004.HAProxy的管理与维护
一 安装
[root@haproxy_master ~]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ make openssl-devel wget openssh-clients #安装编译工具
[root@haproxy_master ~]# service iptables stop
[root@haproxy_master ~]# chkconfig iptables off
[root@haproxy_master ~]# vi /etc/selinux/config
SELINUX=disabled
1.1 yum安装
[root@HAProxy ~]# yum -y install haproxy
二 常见参数
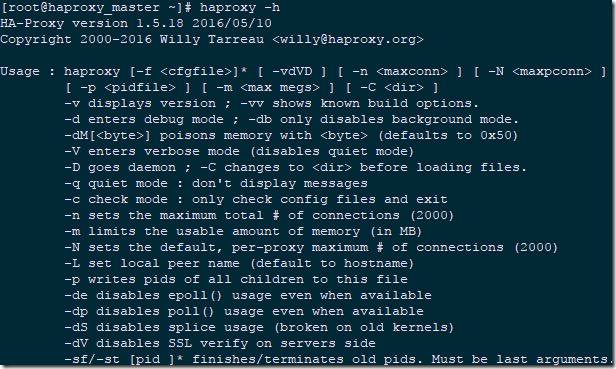
[root@haproxy_master ~]# haproxy -h
三 HAProxy启动脚本
Usage: /etc/init.d/haproxy {start|stop|status|restart|try-restart|reload|force-reload}"
1 #!/bin/sh 2 # 3 # haproxy 4 # 5 # chkconfig: - 85 15 6 # description: HAProxy is a free, very fast and reliable solution \ 7 # offering high availability, load balancing, and \ 8 # proxying for TCP and HTTP-based applications 9 # processname: haproxy 10 # config: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg 11 # pidfile: /var/run/haproxy.pid 12 13 # Source function library. 14 . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions 15 16 # Source networking configuration. 17 . /etc/sysconfig/network 18 19 # Check that networking is up. 20 [ "$NETWORKING" = "no" ] && exit 0 21 22 exec="/usr/sbin/haproxy" 23 prog=$(basename $exec) 24 25 [ -e /etc/sysconfig/$prog ] && . /etc/sysconfig/$prog 26 27 cfgfile=/etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg 28 pidfile=/var/run/haproxy.pid 29 lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/haproxy 30 31 check() { 32 $exec -c -V -f $cfgfile $OPTIONS 33 } 34 35 start() { 36 $exec -c -q -f $cfgfile $OPTIONS 37 if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then 38 echo "Errors in configuration file, check with $prog check." 39 return 1 40 fi 41 42 echo -n $"Starting $prog: " 43 # start it up here, usually something like "daemon $exec" 44 daemon $exec -D -f $cfgfile -p $pidfile $OPTIONS 45 retval=$? 46 echo 47 [ $retval -eq 0 ] && touch $lockfile 48 return $retval 49 } 50 51 stop() { 52 echo -n $"Stopping $prog: " 53 # stop it here, often "killproc $prog" 54 killproc $prog 55 retval=$? 56 echo 57 [ $retval -eq 0 ] && rm -f $lockfile 58 return $retval 59 } 60 61 restart() { 62 $exec -c -q -f $cfgfile $OPTIONS 63 if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then 64 echo "Errors in configuration file, check with $prog check." 65 return 1 66 fi 67 stop 68 start 69 } 70 71 reload() { 72 $exec -c -q -f $cfgfile $OPTIONS 73 if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then 74 echo "Errors in configuration file, check with $prog check." 75 return 1 76 fi 77 echo -n $"Reloading $prog: " 78 $exec -D -f $cfgfile -p $pidfile $OPTIONS -sf $(cat $pidfile) 79 retval=$? 80 echo 81 return $retval 82 } 83 84 force_reload() { 85 restart 86 } 87 88 fdr_status() { 89 status $prog 90 } 91 92 case "$1" in 93 start|stop|restart|reload) 94 $1 95 ;; 96 force-reload) 97 force_reload 98 ;; 99 check) 100 check 101 ;; 102 status) 103 fdr_status 104 ;; 105 condrestart|try-restart) 106 [ ! -f $lockfile ] || restart 107 ;; 108 *) 109 echo $"Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|restart|try-restart|reload|force-reload}" 110 exit 2 111 esac
作者:木二
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/itzgr/
关于作者:云计算、虚拟化,Linux,多多交流!
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接!如有其他问题,可邮件(xhy@itzgr.com)咨询。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号