java--JDBC原理及使用Statement访问数据库
1.JDBC:API
提供了各种操作访问接口,Connection Statement PreparedStatement ResultSet
JDBC API 主要功能:三件事,具体通过以下类/接口实现:
DriverManager: 管理JDBC驱动
Connection: 连接
Statement(PreparedStatement): 增删改查
CallableStatement : 调用数据库中的存储过程/存储函数
Result : 返回的结果集
JDBC访问数据库的具体步骤:
a.导入驱动,加载具体的驱动类
b.与数据库建立连接
c.发送sql,执行
d.处理结果集
数据库驱动
Oracle o jdbc-x.jar
Mysql mysql-connector-java-x.jar
SqlServer sql jdbc-x.jar
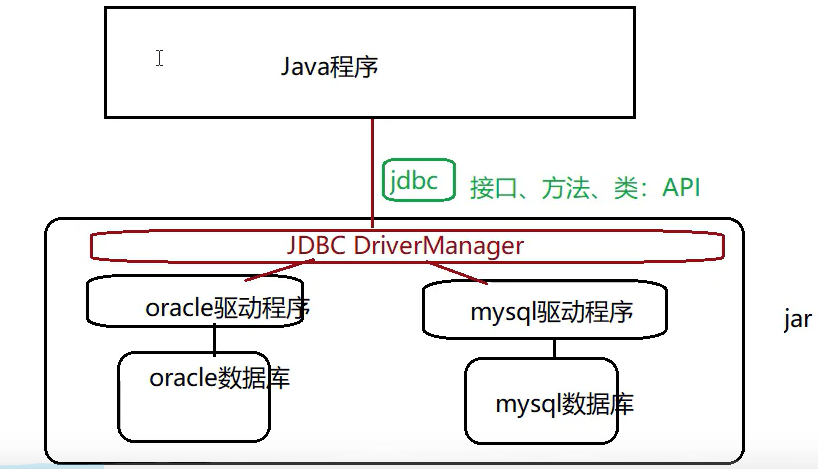
2.JDBC DriverManager:
管理不同的数据库驱动
3.各种数据库驱动:
相应的数据库厂商提供的(第三方公司提供),连接\直接操作数据库。
4.示例图如下
5.具体在eclipse中连接Mysql数据库代码:
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
java.sql.Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ltz","root", "123456");
Statement Stmt = connection.createStatement();
String sql = "insert into student values('zl',10,'1')";
int count = Stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
if(count>0) {
System.out.println("操作成功!");
}
Stmt.close();
connection.close();
}
Statement(PreparedStatement):增删改查(通过Connection产生)
CallableStatement: 调用数据库中的 存储过程/存储函数 (通过Connection产生)
Result: 返回的结果集(上面的Statement等产生)
Connection产生操作数据库的对象:
Connection产生Statement对象:createStatement()
Connection产生PreparedStatement对象:PrepareStatement()
Connection产生CallableStatement对象:prepareCall()
1.1Statement操作数据库:
增删改: executeUpdate()
查询:executeQuery()
ResultSet():保存结果集 select * from xxx
next() : 光标下移,判断是否有下一条数据:true/false
previous() : true/false
getXxx(字段名/位置):获取具体的字段值
PreparedStatement操作数据库:
public interface PreparedStatement extends Statement
1.2推荐使用PreparedStatement:原因如下:
### 1.编码更简单(避免了字符串的拼接)
2.提高了性能(因为有预编译操作,预编译只需要执行一次)
3.安全(可以有效防止sql注入) stmt:存在被sql注入的风险(例如输入 任意值 ' or 1=1 -- 密码:任意值)
String name = "zs";
int age = 23;
stmt:
String sql = "insert into student values(' "+name+" '," +age+ " ) ";
pstmt
String sql = "insert into student values(?,?)";
pstmt = connection.prepareStatement(sql); //预编译sql
pstmt.setString(1,name); //给第一列属性赋值
pstmt.setInt(2,age); //给第二列属性赋值
6.JDBC总结(模板、八股文)
try{
a.导入驱动包、加载具体驱动类Class.forName("具体驱动类");
b.与数据库建立连接connection = DriverManager.getConnection(...);
c.通过connection获取操作数据库的对象(Statement\preparedStatement\callablestatement)
stmt = connection.createStatement();
d.查询需要处理结果集 rs = pstmt.executeQuery()
while(rs.next()){
//判断是否有下一个元素
rs.getXxx(...); //获取这个元素
}
}catch(ClassNotFoundException e)
{
...
}
catch(SQLException e)
{
...
}
catch(Exception e)
{
...
}
finally
{
//打开顺序,与关闭顺序相反
if(rs!=null) {rs.close();}
if(stmt!=null) {stmt.close();}
if(connection!=null) {connection.close();}
}
--------JDBC中,除了Class.forName() 抛出ClassNotFoundException,其余方法全部抛出SQLException
2.CallableStatement:调用存储过程,存储函数
参数格式:
存储过程(无返回值return,用Out参数代替):{call 存储过程名(参数列表)}
存储函数(有返回值return)
{ ?= call 存储函数名(参数列表)}


