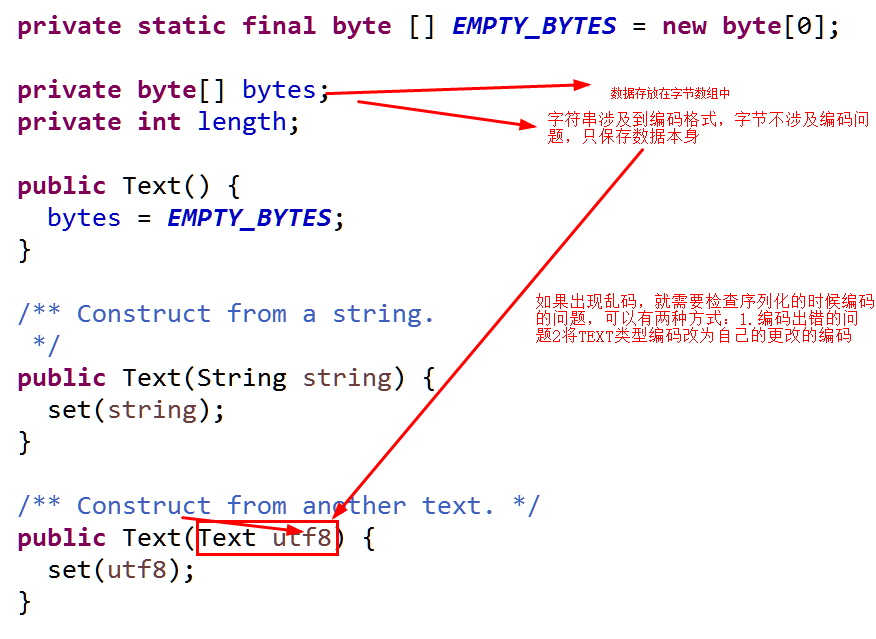
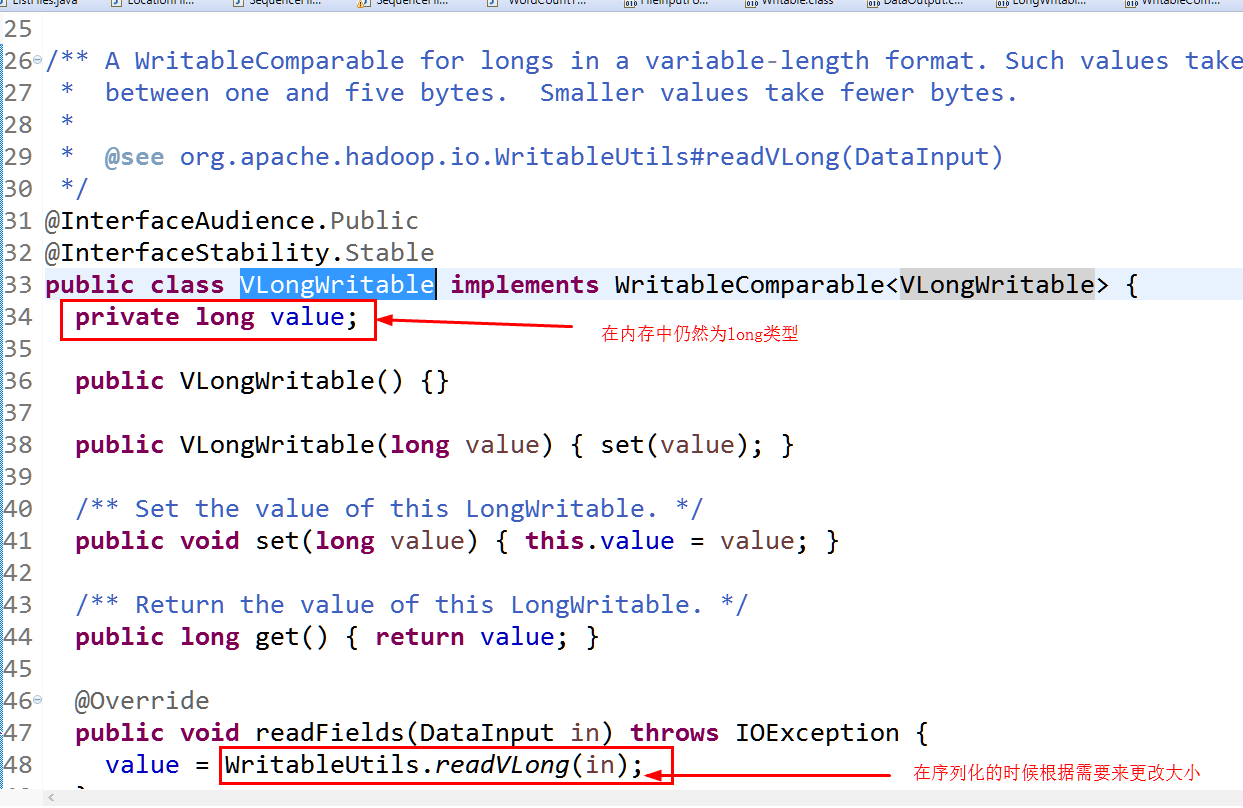
(4)序列化对应:

注:VlongWritable是变长类型
6.总结:

由于java或hadoop本身的类型有限,更多的是自定义的类型,因此自定义类型是更加重要的类型
7. 项目:电信中得手机上网流量的统计(业务中将上行包数+下行包数+上行总流量+下行总流量四个字段进行相加即为流量汇总)
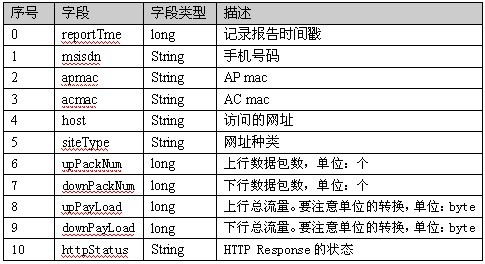
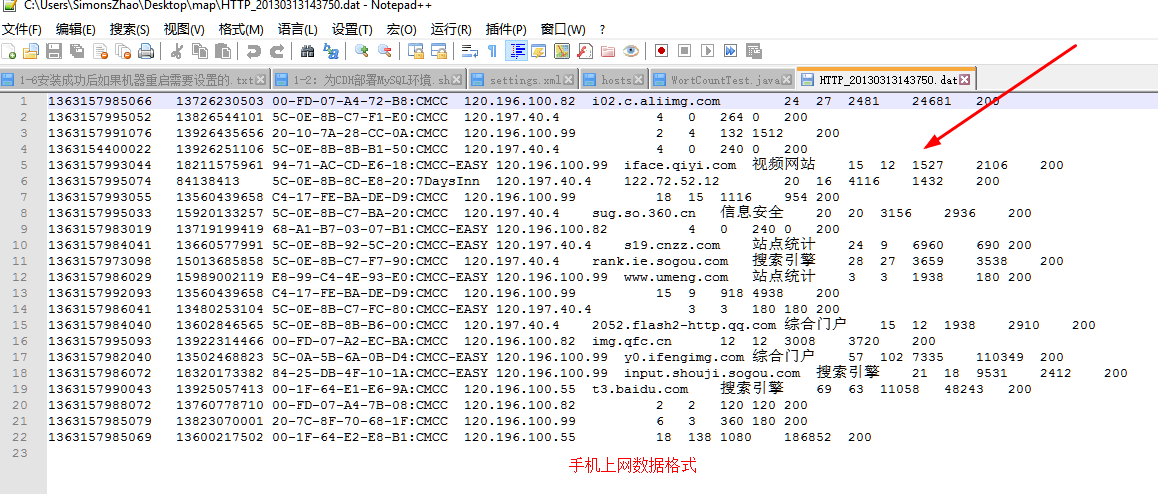
但是,上述四个字段并没有统一的单位,是不能相加的,因此只能一列所有的值进行相加,也就得到的是上行数据包总数,下行数据包总数,下行流量总数和上行流量总数等信息。
Mapreduce实现:
<k1,v1>中k1 是每一行起始位置,v1是每一行内容,k1在代码中没有用到(map的输入)
最终结果<k3,v3>得到的是<手机号码k3,上行数据包总数,下行数据包总数,下行流量总数,上行流量总数v3>
难点:如何算k3,v3(reducer的输出)?
而<k2,v2>确定其含义是至关重要的,原理是根据分组是按照k2分组的,
分组是让相同key的value放在一起,也就是相同key的value相加即为流量数据。
因此,k2为手机号码,v2就是上述4个流量。
解决:Longwritable等只能处理一个数据,而现在要处理四个数据,这时候需要自己自定义这种类型。
t1,t2,t3,t4分别为上行数据包总数,下行数据包总数,下行流量总数,上行流量总数。
下面程序为自定义类型的代码:
private static class TrafficWritable implements Writable{
public long t1;
public long t2;
public long t3;
public long t4;
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(t1);
out.writeLong(t2);
out.writeLong(t3);
out.writeLong(t4);
}
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
//顺序不可颠倒,和写出去的顺序需要一致
this.t1=in.readLong();
this.t2=in.readLong();
this.t3=in.readLong();
this.t4=in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return Long.toString(t1)+"\t"+Long.toString(t2)+"\t"+Long.toString(t3)+"\t"+Long.toString(t4);
}
}
业务实现的Hadoop代码如下:
package Mapreduce;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class Traffic {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Job job = Job.getInstance(new Configuration(), Traffic.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(Traffic.class);
//1.自定义输入路径
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
//2.自定义mapper
//job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
//job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
//job.setMapOutputValueClass(TrafficWritable.class);
//3.自定义reduce
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(TrafficWritable.class);
//4.自定义输出路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
//job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);//对输出的数据格式化并写入磁盘
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
private static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, TrafficWritable>{
Text k2 =new Text(); //k2为第二个字段,手机号码
TrafficWritable v2 = new TrafficWritable();
@Override
protected void map(
LongWritable key,
Text value,
Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, TrafficWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String line = value.toString();
String[] splited = line.split("\t");
//手机号码,第二个字段为手机号
k2.set(splited[1]);
//流量,注:写代码的时候先写方法名在写方法的实现(测试驱动开发s)
v2.set(splited[6],splited[7],splited[8],splited[9]);
context.write(k2, v2);
}
}
private static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, TrafficWritable, Text, TrafficWritable>{
TrafficWritable v3 = new TrafficWritable();
@Override
protected void reduce(
Text k2, //表示手机号码
Iterable<TrafficWritable> v2s, //相同手机号码流量之和
Reducer<Text, TrafficWritable, Text, TrafficWritable>.Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//迭代v2s,将里面的植相加即可
long t1 =0L;
long t2 =0L;
long t3 =0L;
long t4 =0L;
for (TrafficWritable v2 : v2s) {
t1+=v2.t1;
t2+=v2.t2;
t3+=v2.t3;
t4+=v2.t4;
}
v3.set(t1, t2, t3, t4);
context.write(k2, v3);//如果执行没有输出的话,可能reduce没有往外写,或mapper没有写,或源文件没有数据
}
}
//自定义类型
private static class TrafficWritable implements Writable{
public long t1;
public long t2;
public long t3;
public long t4;
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(t1);
out.writeLong(t2);
out.writeLong(t3);
out.writeLong(t4);
}
//t1-4原来是TrafficWritable类型,在set中进行转换
public void set(long t1, long t2, long t3, long t4) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.t1=t1;
this.t2=t2;
this.t3=t3;
this.t4=t4;
}
public void set(String t1, String t2, String t3,String t4) {
// v2的set方法
this.t1=Long.parseLong(t1);
this.t2=Long.parseLong(t2);
this.t3=Long.parseLong(t3);
this.t4=Long.parseLong(t4);
}
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
//顺序不可颠倒,和写出去的顺序需要一致
this.t1=in.readLong();
this.t2=in.readLong();
this.t3=in.readLong();
this.t4=in.readLong();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return Long.toString(t1)+"\t"+Long.toString(t2)+"\t"+Long.toString(t3)+"\t"+Long.toString(t4);
}
}
}
将代码打包并在linux中运行
(1)将文件HTTP开头的文件和Traffic.jar包上传到linux中
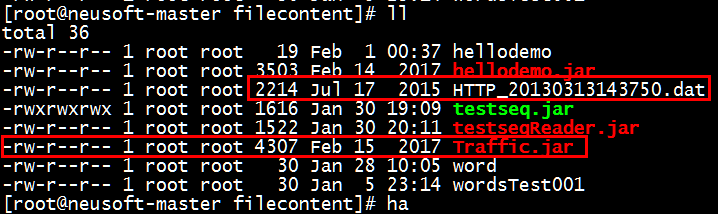
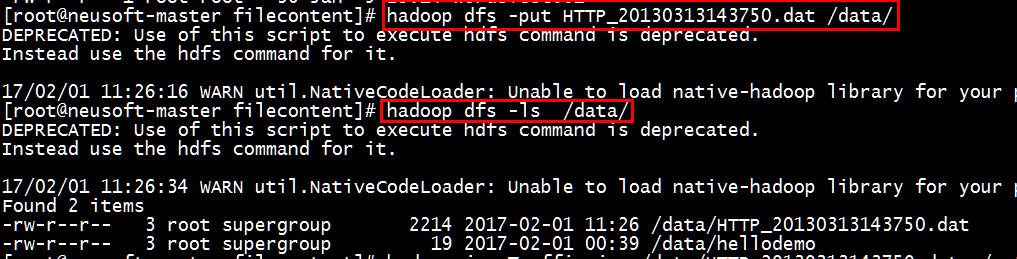
(2)上传HTTP开头的业务文件到HDFS的/data中,并查看此文件信息
(3)执行jar文件

(4)查看输出结果

注意:可能遇到的问题
(1)查看生成的文件,沒有輸出,這時候需要檢查代碼的Reduce端是否寫出來,或map端是否寫出,在或者文件是否爲空
(2)如果在出錯的環境下會產生/out2目錄,此時如果再次運行hadoop代碼會出現文件已經存在的問題,此時采用如下頒發
END~
Tip 优化:
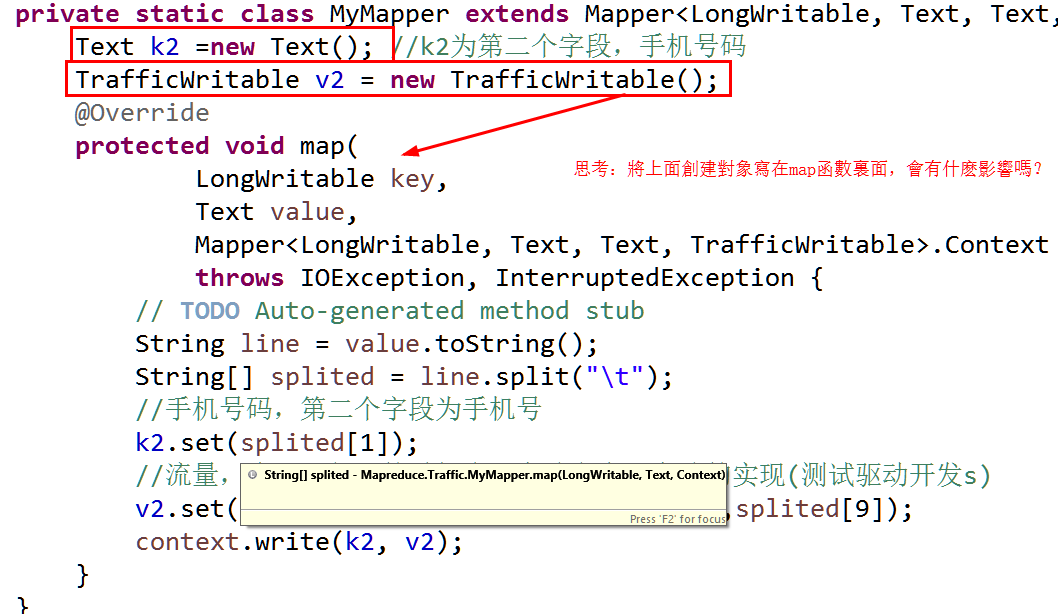
解答:如果new对象写在map函数里面,程序不会出现任何问题,但是,当数据行数非常大的话,每一行调用一次map函数,
会new很多对象,JVM也会一直处于高负荷状态,从而使得程序运行效率下降。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号