async/await 的使用
async :
使用 async 修饰符可将方法、lambda 表达式或匿名方法指定为异步。 如果对方法或表达式使用此修饰符,则其称为异步方法
await:
await 运算符应用于异步方法中的任务,在方法的执行中插入挂起点,直到所等待的任务完成,返回线程池。 任务表示正在进行的工作。
区别:
同步方法:一个程序调用某个同步方法,等到其执行完成之后才进行下一步操作。这也是默认的形式。
异步方法:一个程序调用某个异步方法(创建线程 【线程池】),取处理完成之前就返回该方法,并继续往下执行其他代码。
执行流程:
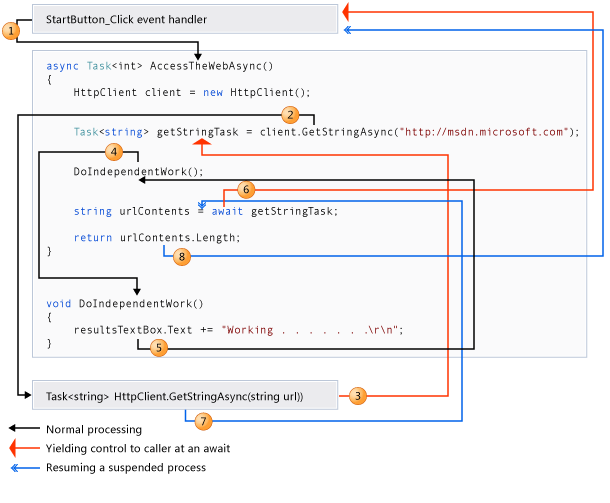
异步用例:
只有拥有async才能在其内部使用await关键字。异步方法可以具有Task、Task<>或void的返回类型;
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("主线程测试开始..");
AsyncMethod();
Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("主线程测试结束..");
Console.ReadLine();
}
static async void AsyncMethod()
{
Console.WriteLine("开始异步代码");
var result = await MyMethod();//var result = MyMethod().Result
Console.WriteLine("异步代码执行完毕");
}
static async Task<int> MyMethod()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("异步执行" + i.ToString() + "..");
await Task.Delay(1000); //模拟耗时操作
}
return 0;
}
}
Thread多线程异步编程例子:
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("主线程测试开始.."); Thread th = new Thread(ThMethod); th.Start(); Thread.Sleep(1000); Console.WriteLine("主线程测试结束.."); Console.ReadLine(); } static void ThMethod() { Console.WriteLine("异步执行开始"); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { Console.WriteLine("异步执行" + i.ToString() + ".."); Thread.Sleep(1000); } Console.WriteLine("异步执行完成"); } }
参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/jara/p/3405098.html //线程池传送门
https://www.cnblogs.com/yifengjianbai/p/5499493.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/color-wolf/p/5448458.html
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/dotnet/csharp/programming-guide/concepts/async/
https://www.cnblogs.com/chengjun/p/5366047.html





