数据结构与算法(二+)——向量的Java实现
数据结构与算法(二+)——向量的Java实现
iwehdio的博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/iwehdio/
Github:https://github.com/iwehdio/DSA_THU_DJH_asJava
1、项目结构
理论部分见:https://www.cnblogs.com/iwehdio/p/12273829.html
-
项目结构:
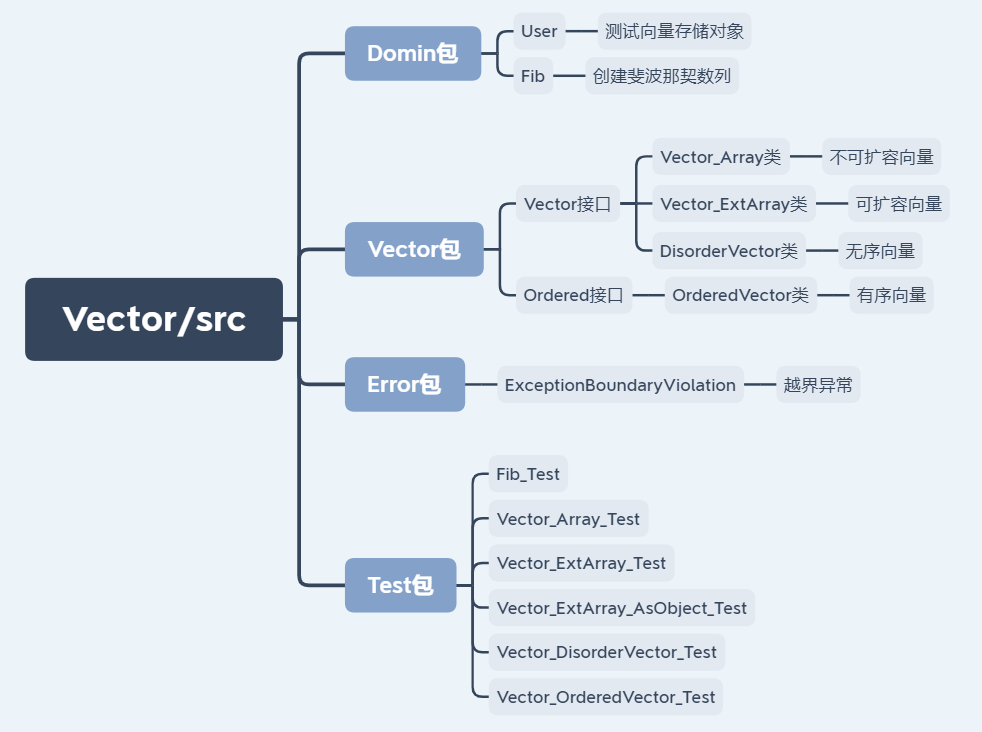
-
核心类体系结构与功能:
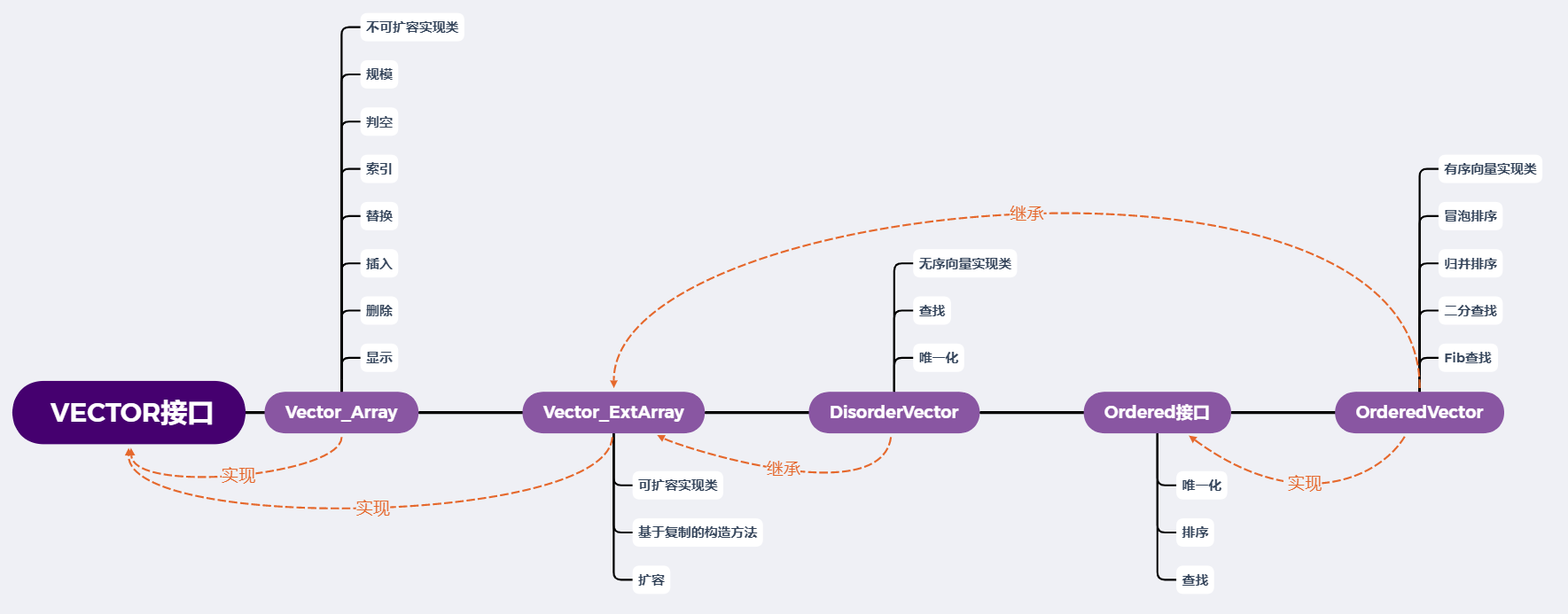
2、辅助类
-
User:
package Domin; public class User { private int id; private int age; private String phoneNumber; public User(int id, int age, String phoneNumber) { this.id = id; this.age = age; this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber; } @Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; User user = (User) o; return id == user.id && age == user.age && phoneNumber.equals(user.phoneNumber); } @Override public String toString() { return "User{id=" + id + ", age=" + age + ", phoneNumber='" + phoneNumber + '\'' + '}'; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getPhoneNumber() { return phoneNumber; } public void setPhoneNumber(String phoneNumber) { this.phoneNumber = phoneNumber; } } -
Fib:
package Domin; public class Fib { private int[] Arr; private int max_num = 5; private int N; private int n; private int index; public Fib(int N) { Arr = new int[max_num]; this.N = N; this.generateTable(); } private int generateTable(){ if(this.N <= 0) return -1; else if(this.N == 1) { Arr[0] = 1; return 1; }else { Arr[0] = 1; Arr[1] = 1; } int i = 1; while (Arr[this.n = i++] < this.N) { if(i >= max_num) this.expand(); Arr[i] = Arr[i-1] + Arr[i-2]; } this.index = i; this.prev(); return this.n; } public int prev(){ return --this.index; } public int get(){ return this.Arr[this.index-1]; } public void show(){ if(this.n == 0){ System.out.println("向量为空"); } else { System.out.print("["); for (int i = 0; i < this.n; i++) { System.out.print(this.Arr[i] + ", "); } System.out.println(this.Arr[this.n] + "]"); } } private int expand(){ int new_size = this.max_num * 2; int[] B = new int[new_size]; for(int i = 0; i < this.max_num; i++){ B[i] = this.Arr[i]; } max_num = new_size; this.Arr = B; System.out.println("Fib数组扩容完成,最大容量为" + this.max_num); return new_size; } } -
Fib_Test 测试类:
package Test; import Domin.Fib; public class Fib_Test { public static void main(String[] args) { int num = 100; Fib fib = new Fib(num); fib.show(); System.out.println("最后一项" + fib.get()); fib.prev(); System.out.println("前移一项" + fib.get()); } }-
结果为:
Fib数组扩容完成,最大容量为10 Fib数组扩容完成,最大容量为20 [1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144] 最后一项89 前移一项55
-
-
ExceptionBoundaryViolation:
package Error; public class ExceptionBoundaryViolation extends RuntimeException { public ExceptionBoundaryViolation(String error){ super(error); } }
3、Vector接口的实现
-
Vector接口:
- 要传入秩作为参数的,都需要考虑下标越界异常。
- 删除重载了单个元素删除和区间删除。
- 引入了泛型,但只用于元素输入输出时的类型转换。
import Error.ExceptionBoundaryViolation; public interface Vector<T> { //规模 public int getSize(); //判空 public boolean isEmpty(); //索引,有索引输入的都抛出下标越界异常 public T get(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation; //替换 public T replace(int rank, T obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation; //插入 public T insert(int rank, T obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation; //删除 public T remove(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation; public int remove(int left, int right) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation; //显示 public void show(); } -
Vector_Array 不可扩容向量实现类:
package Vector; import Error.ExceptionBoundaryViolation; public class Vector_Array<T> implements Vector<T> { private final int max_num = 1024; private int n = 0; private Object[] Array; public Vector_Array() { Array = new Object[max_num]; n = 0; } @Override public int getSize() { return n; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return (n == 0)? true : false; } @Override public T get(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if (rank < 0 || rank >= n){ throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } return (T)Array[rank]; } @Override public T replace(int rank, T new_obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if (rank < 0 || rank >= n){ throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } Object past_obj = Array[rank]; Array[rank] = new_obj; return (T)past_obj; } @Override public T insert(int rank, T obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if (rank < 0 || rank > n) { //注意插入时对越界的判断,与n比较没有=号 throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } else if (n + 1 > max_num) { throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误1:容量不足"); } for (int index = n; index > rank; index--) { Array[n] = Array[n-1]; } n++; Array[rank] = obj; return (T)obj; } @Override public T remove(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if(rank < 0 || rank >= n) { throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } Object past_obj = Array[rank]; for (int index = rank; index < n-1; index++){ Array[index] = Array[index + 1]; } n--; return (T)past_obj; } @Override public int remove(int left, int right){ if(left == right) return 0; while(right < n){ Array[left++] = Array[right++]; } n = left; return right - left; } @Override public void show() { if(n == 0){ System.out.println("向量为空"); } else { System.out.print("["); for (int index = 0; index < n-1; index++) { System.out.print(this.get(index) + ", "); } System.out.println(this.get(n-1) + "]"); } } } -
Vector_ExtArray 可扩容向量实现类:
- 重载了基于复制区间的构造方法。
- 扩容方法每次加倍扩容。
package Vector; import Error.ExceptionBoundaryViolation; public class Vector_ExtArray<T> implements Vector<T> { //protected 可以在子类中使用 protected int max_num = 8; //初始容量 protected int n = 0; protected Object[] Array; public Vector_ExtArray() { Array = new Object[max_num]; n = 0; } public Vector_ExtArray(Vector<T> vector, int left, int right) { if(left < 0 || right > vector.getSize()) throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误2:指定的复制区域错误"); n = right - left; Array = new Object[n]; for(int i=left, j=0; i<right; i++, j++){ Array[j] = vector.get(i); } } @Override public int getSize() { return n; } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return (n == 0)? true : false; } @Override public T get(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if (rank < 0 || rank >= n){ throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } return (T)Array[rank]; } @Override public T replace(int rank, T new_obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if (rank < 0 || rank >= n){ throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } Object past_obj = Array[rank]; Array[rank] = new_obj; return (T)past_obj; } @Override public T insert(int rank, T obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if (rank < 0 || rank > n) { //注意插入时对越界的判断,与n比较没有=号 throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } else if (n == max_num) { System.out.println("容量不足,需要扩容"); this.expand(); } for (int index = n; index > rank; index--) { Array[index] = Array[index-1]; } n++; Array[rank] = obj; return (T)obj; } @Override public T remove(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { if(rank < 0 || rank >= n) { throw new ExceptionBoundaryViolation("错误0:秩越界"); } Object past_obj = Array[rank]; for (int index = rank; index < n-1; index++){ Array[index] = Array[index + 1]; } n--; return (T)past_obj; } @Override public int remove(int left, int right){ if(left == right) return 0; while(right < n){ Array[left++] = Array[right++]; } n = left; return right - left; } @Override public void show() { if(n == 0){ System.out.println("向量为空"); } else { System.out.print("["); for (int index = 0; index < n-1; index++) { System.out.print(this.get(index) + ", "); } System.out.println(this.get(n-1) + "]"); } } private int expand(){ int new_size = max_num * 2; Object[] B = new Object[new_size]; for(int index = 0; index < max_num; index++){ B[index] = Array[index]; } max_num = new_size; Array = B; System.out.println("扩容完成,最大容量为" + max_num); return new_size; } } -
Vector_ExtArray_Test 可扩容向量测试:
package Test; import Vector.Vector; import Vector.Vector_ExtArray; public class Vector_ExtArray_Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector<Integer> vector = new Vector_ExtArray<Integer>(); System.out.println("空向量:"); vector.show(); System.out.println("判空:" + vector.isEmpty()); System.out.println("规模:" + vector.getSize()); int num = 10; int doAt = 5; int new_data = doAt * 2; for (int i=0; i < num; i++){ vector.insert(i, i*i); } vector.show(); vector.insert(3, doAt * doAt); System.out.println("插入数据后"); vector.show(); System.out.println("规模:" + vector.getSize()); System.out.println("在秩为" + doAt + "的数据为:" + vector.get(doAt)); vector.replace(doAt, new_data); System.out.println("将在秩为" + doAt + "的数据替换为:" + new_data); System.out.println("替换后:"); vector.show(); vector.remove(doAt); System.out.println("将在秩" + doAt + "的数据移除后新数据为:" + new_data); System.out.println("删除后:"); vector.show(); System.out.println("规模:" + vector.getSize()); int left = 2; int rigth = 5; System.out.println(left + "到" + rigth + "之间删除"); vector.remove(left, rigth); vector.show(); //测试异常 vector.get(num + 1); } }-
结果为:
空向量: 向量为空 判空:true 规模:0 插入数据后 [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81] 规模:10 在秩为5的数据为:25 将在秩为5的数据替换为:10 替换后: [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 10, 36, 49, 64, 81] 将在秩5的数据移除后新数据为:10 删除后: [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 36, 49, 64, 81] 规模:9 Exception in thread "main" Error.ExceptionBoundaryViolation: 错误0:秩越界 at Vector.Vector_Array.get(Vector_Array.java:28) at Test.Vector_Array_Test.main(Vector_Array_Test.java:39)
-
-
Vector_ExtArray_AsObject_Test 向量元素为对象测试:
package Test; import Domin.User; import Vector.Vector; import Vector.Vector_ExtArray; public class Vector_ExtArray_AsObject_Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Vector<User> vector = new Vector_ExtArray<User>(); System.out.println("空向量:"); vector.show(); System.out.println("判空:" + vector.isEmpty()); System.out.println("规模:" + vector.getSize()); int num = 10; int doAt = 5; User new_data = new User(20, 22, "10086" + Integer.toString(20 * 2)); for (int i=0; i < num; i++){ vector.insert(i, new User(i, 22, "10086" + Integer.toString(i * 2))); } System.out.println("插入数据后"); vector.show(); System.out.println("规模:" + vector.getSize()); System.out.println("在秩为" + doAt + "的数据为:" + vector.get(doAt)); vector.replace(doAt, new_data); System.out.println("将在秩为" + doAt + "的数据替换为:" + new_data); System.out.println("替换后:"); vector.show(); vector.remove(doAt); System.out.println("将在秩" + doAt + "的数据移除后新数据为:" + new_data); System.out.println("删除后:"); vector.show(); System.out.println("规模:" + vector.getSize()); //测试异常 vector.get(num + 1); } }
4、无序向量与有序向量
-
DisorderVector 无序向量:
package Vector; import Error.ExceptionBoundaryViolation; public class DisorderVector<T> extends Vector_ExtArray<T>{ public int find(T e, int left, int right){ if(left < 0 || right > super.n) return -1; //right是右哨兵节点,可以等于n while((left < right--) && (!e.equals(super.Array[right]))); return right; } public int find(T e){ return find(e, 0, super.n); } //唯一化 public int uniquify(){ int removeNum = 0; for(int index=1 ; index<super.n; index++){ //从第二个元素开始 int Rank = this.find((T)super.Array[index], 0, index); if(Rank != -1){ remove(index--); removeNum++; } } return removeNum; } public DisorderVector() { super(); } @Override public T remove(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { return super.remove(rank); } @Override public int remove(int left, int right) { return super.remove(left, right); } @Override public int getSize() { return super.getSize(); } @Override public boolean isEmpty() { return super.isEmpty(); } @Override public T get(int rank) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { return super.get(rank); } @Override public T replace(int rank, T new_obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { return super.replace(rank, new_obj); } @Override public T insert(int rank, T obj) throws ExceptionBoundaryViolation { return super.insert(rank, obj); } @Override public void show() { super.show(); } } -
Vector_DisorderVector_Test 无序向量测试:
package Test; import Vector.Vector; import Vector.DisorderVector; public class Vector_DisorderVector_Test { public static void main(String[] args) { DisorderVector<Integer> vector = new DisorderVector<Integer>(); int num = 10; int doAt = 25; for (int i=0; i < num; i++){ vector.insert(i, i*i); } vector.insert(3, doAt); vector.insert(5, doAt); vector.insert(7, doAt); vector.insert(9, doAt); vector.insert(11, 64); vector.insert(13, 0); System.out.println("插入数据后:"); vector.show(); System.out.println("寻找数据为" + doAt + "的位置:"); int Rank = vector.find(doAt); System.out.println(Rank); System.out.println("去重:"); int removeNum = vector.uniquify(); vector.show(); System.out.println("共移除了" + removeNum + "个重复元素"); } }-
结果为:
容量不足,需要扩容 扩容完成,最大容量为16 插入数据后: [0, 1, 4, 25, 9, 25, 16, 25, 25, 25, 36, 64, 49, 0, 64, 81] 寻找数据为25的位置: 9 去重: [0, 1, 4, 25, 9, 16, 36, 64, 49, 81] 共移除了6个重复元素
-
-
Ordered 有序接口:
- 泛型必须已经实现了
compareTo()方法。
package Vector; public interface Ordered<T extends Comparable> { //唯一化 public int uniquify(); //冒泡排序 public void bubbleSort(int left, int right); public void bubbleSort(); //归并排序 public void mergeSort(int left, int right); public void mergeSort(); //二分查找 public int binsearch(T e, int left, int right); public int binsearch(T e); //Fib查找 public int fibsearch(T e, int left, int right); public int fibsearch(T e); } - 泛型必须已经实现了
-
OrderedVector 有序向量:
- 归并排序要注意,索引后半段向量的起始位置要加 mid,赋值原向量的起始位置要加 left 。
package Vector; import Domin.Fib; public class OrderedVector<T extends Comparable> extends Vector_ExtArray<T> implements Ordered<T> { @Override public int uniquify() { int left = 0; //双指针 int right = 0; while(++right < super.n){ if(!super.Array[left].equals(super.Array[right])){ super.Array[++left] = super.Array[right]; } } super.n = ++left; //左指针左侧是结果 return right - left; } @Override public void bubbleSort(int left, int right) { while (left < (right = bubble(left, right))); } @Override public void bubbleSort() { bubbleSort(0, super.n); } private int bubble(int left, int right){ int last = left; while (++left < right){ if(((T)super.Array[left]).compareTo(super.Array[left-1]) == -1){ last = left; T temp = (T)super.Array[left-1]; super.Array[left-1] = super.Array[left]; super.Array[left] = temp; } } return last; } @Override public void mergeSort(int left, int right) { if(right - left < 2)return; int mid = (left + right) >> 1; mergeSort(left, mid); mergeSort(mid, right); merge(left, mid, right); } @Override public void mergeSort() { mergeSort(0, super.n); } private void merge(int left, int mid, int right) { Vector_ExtArray<T> vector = new Vector_ExtArray<T>(this, left, mid); int lb = mid - left; int lc = right - mid; for(int i=0, j=0, k=0; (j<lb) || (k<lc); ) { if((j<lb) && (lc<=k || (vector.get(j).compareTo(super.Array[k + mid])<1))){ super.Array[left + i++] = vector.get(j++); } if((k<lc) && (lb<=j || (vector.get(j).compareTo(super.Array[k + mid])==1))){ super.Array[left + i++] = super.Array[k++ + mid]; } } } public int binsearch_A(T e, int left, int right) { while(left < right){ int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if(e.compareTo(super.Array[mid]) == -1){ right = mid; } else if(e.compareTo(super.Array[mid]) == 1){ left = mid + 1; } else { return mid; } } return -1; } public int binsearch_A(T e) { return binsearch_A(e, 0, super.n); } public int binsearch_B(T e, int left, int right) { int mid = (left + right) >> 1; while(right - left > 1){ mid = (left + right) >> 1; if(e.compareTo(super.Array[mid]) == -1){ right = mid; } else { left = mid ; } } return (e.equals(super.Array[mid]))? mid : -1; } public int binsearch_B(T e) { return binsearch_A(e, 0, super.n); } @Override public int binsearch(T e, int left, int right) { while(left < right){ int mid = (left + right) >> 1; if(e.compareTo(super.Array[mid]) == -1){ right = mid; } else if(e.compareTo(super.Array[mid]) == 1){ left = mid + 1; } } return --left; } @Override public int binsearch(T e) { return binsearch(e, 0, super.n); } @Override public int fibsearch(T e, int left, int right) { Fib fib = new Fib(right - left); int mid; while (right - left > fib.get()){ fib.prev(); mid = left + fib.get() -1; if(e.compareTo(super.Array[mid]) == -1){ right = mid; } else if(e.compareTo(super.Array[mid]) == 1){ left = mid + 1; } else { return mid; } } return -1; } @Override public int fibsearch(T e) { return fibsearch(e, 0, super.n); } } -
Vector_OrderedVector_Test 有序向量测试:
package Test; import Vector.Vector; import Vector.OrderedVector; import Vector.Vector_ExtArray; import java.util.Random; public class Vector_OrderedVector_Test { public static void main(String[] args) { OrderedVector<Integer> vector = new OrderedVector<Integer>(); Random random = new Random(); int num = 20; System.out.println("查找:"); int doAt1 = 3*3; int doAt2 = 7*7; int doAt3 = 11*11; int doAt4 = 15*15; for (int i=0; i < num; i++){ vector.insert(i, i * i); } System.out.println("插入数据后"); vector.show(); int Rank = vector.binsearch_A(doAt1); System.out.println("binsearch_A:数据" + doAt1 + "在位置" + Rank); Rank = vector.binsearch_B(doAt2); System.out.println("binsearch_B:数据" + doAt2 + "在位置" + Rank); Rank = vector.binsearch_A(doAt3); System.out.println("binsearch_C:数据" + doAt3 + "在位置" + Rank); Rank = vector.fibsearch(doAt4); System.out.println("fibsearch:数据" + doAt4 + "在位置" + Rank); System.out.println("-------------------------"); System.out.println("排序:"); OrderedVector<Integer> vector1 = new OrderedVector<Integer>(); for (int i=0; i < num; i++){ vector1.insert(i, random.nextInt(100)); } System.out.println("插入数据后"); vector1.show(); System.out.println("冒泡排序:"); vector1.bubbleSort(); vector1.show(); OrderedVector<Integer> vector2 = new OrderedVector<Integer>(); for (int i=0; i < num; i++){ vector2.insert(i, random.nextInt(100)); } System.out.println("插入数据后"); vector2.show(); System.out.println("归并排序:"); vector2.mergeSort(); vector2.show(); } }-
结果为:
查找: 容量不足,需要扩容 扩容完成,最大容量为16 容量不足,需要扩容 扩容完成,最大容量为32 插入数据后 [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, 144, 169, 196, 225, 256, 289, 324, 361] binsearch_A:数据9在位置3 binsearch_B:数据49在位置7 binsearch_C:数据121在位置11 Fib数组扩容完成,最大容量为10 fibsearch:数据225在位置15 ------------------------- 排序: 容量不足,需要扩容 扩容完成,最大容量为16 容量不足,需要扩容 扩容完成,最大容量为32 插入数据后 [89, 17, 15, 88, 80, 95, 93, 57, 21, 93, 67, 69, 30, 79, 84, 5, 19, 6, 70, 2] 冒泡排序: [2, 5, 6, 15, 17, 19, 21, 30, 57, 67, 69, 70, 79, 80, 84, 88, 89, 93, 93, 95] 容量不足,需要扩容 扩容完成,最大容量为16 容量不足,需要扩容 扩容完成,最大容量为32 插入数据后 [39, 89, 73, 24, 3, 57, 54, 83, 11, 81, 30, 42, 24, 78, 29, 73, 48, 31, 7, 38] 归并排序: [3, 7, 11, 24, 24, 29, 30, 31, 38, 39, 42, 48, 54, 57, 73, 73, 78, 81, 83, 89]
-
5、思考
-
查看课程提供的源码,其提供了更多的接口,用于抽象不同层次的共性。
-
判等器和比较器:
-
Java 不像 C++ 中支持运算符的重载,所以需要调用方法来实现判等和比较。
-
判等 比较简单,调用
.equals()方法,如果是自定义类型需要在类中重写。在课程源码中,构造了判等器进行格式统一。实际上与直接调用无本质区别。//判等器接口 public interface EqualityTester { public boolean isEqualTo(Object a, Object b);//若a与b相等,则返回true;否则,返回false } //默认判等器 public class EqualityTesterDefault implements EqualityTester { public EqualityTesterDefault() {} public boolean isEqualTo(Object a, Object b) { return (a.equals(b)); }//使用Java提供的判等器 } -
比较 相对而言比较麻烦。
-
第一种方法是,类似于判等,在类型中重写
.compareTo()方法。但是.equals()方法是有默认实现(即比较对象的地址),但.compareTo()方法没有默认实现。 -
为了让编译器知道,所传入的类型实现了比较方法,该类型需要实现
Comparable接口,同时传入的泛型也为可比较的类型<T extends Comparable>。 -
只有继承了Comparable接口并重写了compareTo方法,这个类才视为Compareable类,如果值写了compareTo方法,没有明确implement Comparable则其只是一个普通的类。
-
第一种方法需要更改传入类型的源代码,比较麻烦。第二种方法是,构造比较器,实现
Comparator接口,这样可以对比较器调用compare()方法。在使用时,传入比较器即可。//比较器接口 public interface Comparator { public int compare(Object a, Object b);//若a>(=或<)b,返回正数、零或负数 } //默认比较器 public class ComparatorDefault implements Comparator { public ComparatorDefault() {} public int compare(Object a, Object b) throws ClassCastException { return ((Comparable) a).compareTo(b); } }
-
-
-
排序器:
-
所有的排序算法都是排序器的一个实现类,Sequence 是继承自向量和列表的接口。
//排序器接口 public interface Sorter { public void sort(Sequence s); } //冒泡排序 public class Sorter_Bubblesort implements Sorter { private Comparator C; public Sorter_Bubblesort() { this(new ComparatorDefault()); } public Sorter_Bubblesort(Comparator comp) { C = comp; } public void sort(Sequence S) { /* 冒泡排序实现 */ } } -
具体的排序实现类中,空参构造使用默认比较器,有参构造使用传入的比较器。
-
-
实现对 User 类的比较器并进行排序:
-
ComparatorAsUser:
public class ComparatorAsUser implements Comparator{ //User 类的比较器,先比Id大小,再比Age大小,最后是PhoneNumber长度 @Override public int compare(Object a, Object b) { int res; User user_a = (User) a; User user_b = (User) b; if (user_a.equals(user_b)) { res = 0; } else { int comForId = Integer.compare(user_a.getId(), user_b.getId()); if (comForId == 0) { int comForAge = Integer.compare(user_a.getAge(), user_b.getAge()); if (comForAge == 0) { res = Integer.compare(user_a.getPhoneNumber().length(), user_b.getPhoneNumber().length()); } else { res = comForAge; } } else { res = comForId; } } return res; } } -
Comparator_User_Test:
public class Comparator_User_Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Sorter_Bubblesort sorter_Bubblesort = new Sorter_Bubblesort(new ComparatorAsUser()); Vector_ExtArray<User> vector = new Vector_ExtArray<User>(); vector.insert(0, new User(5, 19, "13568")); vector.insert(1, new User(4, 16, "13568")); vector.insert(2, new User(2, 17, "13568")); vector.insert(3, new User(1, 11, "13568")); vector.insert(4, new User(3, 14, "13568")); vector.insert(5, new User(2, 11, "13568")); vector.insert(6, new User(3, 20, "13568")); vector.insert(6, new User(3, 20, "1356648")); System.out.println("插入数据后"); vector.show(); System.out.println("排序:"); sorter_Bubblesort.sort(vector); vector.show(); } } -
结果为:
插入数据后 [User{id=5, age=19, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=4, age=16, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=2, age=17, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=1, age=11, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=3, age=14, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=2, age=11, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=3, age=20, phoneNumber='1356648'} , User{id=3, age=20, phoneNumber='13568'} ] 排序: [User{id=1, age=11, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=2, age=11, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=2, age=17, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=3, age=14, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=3, age=20, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=3, age=20, phoneNumber='1356648'} , User{id=4, age=16, phoneNumber='13568'} , User{id=5, age=19, phoneNumber='13568'} ]
-
-
课程源码中没有使用泛型,所有可能无法对输入的元素进行类型检查。
-
不是很明白对向量和列表接口的继承:Sequence 接口有何意义,先将 Sequence 都改为了 Vector。
-
向量部分的异常:
- Vector_ExtArray:错误0:秩越界。
- Vector_Array:错误1:容量不足。
- Vector_ExtArray:错误2:指定的复制区域错误。
参考:数据结构与算法(清华大学C++描述):https://www.bilibili.com/video/av49361421
iwehdio的博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/iwehdio/


