实验一
实验任务1:
// 现代C++标准库、算法库体验
// 本例用到以下内容:
// 1. 字符串string, 动态数组容器类vector、迭代器
// 2. 算法库:反转元素次序、旋转元素
// 3. 函数模板、const引用作为形参
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 声明
// 模板函数声明
template <typename T> void output(const T &c);
// 普通函数声明
void test1();
void test2();
void test3();
int main() {
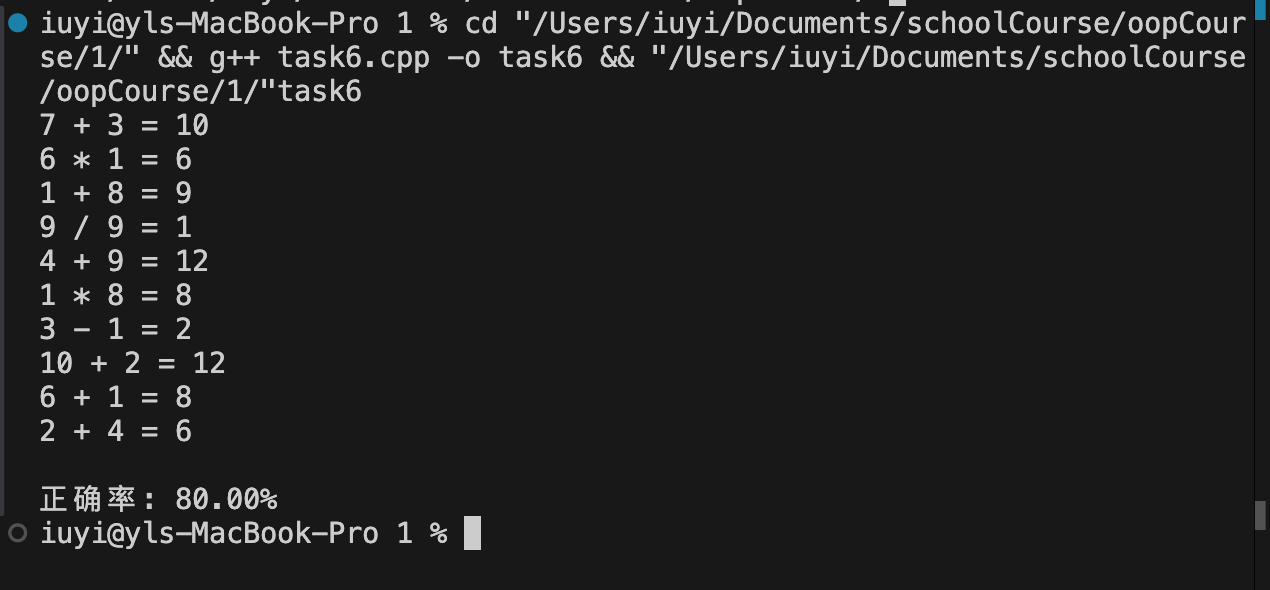
cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
cout << "\n测试3: \n";
test3();
}
// 函数实现
// 输出容器对象c中的元素
template <typename T> void output(const T &c) {
for (auto &i : c)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// 测试1
// 组合使用算法库、迭代器、string反转字符串
void test1() {
string s0{"0123456789"};
cout << "s0 = " << s0 << endl;
string s1{s0};
reverse(s1.begin(), s1.end()); // 反转指定迭代器区间的元素
cout << "s1 = " << s1 << endl;
string s2{s0};
reverse_copy(
s0.begin(), s0.end(),
s2.begin()); // 将指定迭代区间的元素拷贝到指定迭代器开始的目标区间,并且在复制过程中反转次序
cout << "s2 = " << s2 << endl;
}
// 测试2
// 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector反转动态数组对象vector内数据
void test2() {
vector<int> v0{2, 0, 4, 9};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
reverse(v1.begin(), v1.end());
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
reverse_copy(v0.begin(), v0.end(), v2.begin());
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
}
// 测试3
// 组合使用算法库、迭代器、vector实现元素旋转移位
void test3() {
vector<int> v0{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
rotate(
v1.begin(), v1.begin() + 1,
v1.end()); // 旋转指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(),
// v1.end())之间的数据项,旋转后从迭代器v1.begin()+1位置的数据项开始
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
rotate(v2.begin(), v2.begin() + 2, v2.end());
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
vector<int> v3{v0};
rotate(v3.begin(), v3.end() - 1, v3.end());
cout << "v3: ";
output(v3);
vector<int> v4{v0};
rotate(v4.begin(), v4.end() - 2, v4.end());
cout << "v4: ";
output(v4);
}
实验任务2:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
// 函数声明
// 模板函数声明
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c);
// 普通函数声明
int rand_int_100();
void test1();
void test2();
int main() {
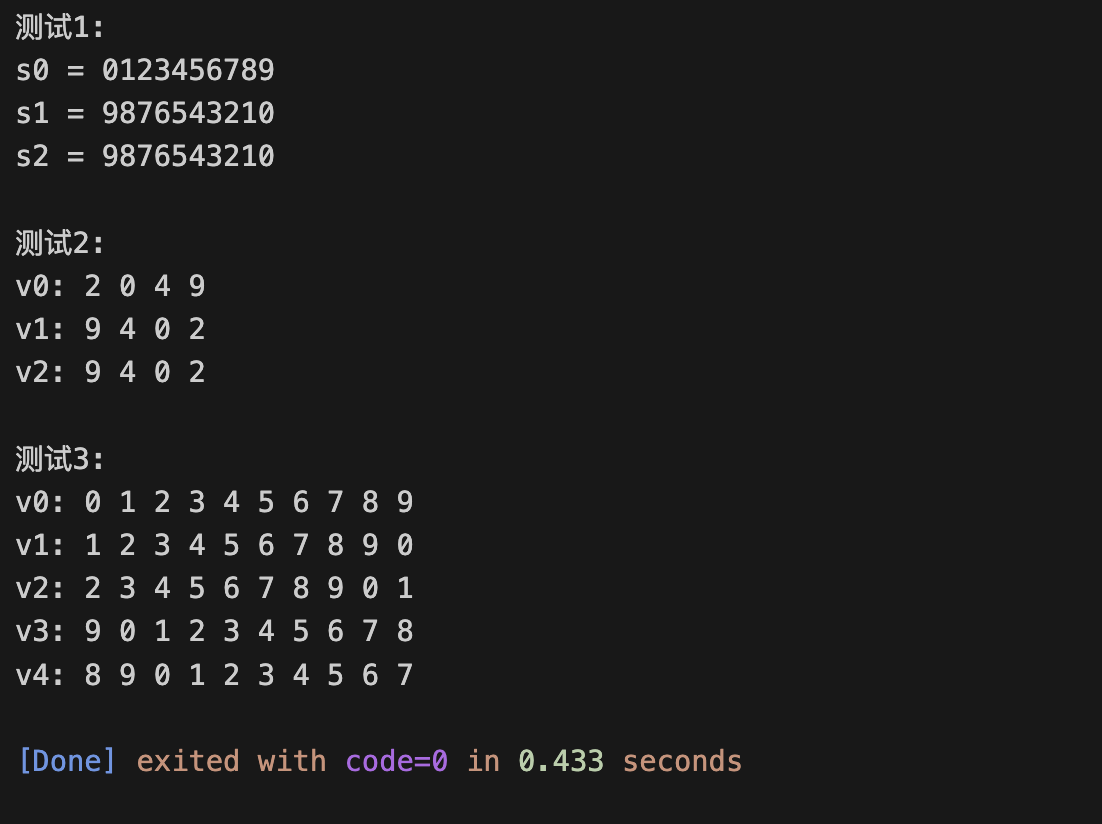
cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
}
// 函数实现
// 输出容器对象c中的元素
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c) {
for(auto &i: c)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数
int rand_int_100() {
return rand() % 101;
}
// 测试1
// 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、排序
void test1() {
vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); // 产生[0, 100]之间的随机整数赋值给指定迭代器区间[v0.begin(), v0.end())内的每个数据项
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())内数据项进行升序排序
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1)内数据项进行升序排序
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
}
// 测试2
// 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值
void test2() {
vector<int> v0(10);
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100);
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
auto iter1 = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *iter1 << endl;
auto iter2 = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最大值: " << *iter2 << endl;
auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl;
cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl;
double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0)/v0.size();
cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl;
cout << endl;
vector<int> v1{v0};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end());
double avg2 = accumulate(v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1, 0)/(v1.size()-2);
cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl;
}#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <numeric>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
// 函数声明
// 模板函数声明
template<typename T>
void output(const T &c);
// 普通函数声明
int rand_int_100();
void test1();
void test2();
int main() {
cout << "测试1: \n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2: \n";
test2();
}
// 函数实现
// 输出容器对象c中的元素
template <typename T>
void output(const T &c) {
for(auto &i: c)
cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
}
// 返回[0, 100]区间内的一个随机整数
int rand_int_100() {
return rand() % 101;
}
// 测试1
// 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、排序
void test1() {
vector<int> v0(10); // 创建一个动态数组对象v0, 对象大小为10
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100); // 产生[0, 100]之间的随机整数赋值给指定迭代器区间[v0.begin(), v0.end())内的每个数据项
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
vector<int> v1{v0};
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin(), v1.end())内数据项进行升序排序
cout << "v1: ";
output(v1);
vector<int> v2{v0};
sort(v2.begin()+1, v2.end()-1); // 对指定迭代器区间[v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1)内数据项进行升序排序
cout << "v2: ";
output(v2);
}
// 测试2
// 对容器类对象指定迭代器区间进行赋值、计算最大值/最小值/均值
void test2() {
vector<int> v0(10);
generate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), rand_int_100);
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
auto iter1 = min_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *iter1 << endl;
auto iter2 = max_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最大值: " << *iter2 << endl;
auto ans = minmax_element(v0.begin(), v0.end());
cout << "最小值: " << *(ans.first) << endl;
cout << "最大值: " << *(ans.second) << endl;
double avg1 = accumulate(v0.begin(), v0.end(), 0)/v0.size();
cout << "均值: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << avg1 << endl;
cout << endl;
vector<int> v1{v0};
cout << "v0: ";
output(v0);
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end());
double avg2 = accumulate(v1.begin()+1, v1.end()-1, 0)/(v1.size()-2);
cout << "去掉最大值、最小值之后,均值: " << avg2 << endl;
}
实验任务3:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
bool is_palindrome(std::string s);
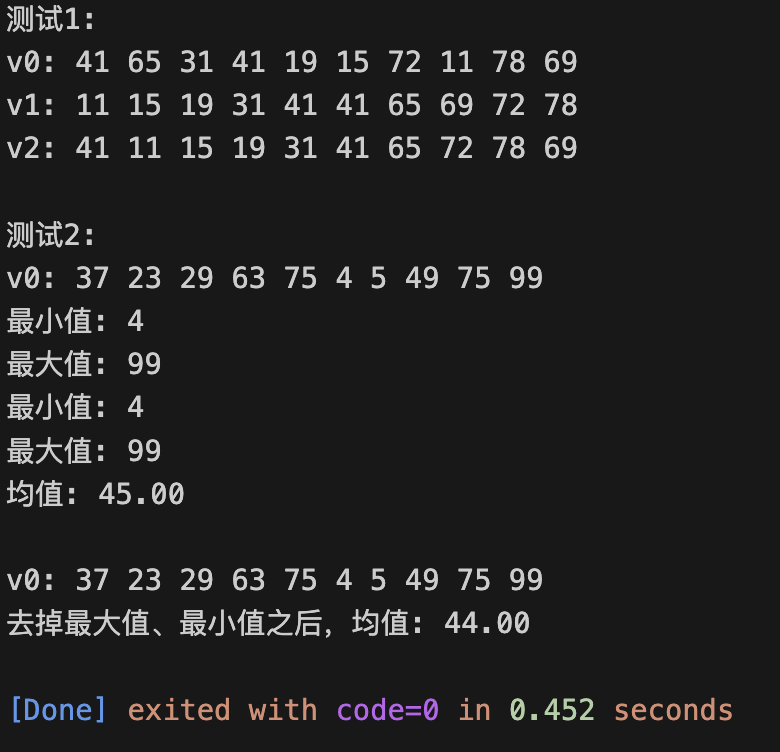
int main() {
using namespace std;
string s;
while(cin >> s) // 多组输入,直到按下Ctrl+Z后结束测试
cout << boolalpha << is_palindrome(s) << endl;
}
// 函数is_palindrom定义
// 待补足
// ×××
bool is_palindrome(std::string s) {
auto _s = s;
reverse(_s.begin(), _s.end());
return _s == s;
}
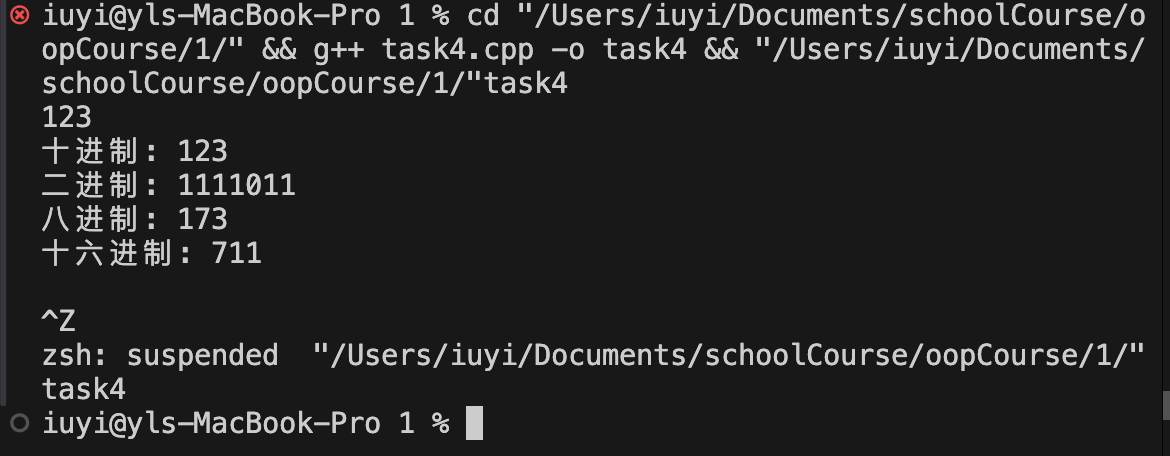
实验任务4:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
std::string dec2n(int x, int n = 2);
int main() {
using namespace std;
int x;
while(cin >> x) {
cout << "十进制: " << x << endl;
cout << "二进制: " << dec2n(x) << endl;
cout << "八进制: " << dec2n(x, 8) << endl;
cout << "十六进制: " << dec2n(x, 16) << endl << endl;
}
}
// 函数dec2n定义
// 待补足
// ×××
std::string dec2n(int x, int n) {
std::string res;
while(x > 0) {
res = std::to_string(x % n) + res;
x /= n;
}
return res;
}
实验任务5:
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
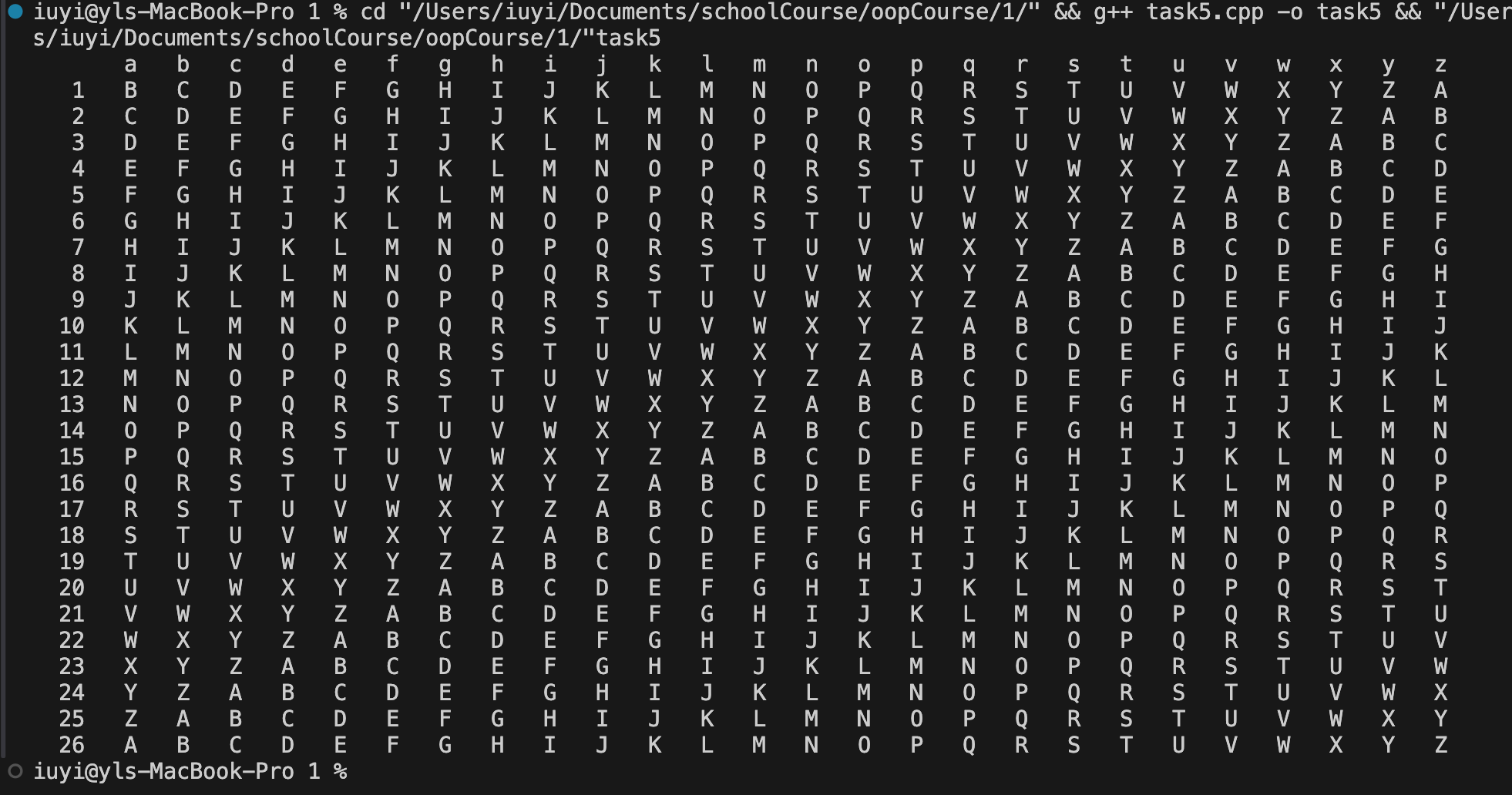
void generateCaesarCipherTable() {
const int alphabetSize = 26; // 字母表大小
char alphabet[alphabetSize];
// 输出表头
std::cout << std::setw(4) << ' '; // 空位
for (int j = 0; j < alphabetSize; ++j) {
std::cout << std::setw(4) << char(j + 'a'); // 输出字母
}
std::cout << std::endl;
// 输出密文对照表
for (int i = 1; i <= alphabetSize; ++i) {
std::cout << std::setw(4) << i; // 输出数字
// 输出每个字母向后偏移的 i 个字母
for (int j = 0; j < alphabetSize; ++j) {
char cipheredChar = (i + j) % alphabetSize + 'A'; // 计算偏移字母
std::cout << std::setw(4) << cipheredChar;
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
}
int main() {
generateCaesarCipherTable();
return 0;
}
实验任务6:
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <random>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
pair<string, int> generateProblem(mt19937 &gen) {
const array<string, 4> operators = {"+", "-", "*", "/"};
const array<function<int(int, int)>, 4> operatorsFunc = {
[](int a, int b) { return a + b; },
[](int a, int b) { return a > b ? a - b : -1; },
[](int a, int b) { return a * b; },
[](int a, int b) { return a % b == 0 ? a / b : -1; }
};
uniform_int_distribution<int> opDist(0, 3);
uniform_int_distribution<int> numDist(1, 10);
int opIndex = opDist(gen);
int num1 = numDist(gen);
int num2 = numDist(gen);
string problem = to_string(num1) + " " + operators[opIndex] + " " + to_string(num2) + " = ";
int answer = operatorsFunc[opIndex](num1, num2);
if (answer == -1) {
return generateProblem(gen);
}
return make_pair(problem, answer);
}
int main() {
mt19937 gen(hash<string>()("https://www.cnblogs.com/iuyi"));
int correctCount = 0;
const int totalProblems = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < totalProblems; i++) {
auto [problem, answer] = generateProblem(gen);
cout << problem;
int userAnswer;
cin >> userAnswer;
if (userAnswer == answer) {
correctCount++;
} else {
;
}
}
double accuracy = (static_cast<double>(correctCount) / totalProblems) * 100;
cout << "\n正确率: " << fixed << setprecision(2) << accuracy << "%" << endl;
return 0;
}