java排序算法总结
总结排序算法前,先对排序算法中出现的术语进行说明。
1.术语说明
- 稳定与不稳定:a在b前,若a=b,排序后a一定还在b前,这就说明稳定
- 内外排序:基于内存排序,就是内排序
- 时间复杂度:算法耗费的时间
- 空间复杂度:耗费内存的大小
2.算法分类
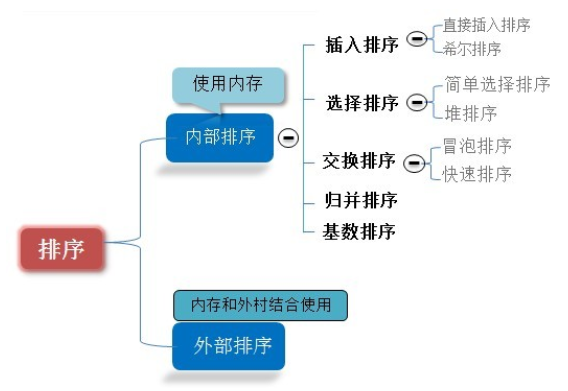
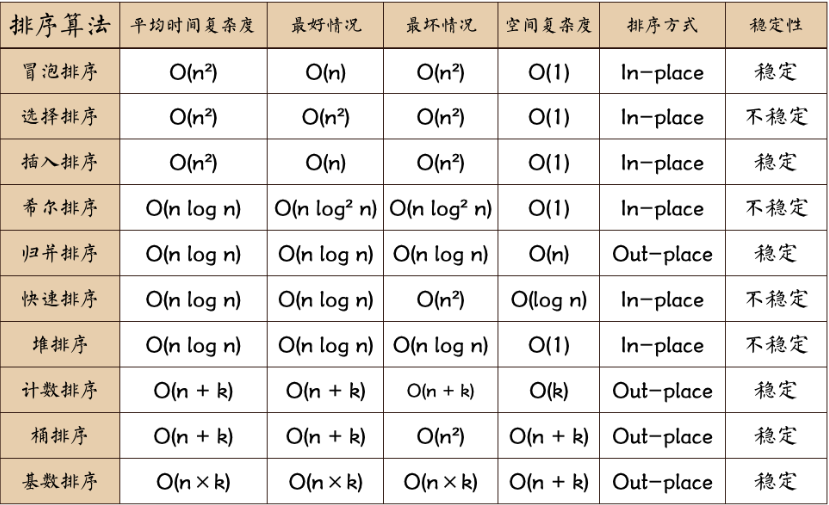
下面详细介绍算法。
1.冒泡排序
这是最常见的排序。从第一个到最后一个元素,相邻元素比大小,互换位置。
举例说明:
1 public static int[] bubble(int[] arr){ 2 if (arr.length == 0) { 3 return arr; 4 } 5 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 6 for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) { 7 if (arr[j] < arr[i]) { 8 int temp = arr[i]; 9 arr[i] = arr[j]; 10 arr[j] = temp; 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 return arr; 15
2.快速排序
它是冒泡排序的升级版。原理,随机找出一个元素,把数列分成两部分,使一部分比另一部分元素小,按照同样的方法,把子数列再分成更小的子数列,直到不能分为止。
举例说明:
1 public static int[] quick(int[] arr, int start, int end) { 2 if (arr.length < 1 || start < 0 || end > arr.length || start > end) { 3 return null; 4 } 5 int point = partition(arr, start, end); 6 //左子序排序 7 if (point > start) { 8 quick(arr, start, point - 1); 9 } 10 //右子序排序 11 if (point < end) { 12 quick(arr, point + 1, end); 13 } 14 return arr; 15 } 16 17 private static int partition(int[] arr, int start, int end) { 18 int temp = (int) (start + Math.random() * (end - start + 1)); 19 int index = start - 1; 20 swap(arr,temp,end); 21 for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) { 22 if (arr[i] <= arr[end]) { 23 index++; 24 if (i > index) { 25 swap(arr,i,index); 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 return index; 30 31 } 32 33 private static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) { 34 if (arr != null && arr.length > 0) { 35 int temp = arr[i]; 36 arr[i] = arr[j]; 37 arr[j] = temp; 38 } 39 }
3.堆排序
堆物理上是完全二叉树。数列构成大顶堆。将堆顶与末尾元素交换,将剩余元素重新构成大顶堆。将堆顶与末尾元素交换,以此类推。
举例说明:
1 private static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) { 2 if (arr != null && arr.length > 0) { 3 int temp = arr[i]; 4 arr[i] = arr[j]; 5 arr[j] = temp; 6 } 7 } 8 9 public static int[] heap(int[] arr) { 10 len = arr.length; 11 if (len < 1) { 12 return arr; 13 } 14 buildMaxHeap(arr); 15 while (len > 0) { 16 //堆顶与末尾元素交换 17 swap(arr,0,len - 1); 18 len--; 19 adjustHeap(arr, 0); 20 } 21 return arr; 22 } 23 24 private static void adjustHeap(int[] arr, int i) { 25 int maxIndex = i; 26 //右节点 27 if (i * 2 + 2 < len && arr[i * 2 + 2] > arr[maxIndex]) { 28 maxIndex = i * 2 + 2; 29 } 30 //左节点 31 if (i * 2 + 1 < len && arr[i * 2 + 1] > arr[maxIndex]) { 32 maxIndex = i * 2 + 1; 33 } 34 if (maxIndex != i) { 35 swap(arr,maxIndex,i); 36 adjustHeap(arr,maxIndex); 37 } 38 } 39 40 private static void buildMaxHeap(int[] arr) { 41 for (int i = (len/2 - 1); i >= 0; i--) { 42 adjustHeap(arr,i); 43 } 44 }
这里有一个问题,表示右节点2*i+2,为什么不能是2*1?
4.选择排序
找到最值放到起始位置,再次剩余元素中找最值放在已排序序列末尾。以此类推。
举例说明:
1 public static int[] select(int[] arr) { 2 if (arr.length == 0) { 3 return arr; 4 } 5 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 6 int mixIndex = i; 7 for (int j = i; j < arr.length; j++) { 8 if (arr[j] < arr[mixIndex]) { 9 mixIndex = j; 10 } 11 } 12 swap(arr,mixIndex,i); 13 } 14 return arr; 15 }
5.插入排序
将数列第一个元素认为有序,在已排序列中从后向前(从前往后)寻找插入位置插入数据。
举例说明:
1 public static int[] insert(int[] arr) { 2 if (arr.length == 0) { 3 return arr; 4 } 5 int curr; 6 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length - 1; i++) { 7 curr = arr[i + 1]; 8 int preIndex = i; 9 while (preIndex >= 0 && curr < arr[preIndex]) { 10 arr[preIndex + 1] = arr[preIndex]; 11 preIndex--; 12 } 13 arr[preIndex + 1] = curr; 14 } 15 return arr; 16 }
6.希尔排序
按下标的一定增量分组,对每组使用插入排序排序。增量减少,每组包含元素增多,对每组使用插入排序排序。以此类推,直到增量为1。
举例说明:
1 public static int[] shell(int[] arr) { 2 int len = arr.length; 3 int temp,gap = len / 2; 4 while (gap > 0) { 5 for (int i = gap; i < len; i++) { 6 temp = arr[i]; 7 int preIndex = i - gap; 8 while (preIndex >= 0 && arr[preIndex] > temp) { 9 arr[preIndex + gap] = arr[preIndex]; 10 preIndex -= gap; 11 } 12 arr[preIndex + gap] = temp; 13 } 14 gap /= 2; 15 } 16 return arr; 17 }
7.归并排序
先使每个子数列有序,再使子序列间有序,最后合并。
举例说明:
1 /** 2 * 归并排序 3 * 4 * @param array 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public static int[] MergeSort(int[] array) { 8 if (array.length < 2) return array; 9 int mid = array.length / 2; 10 int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, 0, mid); 11 int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, mid, array.length); 12 return merge(MergeSort(left), MergeSort(right)); 13 } 14 /** 15 * 归并排序——将两段排序好的数组结合成一个排序数组 16 * 17 * @param left 18 * @param right 19 * @return 20 */ 21 public static int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) { 22 int[] result = new int[left.length + right.length]; 23 for (int index = 0, i = 0, j = 0; index < result.length; index++) { 24 if (i >= left.length) 25 result[index] = right[j++]; 26 else if (j >= right.length) 27 result[index] = left[i++]; 28 else if (left[i] > right[j]) 29 result[index] = right[j++]; 30 else 31 result[index] = left[i++]; 32 } 33 return result; 34 }
1 /** 2 * 归并排序 3 * 4 * @param array 5 * @return 6 */ 7 public static int[] MergeSort(int[] array) { 8 if (array.length < 2) return array; 9 int mid = array.length / 2; 10 int[] left = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, 0, mid); 11 int[] right = Arrays.copyOfRange(array, mid, array.length); 12 return merge(MergeSort(left), MergeSort(right)); 13 } 14 /** 15 * 归并排序——将两段排序好的数组结合成一个排序数组 16 * 17 * @param left 18 * @param right 19 * @return 20 */ 21 public static int[] merge(int[] left, int[] right) { 22 int[] result = new int[left.length + right.length]; 23 for (int index = 0, i = 0, j = 0; index < result.length; index++) { 24 if (i >= left.length) 25 result[index] = right[j++]; 26 else if (j >= right.length) 27 result[index] = left[i++]; 28 else if (left[i] > right[j]) 29 result[index] = right[j++]; 30 else 31 result[index] = left[i++]; 32 } 33 return result; 34 }
8.计数排序
数列最值差值范围申请额外空间,将元素出现的次数记录元素值对应的额外空间,计算元素位置,将元素移到计算出的位置上。
举例说明:
1 { 2 if (arr.length == 0) { 3 return arr; 4 } 5 int bias, min = arr[0], max = arr[0]; 6 for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) { 7 if (arr[i] > max) { 8 max = arr[i]; 9 } 10 if (arr[i] < min) { 11 min = arr[i]; 12 } 13 } 14 bias = 0 - min; 15 //确定统计数组的长度 16 int[] bucket = new int[max - min + 1]; 17 Arrays.fill(bucket,0); 18 //填充统计数据 19 for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) { 20 bucket[arr[i] + bias]++; 21 } 22 int index = 0,i = 0; 23 while (index < arr.length) { 24 if (bucket[i] != 0) { 25 arr[index] = i - bias; 26 bucket[i]--; 27 index++; 28 } else { 29 i++; 30 } 31 } 32 return arr; 33 }
9.桶排序
设置bucketsize(每个桶能放多少不同数值),把数据依次放入对应的桶中。对每个桶排序,最后拼接数据。
举例说明:
1 { 2 if (arr == null || arr.size() < 2) { 3 return arr; 4 } 5 int max = arr.get(0), min = arr.get(0); 6 for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { 7 if (arr.get(i) >max) { 8 max = arr.get(i); 9 } 10 if (arr.get(i) < min) { 11 min = arr.get(i); 12 } 13 } 14 int bucketCount = (max - min) / bucketsize + 1; 15 List<List<Integer>> bucketArr = new ArrayList<>(bucketCount); 16 List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>(); 17 for (int i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) { 18 bucketArr.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); 19 } 20 for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) { 21 bucketArr.get((arr.get(i) - min) / bucketsize).add(arr.get(i)); 22 } 23 for (int i = 0; i < bucketCount; i++) { 24 if (bucketsize == 1) { 25 for (int j = 0; j < bucketArr.get(i).size(); j++) { 26 result.add(bucketArr.get(i).get(j)); 27 } 28 } else { 29 if (bucketCount == 1) { 30 bucketsize--; 31 } 32 List<Integer> temp = bucket(bucketArr.get(i), bucketsize); 33 for (int j = 0; j < temp.size(); j++) { 34 result.add(temp.get(j)); 35 } 36 } 37 } 38 return result; 39 }
10.基数排序
按照低位先排序,然后收集;再按照高位排序,然后再收集;依次类推,直到最高位。有时候有些属性是有优先级顺序的,先按低优先级排序,再按高优先级排序。最后的次序就是高优先级高的在前,高优先级相同的低优先级高的在前。
1 /** 2 * 基数排序 3 * @param array 4 * @return 5 */ 6 public static int[] RadixSort(int[] array) { 7 if (array == null || array.length < 2) 8 return array; 9 // 1.先算出最大数的位数; 10 int max = array[0]; 11 for (int i = 1; i < array.length; i++) { 12 max = Math.max(max, array[i]); 13 } 14 int maxDigit = 0; 15 while (max != 0) { 16 max /= 10; 17 maxDigit++; 18 } 19 int mod = 10, div = 1; 20 ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> bucketList = new ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>(); 21 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 22 bucketList.add(new ArrayList<Integer>()); 23 for (int i = 0; i < maxDigit; i++, mod *= 10, div *= 10) { 24 for (int j = 0; j < array.length; j++) { 25 int num = (array[j] % mod) / div; 26 bucketList.get(num).add(array[j]); 27 } 28 int index = 0; 29 for (int j = 0; j < bucketList.size(); j++) { 30 for (int k = 0; k < bucketList.get(j).size(); k++) 31 array[index++] = bucketList.get(j).get(k); 32 bucketList.get(j).clear(); 33 } 34 } 35 return array; 36 }



