Java中IO流和文件操作
前言
学习JAVA过程对IO流知识比较陌生,在平时刷题中也不会遇见。对于文件操作也是一样,今天重学JAVA,在此整理一篇。
1. IO流分类
流可以理解为 内存与硬盘 之间的通道。
- 字节输入/输出流 (万能 包括图片声音视频文本)
java.io.InputStream/OutputStream - 字符输入/输出流 (对于文本文件才可以使用;对与含有中文字符的一定是使用字符流)
java.io.Reader/Writer - 所有流都实现了Closeable接口,可以调用close关闭
- 所有输出流都实现了Flushable接口,可以调用flush方法刷新。即将通道内的数据输出完,一般在输出流的最后都要
flush()
2. 要掌握的所有的流(java.io.~)
- 文件流
- FileInputStream
- FileOutputStream
- FileReader
- FileWriter
- 转换流
- InputStreamReader
- OutputStreamWriter
- 缓冲流
- Buffered~(4种)
- 数据流
- DataInputStream
- DateOutputStream
- 标准输出流
- PrintWriter
- PrintStream
- 对象流
- ObjectInputStream
- ObjectOutputStream
- 文件类
- File
3.文件流
3.1 FileInputStream
文件字节输入流是万能的。
构造方法
FiliInputStream(String name) //name 为文件路径
FileInputStream(File file)
方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 1.作用读取一个字节,2.返回值为字节的ASCII码,3. 读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int read(byte[]b) | 1.作用读取b数组大小的字节到b数组中,2. 返回值为读到的字节个树;3.读到文件末尾返回-1 |
| int read(byte[]b,int offset,int len) | |
| int available() | 返回文件有效的字节数 |
| long skip(long n) | 跳过n个字节 |
| void close() |
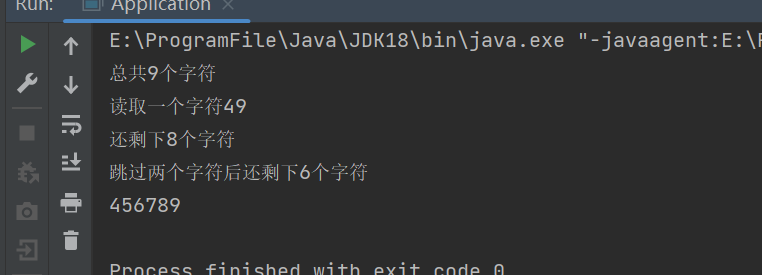
public void test2() {
FileInputStream fi=null;
try {
fi=new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/a.txt");
System.out.println("总共"+fi.available()+"个字符");
System.out.println("读取一个字符"+ fi.read());
System.out.println("还剩下"+fi.available()+"个字符");
fi.skip(2);
System.out.println("跳过两个字符后还剩下"+fi.available()+"个字符");
//剩下的全读完
int len= fi.available();
int count=0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[len];
while ((count= fi.read(bytes))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fi!=null) { //流不为空时关闭避免空指针异常
try {
fi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.2 FileOutputStream
构造方法
| 构造方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| (String name) | name为文件路径 |
| (String name,boolean append) | name为文件路径,append为true表示在文件末尾追加;false表示清空文件内容,重新写。 |
| (File file) | |
| (File file,boolean append) |
方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| void write(int b) | 将指定字节写入文件 |
| void write(byte[] b) | 将b写入文件中。 |
| void write(byte[] b,int offset,int len) | |
| void flush() | 刷新输出流,强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节 |
| void close() |
public void test2() {
FileOutputStream fi=null;
try {
fi=new FileOutputStream("src/main/resources/b.txt",false);
fi.write('1');
byte[] bytes={'2','3','4','5'};
fi.write(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fi!=null) { //流不为空时关闭避免空指针异常
try {
fi.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3.3 FileReader
字符输入流,只能读取普通文本。使用时注意byte变char
构造方法
(String fileName) name为文件路径
(File file)
方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 读取一个字符,返回值为改字符的ASCII码;读到文件尾返回-1 |
| int read(char[]c) | 读取到字符数组c中;读到文件尾返回-1 |
| int read(char[]c,int off,int len) | |
| long skip(long n) | |
| void close() |
public void readTest(){
FileReader fr=null;
try {
fr=new FileReader("src/main/resources/c.txt"); //文件内容:卧室阳台,java中一个char时两个字节,可以存储一个汉字。
char[] chars=new char[4];
int count=0;
while((count=fr.read(chars))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(chars));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
FileWriter
文件字符输出流,只能输出普通文本
构造方法
| 方法名 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| (String name) | name为文件路径 |
| (String name,boolean append) | |
| (File file) | |
| (File file,boolean append) |
方法
同以上 + String
void write(String str)
void write(String str,int off,int len)
FileWriter out = null;
try {
// 创建文件字符输出流对象
//out = new FileWriter("file");
out = new FileWriter("file", true);
// 开始写。
char[] chars = {'我','是','中','国','人'};
out.write(chars);
out.write(chars, 2, 3);
out.write("我是一名java软件工程师!");
// 写出一个换行符。
out.write("\n");
out.write("hello world!");
// 刷新
out.flush();
4. 缓冲流
BufferedReader/Writer/In/OuputStream
以BufferedReader为例
- 自带缓冲区的字符输入流,也就是不需要自定义char数组
- 关闭包装流,节点流会自动关闭
构造方法
(Reader in) in为reader对象或实现类(比如FileReader
当一个流的构造方法中需要一个流时,这个传入的叫节点流,外面的叫做包装流/处理流,对于包装流来说只需要关闭最外层
方法
| 方法名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 读一个字符,返回ASCII,末尾返回-1 |
| int read(char[]c) | 读c长度的,返回读取个数,末尾返回-1 |
| String readLine() | 读取文件的一行,但不带换行符 |
| long skip(long n) | |
| void close |
public void readTest(){
FileReader fileReader=null; //节点流
BufferedReader bufferedReader=null; //包装流
try {
fileReader = new FileReader("src/main/resources/c.txt");
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(fileReader);
String str=null;
while ((str=(bufferedReader.readLine()))!=null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
bufferedReader.close(); //只需关闭处理流,节点流会自动关闭
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
5.转换流
InputStreamReader OutputStreamWriter
以InputStreamReader为例
InputStreamReader
将字节输入流 转为 字符输入流
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream("Copy02.java");
// 通过转换流转换(InputStreamReader将字节流转换成字符流。)
// in是节点流。reader是包装流。
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(in);
6.数据字节流
6.1 DataInputStream
数据字节输入流,用来装饰其他的输入流, 允许应用程序读取基本Java数据类型.
DataOutputStream写的文件,只能使用DataInputStream去读。并且读的时候你需要提前知道写入的顺序。
构造方法
(InputStream in) in是底层输入流
方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| int read(byte[]b) | 读到b中 |
| boolean readBoolean() | 读取并返回读取的字节 |
| byte readByte() | |
| char readChar() | 读取2个字节 |
| double readDouble() | 读取8字节 |
| String readUTF() | 读取已使用UTF-8格式编码的字符串 |
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("data"));
// 开始读
byte b = dis.readByte();
short s = dis.readShort();
int i = dis.readInt();
long l = dis.readLong();
float f = dis.readFloat();
double d = dis.readDouble();
boolean sex = dis.readBoolean();
char c = dis.readChar();
6.2 DataOutputStream
这个流可以将数据连同数据类型一同写入文件,这个文件不是普通的文本文档,只能用DataInputStream打开。
构造方法
(OutputStream out) out为底层输出流
方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| writeByte(int v) | 将1字节写入输出流 |
| Char/Double/~Float、Int、Long、Short、Boolean | |
| flush() |
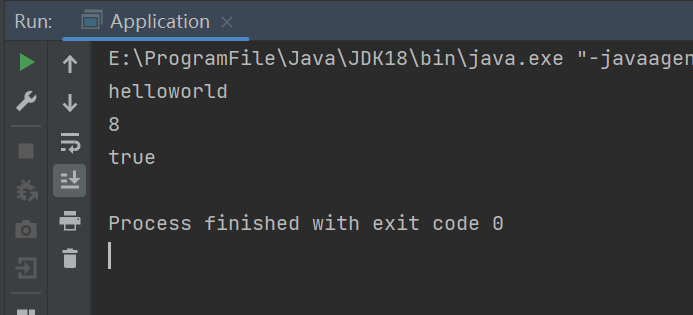
public void write(){
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream=null;
try {
dataOutputStream=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("src/main/resources/x.txt"));
dataOutputStream.writeUTF("helloworld");
dataOutputStream.writeInt(8);
dataOutputStream.writeBoolean(true);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if(dataOutputStream==null) {
try {
dataOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
public void read() {
DataInputStream dataInputStream=null;
try {
dataInputStream = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/x.txt"));
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readUTF());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readInt());
System.out.println(dataInputStream.readBoolean());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if(dataInputStream!=null) {
try {
dataInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
7.标准输出流
以PrintStream为例
- 不需要手动关闭流
- 可以改变输出流的输出方向
- 默认输出到控制台,经过setOut可以改到文件。
构造方法
(File file) / (OutStream out) /(String fileName)
方法
| 方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| println(参数类型不定x) | 输出x换行 |
| print(参数类型不定x) | |
| flush close | |
| System.setOut(PrintStream对象) | 改变流的输出方向 |
public void test() {
PrintStream printStream = null;
try {
printStream = new PrintStream("src/main/resources/d.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.setOut(printStream);
System.out.println("heelo world");
}
8. 对象流
- 序列化和反序列化的对象,必须实现Serializable接口
- 此接口是空的,作用是标识,给Java虚拟机参考的,会为该类生成一个序列化版本号。
- 版本号是区分两个类是否相同。(同类名不同序列号)
- transient关键字,可以取消序列化
- static修饰的不属于对象,而属于类,所以不能被序列化。
public user implements Serializable{
private int no;
private transient String name; // name不参与序列化操作!
}
8.1 ObjectOutputStream
序列化对象,把对象转为字节数据的输出到文件。对象的输出过程叫序列化,实现了对象的持久存储。
构造方法
(OutputStream out)
方法
writeObject(Obj s) 将对象写入文件
8.2 ObjectInputStream
反序列化对象,将之前通过ObjectOutputStream序列化的原始数据恢复为对象,以流的方式读取对象。
构造方法
(InputStream in)
方法
Object readObject()
public void write(){
Person person = new Person(4, "hello");
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = null;
try {
objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("src/main/resources/re.txt"));
objectOutputStream.writeObject(person);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void read(){
Person person=null;
try {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/re.txt"));
person=(Person) objectInputStream.readObject();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(person);
}
9.文件对象 File
File类与四流无关,不能完成文件的读写。File对象代表了 文件或目录路径名的抽象表示
构造方法
File(String pathname) pathname为文件/文件夹的路径。
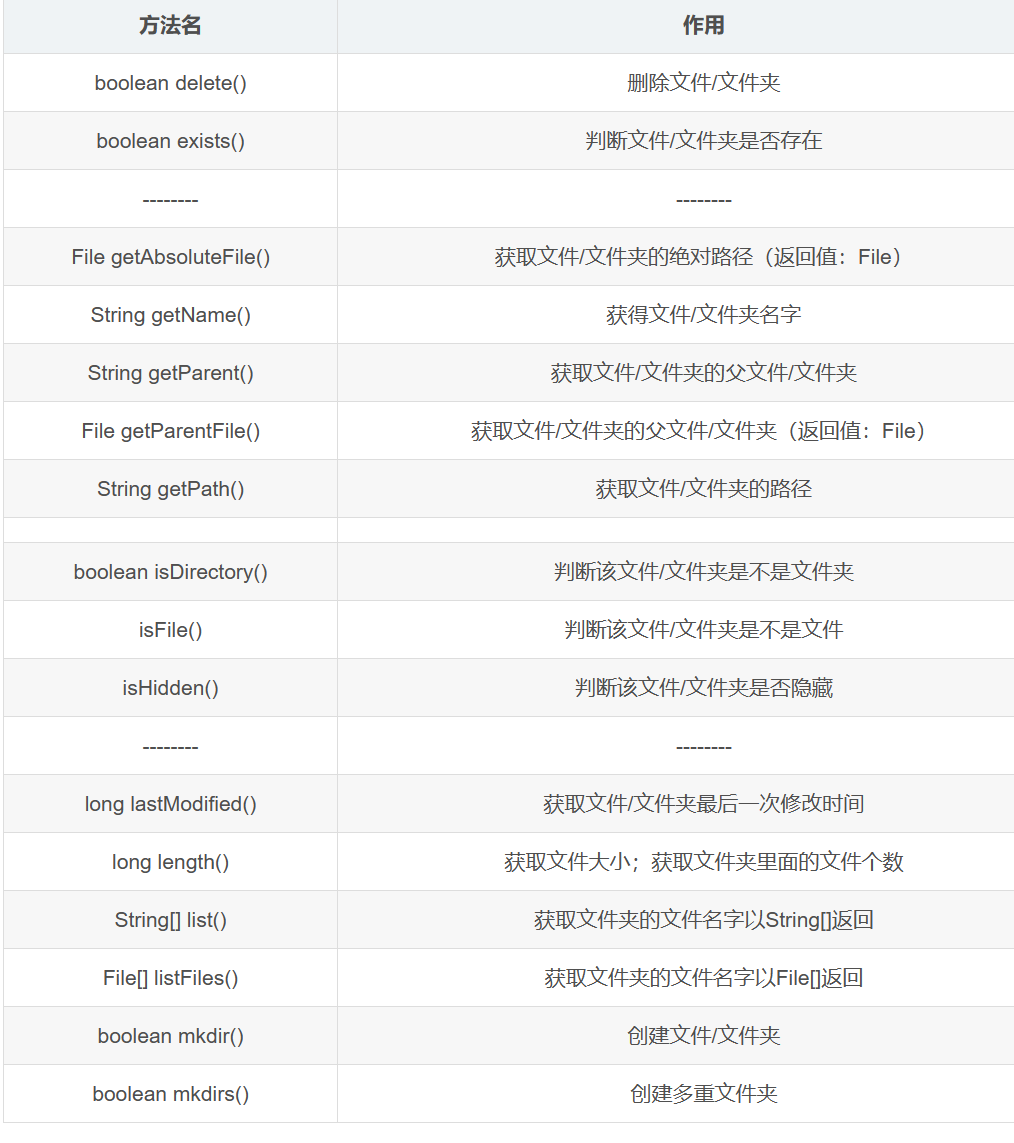
方法
class FileTest01{
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f1 = new File("D:/IO/File1");
if (!f1.exists()){
try {
f1.createNewFile();//创建文件
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
File f2 = new File("D:/IO/File2");
if (!f2.exists()){
f2.mkdir();//创建文件夹
}
File f3 = new File("D:/IO/File3/a/b/c/d/e/f/g/h/i");
if (!f3.exists()){
f3.mkdirs();//创建多重文件夹
}
File f5 = new File("D:\\IO\\FileDelete");
f5.delete();
File f4 = new File("D:\\Data\\新建文件夹");
String s1 = f4.getName();//新建文件夹
System.out.println(s1);
String s2 = f4.getParent();//D:\Data
System.out.println(s2);
String s3 = f4.getPath();//D:\Data\新建文件夹
System.out.println(s3);
String s4 = f4.getAbsolutePath();//D:\Data\新建文件夹
System.out.println(s4);
File asf = f4.getAbsoluteFile();
System.out.println(asf.getAbsolutePath());//D:\Data\新建文件夹
File pf = f4.getParentFile();
System.out.println(pf.getAbsolutePath());//D:\Data
System.out.println(f4.isDirectory());//true
System.out.println(f4.isFile());//false
System.out.println(f4.isHidden());//false
System.out.println(f4.isAbsolute());//true
File f6 = new File("D:\\IO\\Day24.java");
System.out.println(f6.length());//5743字节
long lastModify = f6.lastModified();//最后修改时间
Date d = new Date(lastModify);
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String date = sdf.format(d);
System.out.println(date);//2021-05-03 22:55:06
File f7 = new File("D:\\Data\\新建文件夹\\6、2020年最新 Java零基础入门到精通【完整资料】\\00_课程引入【马士兵说】");
String[] strList = f7.list();
for (String s : strList){
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("-----------------------------------------");
File[] fileList = f7.listFiles();
for (File f : fileList){
//System.out.println(f.getPath());
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号