LeetCode 160. 相交链表
我的LeetCode:https://leetcode-cn.com/u/ituring/
我的LeetCode刷题源码[GitHub]:https://github.com/izhoujie/Algorithmcii
LeetCode 160. 相交链表
题目
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
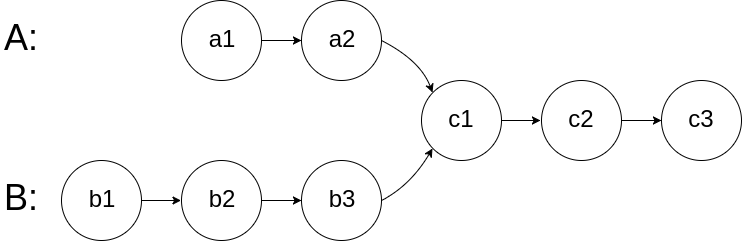
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
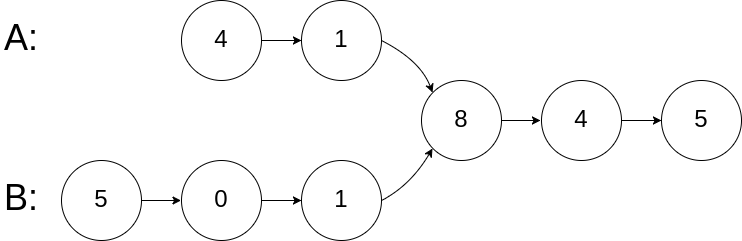
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
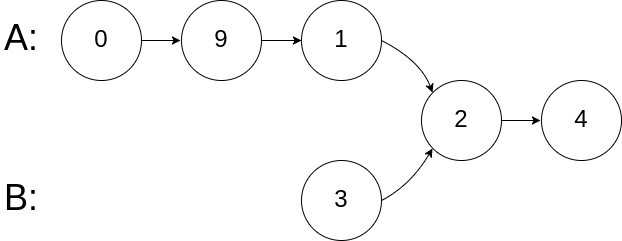
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
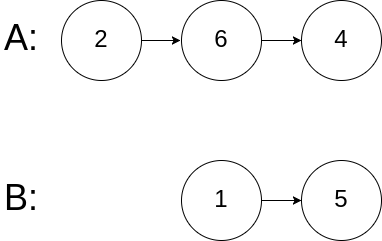
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
- 如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
- 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
- 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
- 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
解题思路
思路1-两次遍历,一次求长度差然后对齐开始第二次遍历并校验交点
步骤:
- 各遍历一次链表,求两者的长度差;
- 长的链表先走差值个节点,然后两个链表同步next并校验next是否相同,相同即表示找到了交点,否则最终为null;
算法复杂度:
- 时间复杂度: $ {\color{Magenta}{\Omicron\left(n\right)}} $
- 空间复杂度: $ {\color{Magenta}{\Omicron\left(1\right)}} $
思路2-两次遍历,但是设计上是两个链表首位相接
思路解析:代码的写法等价于在各自链表的末尾拼接了另一个链表,代码短简且优雅;
这样的拼接首先解决了链表的长度差,拼接后的长度一样,遍历时的情况:
- 两个链表原长度一样:
- 无交点,则在尾部时null==null,退出循环,无需遍历拼接部分;
- 有交点,则在到达尾部之前即可找到交点退出; - 两个链表原长度不一样:
- 无交点,则在遍历完自身后在遍历到拼接链表的尾部时有null==null,退出循环;
- 有交点,则在遍历完自身后在遍历拼接链表时相当于思路1的对齐,两指针必同时遍历到交点然后退出循环;
算法复杂度:
- 时间复杂度: $ {\color{Magenta}{\Omicron\left(n\right)}} $
- 空间复杂度: $ {\color{Magenta}{\Omicron\left(1\right)}} $
算法源码示例
package leetcode;
/**
* @author ZhouJie
* @date 2020年5月19日 下午1:26:38
* @Description: 160. 相交链表
*
*/
public class LeetCode_0160 {
}
// Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode_0160 {
int val;
ListNode_0160 next;
ListNode_0160(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
class Solution_0160 {
/**
* @author: ZhouJie
* @date: 2020年5月19日 下午1:32:36
* @param: @param headA
* @param: @param headB
* @param: @return
* @return: ListNode_0160
* @Description: 1-链表各需要遍历两次,一次统计长度,然后让长的先移动比短的多出的节点数,最后一起移动找相同节点;
*
*/
public ListNode_0160 getIntersectionNode_1(ListNode_0160 headA, ListNode_0160 headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
int a = 0, b = 0;
ListNode_0160 A = headA, B = headB;
// 统计链表长度
while (headA != null) {
a++;
headA = headA.next;
}
while (headB != null) {
b++;
headB = headB.next;
}
// 链表头对齐
if (a > b) {
a -= b;
while (a-- > 0) {
A = A.next;
}
} else if (a < b) {
b -= a;
while (b-- > 0) {
B = B.next;
}
}
// 寻找相交点,有则返回相交点,无则返回null
while (A != B) {
A = A.next;
B = B.next;
}
return A;
}
/**
* @author: ZhouJie
* @date: 2020年5月19日 下午1:44:52
* @param: @param headA
* @param: @param headB
* @param: @return
* @return: ListNode_0160
* @Description: 2-对方法1的优化
*
*/
public ListNode_0160 getIntersectionNode_2(ListNode_0160 headA, ListNode_0160 headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode_0160 A = headA, B = headB;
// 这里实际上相当于在A链表后面拼接了一个B链表,在B链表后面拼接了一个A链表,这样就保证了两个链表都有了相同的长度
// 且最多遍历两次即可得到结果
while (A != B) {
A = A == null ? headB : A.next;
B = B == null ? headA : B.next;
}
return A;
}
}
Talk is cheap. Show me the code.



