多线程的创建
方式一:
1.创建一个继承Thread类的子类
2.重写Thread类的run()
3.创建Thread类的子类的对象
4.通过此对象调用start()
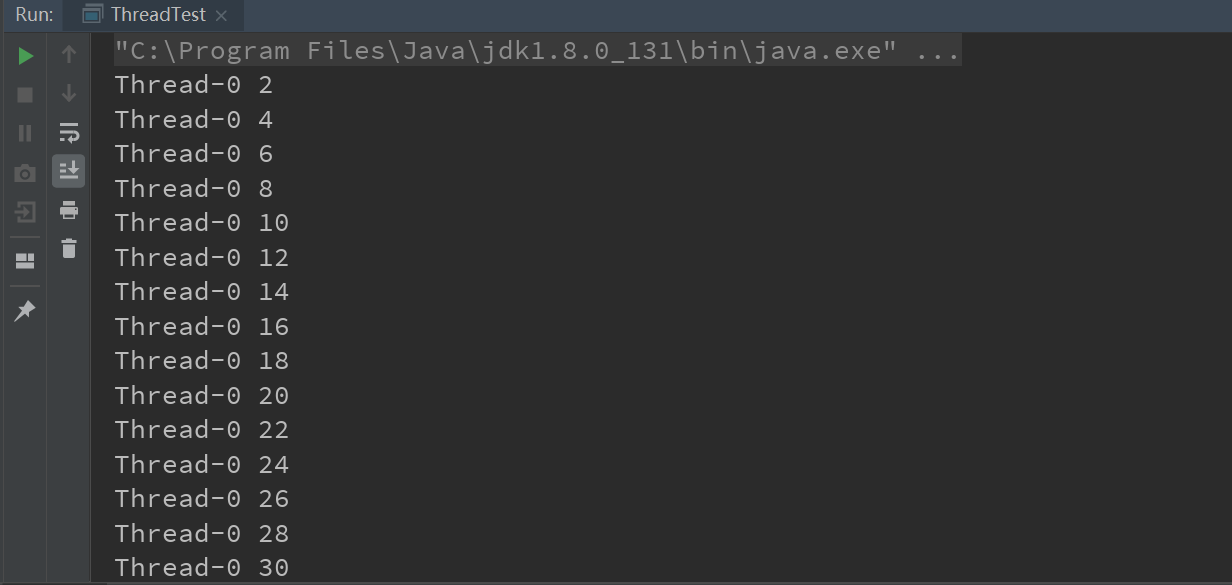
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | public class ThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread t1 = new MyThread(); t1.start(); }}class MyThread extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) { if(i%2==0){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+i); } } }} |
方式二:
1.创建一个实现了Runnable接口的类
2.实现类去实现Runnable抽象方法:run()
3,创建实现类的对象
4.将此对象作为参数传递到Thread类的构造器中,创建Thread类的对象
5.通过Thread类的对象调用start()
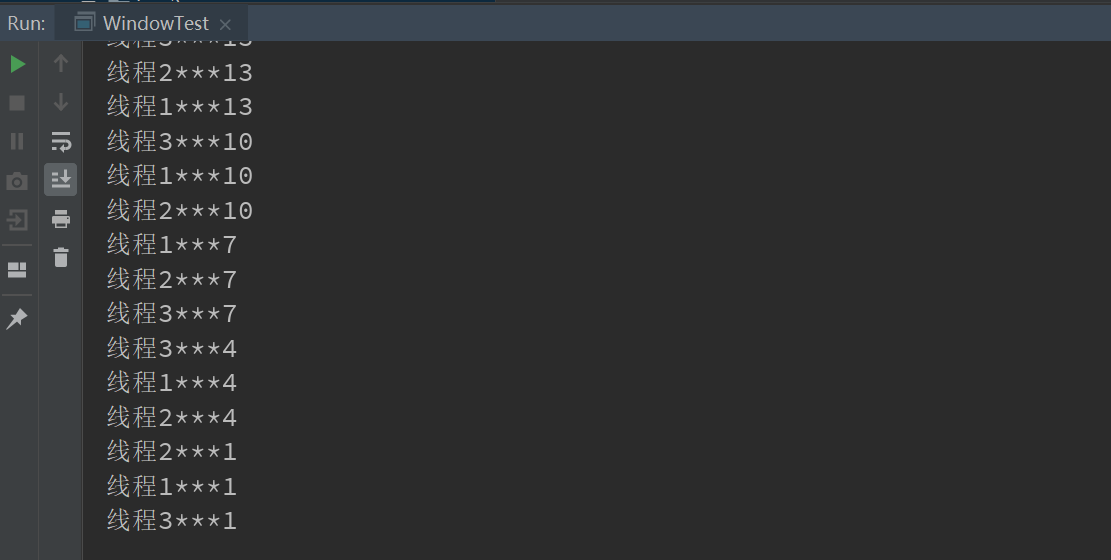
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 | public class Window implements Runnable { private int ticket = 100; @Override public void run() { while (true) { if (ticket > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(100); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "***" + ticket); ticket--; } else { break; } } }}class WindowTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Window w = new Window(); Thread t1 = new Thread(w); Thread t2 = new Thread(w); Thread t3 = new Thread(w); t1.setName("线程1"); t2.setName("线程2"); t3.setName("线程3"); t1.start(); t2.start(); t3.start(); }} |
方式三:实现Callable接口
1.创建一个实现Callable接口的实现类
2.实现call方法,将此线程需要执行的操作声明在call()中。
3.创建Callable接口实现类的对象
4.将此Callable接口实现类的对象作为参数传递到FutureTask构造器中,创建FutureTask的对象
5.将FutureTask的对象作为参数传递到Thread类的构造器中,创建Thread对象,并调用start()
6.获取Callable中call()方法返回值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 | public class CallableTest { public static void main(String[] args) { NumThread numThread = new NumThread(); FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(numThread); Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask); t1.start(); try { //get()返回值即为FutureTask构造器参数Callable实现类重写的call()的返回值 Object sum = futureTask.get(); System.out.println(sum); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}class NumThread implements Callable{ @Override public Object call() throws Exception { int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; }} |
使用泛型
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 | public class CallableTest { public static void main(String[] args) { NumThread numThread = new NumThread(); FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(numThread); Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask); t1.start(); try { //get()返回值即为FutureTask构造器参数Callable实现类重写的call()的返回值 Integer sum = futureTask.get(); System.out.println(sum); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (ExecutionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }}class NumThread implements Callable<Integer>{ @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; }} |
方式四:线程池
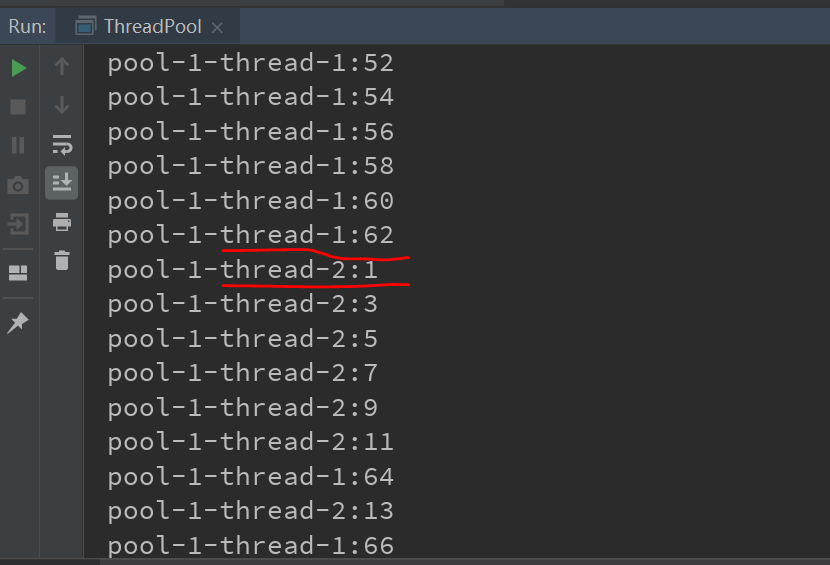
1 public class ThreadPool { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 //1.提供指定线程数量的线程池 4 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); 5 //2.执行指定的线程的操作,需要提供实现Runnable接口或Callable接口实现类的对象 6 executorService.execute(new NumberThread());//适用于Runnable 7 executorService.execute(new NumberThread2());//适用于Runnable 8 //executorService.submit(Callable callable);//适用于Callable 9 //关闭连接池 10 executorService.shutdown(); 11 } 12 } 13 14 class NumberThread implements Runnable{ 15 16 @Override 17 public void run() { 18 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 19 if(i%2==0){ 20 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 26 class NumberThread2 implements Runnable{ 27 28 @Override 29 public void run() { 30 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 31 if(i%2!=0){ 32 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+i); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY