6.依赖注入(DI)
6.依赖注入(DI)
1.构造器注入
2.set方式注入【重点☆】
依赖注入:set注入
依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
注入:bean对象中所有属性,由容器注入。
【环境搭建】
1.复杂类型
public classAddress {
private String address;
publicString getAddress() {
returnaddress;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address= address;
}
}
2.真实测试对象
public classStudent {
privateStringname;
privateAddressaddress;
privateString[]books;
privateList<String>hobbys;
privateMap<String,String>card;
privateSet<String>games;
privateStringwife;//空指针,有无妻子
privatePropertiesinfo;//学生信息
}
3.beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0"encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>"
xmlns:xsi="<http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>"
xsi:schemaLocation="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd>">
<bean id="student" class="com.itxiaofei.pojo.Student">
<!--第一种,普通值注入,直接使用value-->
<property name="name"value="小飞"/>
</bean>
</beans>
4.测试类
public classAddress {
privateStringaddress;
publicString getAddress() {
returnaddress;
}
public voidsetAddress(String address) {
this.address= address;
}
}
完善注入信息:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>"
xmlns:xsi="<http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>"
xsi:schemaLocation="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd>">
<bean id="address" class="com.itxiaofei.pojo.Address">
<property name="address" value="山西"/>
</bean>
<bean id="student" class="com.itxiaofei.pojo.Student">
<!--第一种,普通值注入,直接使用value-->
<property name="name" value="小飞飞"/>
<!--第二种,bean注入-->
<property name="address" ref="address"/>
<!--第三种,数组注入-->
<property name="books">
<array>
<value>红楼梦</value>
<value>水浒传</value>
<value>西游记</value>
<value>三国演义</value>
</array>
</property>
<!--第四种,List-->
<property name="hobbys">
<list>
<value>听音乐</value>
<value>敲代码</value>
<value>打篮球</value>
</list>
</property>
<!--第五种,Map-->
<property name="card">
<map>
<entry key="学号" value="1931030***"/>
<entry key="电话" value="18104131***"/>
</map>
</property>
<!--第六种,Set-->
<property name="games">
<set>
<value>英雄联盟</value>
<value>地下城与勇士</value>
</set>
</property>
<!--第七种,Null-->
<property name="wife">
<null/>
</property>
<!--第八种,properties(特殊类型) key=value...-->
<property name="info">
<props>
<prop key="学号">1931030***</prop>
<prop key="性别">男</prop>
<prop key="姓名">小飞</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
3.拓展方式注入
生成有参构造:
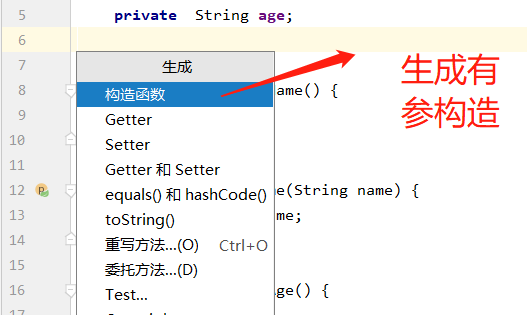
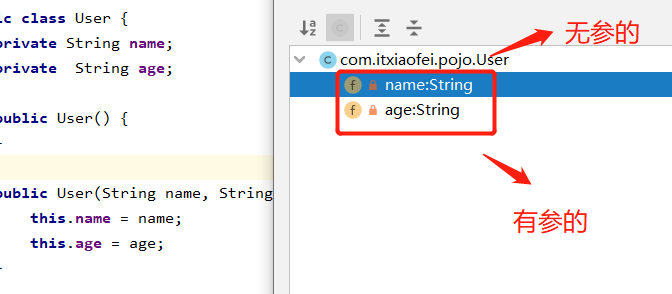
我们可以使用p命名空间和c命名空间进行注入
官方解释:
p命名:

<beans xmlns="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>"
xmlns:xsi="<http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>"
xmlns:p="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/p>"
xsi:schemaLocation="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd>">
<bean name="classic" class="com.example.ExampleBean">
<property name="email" value="someone@somewhere.com"/>
</bean>
<bean name="p-namespace" class="com.example.ExampleBean"
p:email="someone@somewhere.com"/>
</beans>
测试:
@Test
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext Context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("Userbeans.xml");
User user = Context.getBean("user", User.class);
User user2 = Context.getBean("user2", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(user2);
}
缺点:p 命名空间不如标准 XML 格式灵活。例如,用于声明属性引用的格式与以 结尾的属性冲突,而标准 XML 格式则不然。我们建议您仔细选择方法并将其传达给团队成员,以避免生成同时使用所有三种方法的 XML 文档
c命名:
与带有 p 命名空间的 XML 快捷方式类似,Spring 3.1 中引入的 c-命名空间允许内联属性用于配置构造函数参数,而不是嵌套元素。
<beans xmlns="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>"
xmlns:xsi="<http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance>"
xmlns:c="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/c>"
xsi:schemaLocation="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans>
<https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd>">
<bean id="beanTwo" class="x.y.ThingTwo"/>
<bean id="beanThree" class="x.y.ThingThree"/>
<!-- traditional declaration with optional argument names -->
<bean id="beanOne" class="x.y.ThingOne">
<constructor-arg name="thingTwo" ref="beanTwo"/>
<constructor-arg name="thingThree" ref="beanThree"/>
<constructor-arg name="email" value="something@somewhere.com"/>
</bean>
<!-- c-namespace declaration with argument names -->
<bean id="beanOne" class="x.y.ThingOne" c:thingTwo-ref="beanTwo"
c:thingThree-ref="beanThree" c:email="something@somewhere.com"/>
</beans>
缺点:由于 XML 语法,索引表示法需要存在 前导 ,因为 XML 属性名称不能以数字开头(即使某些 IDE 允许)。相应的索引表示法也可用于元素,但不常用,因为声明的简单顺序通常就足够了。
总结:在实践中,构造函数解析机制在匹配参数方面非常有效,因此,除非确实需要,否则我们建议在整个配置中使用名称表示法。p命名与c命名空间不能直接使用,需要导入xml约束。
xmlns:p="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/p>"
xmlns:c="<http://www.springframework.org/schema/c>"
4.bean soupes(bean的作用域)
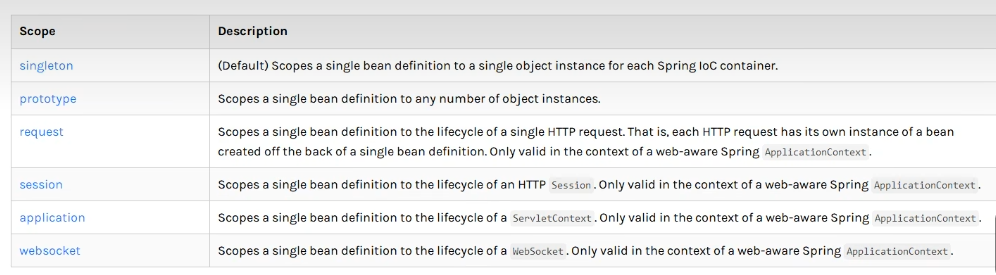

1.单例模式(spring默认机制)
<bean id="user2" class="com.itxiaofei.pojo.User" c:name="小飞学java" c:age="23"
scope="**singleton**"/>
User user = Context.getBean("user2", User.class);
User user2 = Context.getBean("user2", User.class);
System.out.println(user==user2);
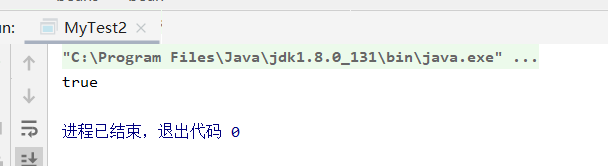
2.原型模式:每次从容器中get的时候都会产生新对象
<bean id="user2" class="com.itxiaofei.pojo.User" c:name="小飞学java" c:age="23"
scope="**prototype**"/>
User user = Context.getBean("user2", User.class);
User user2 = Context.getBean("user2", User.class);
System.out.println(user==user2);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号