深度学习面试题34:RNN中的Embedding是随机初始化的吗
目录
随机初始化
使用预训练模型
参考资料
可以随机初始化、也可以使用预训练好的,这里我们分类讨论
|
随机初始化 |
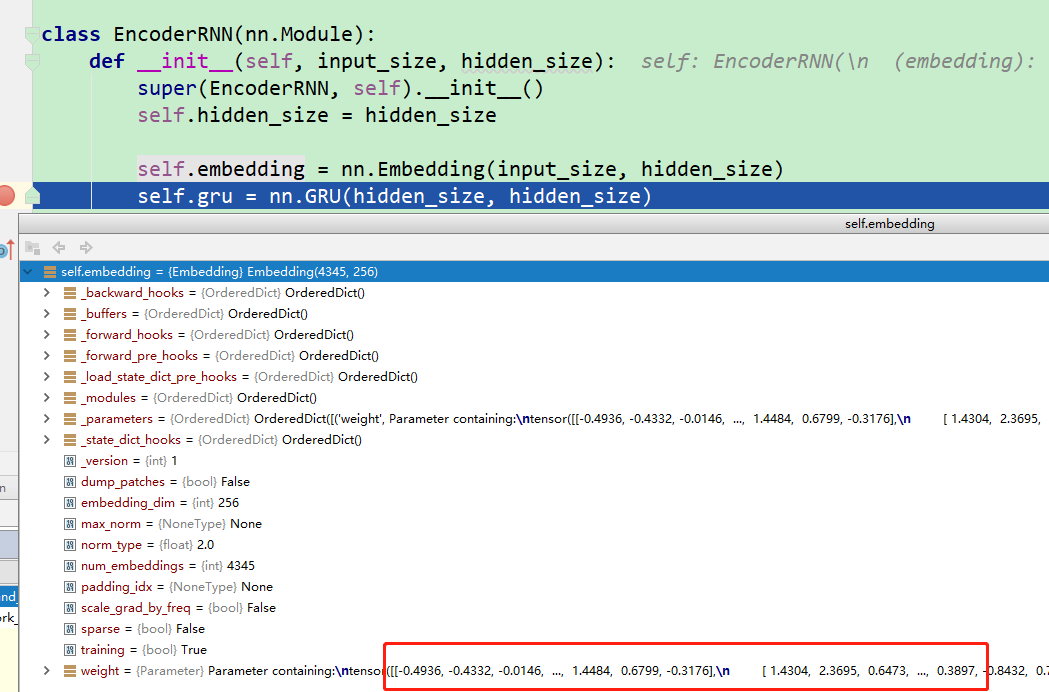
从上图可以看到,pytorch的embedding可以是用一个正态分布随机初始化的
对应代码

from io import open import unicodedata import string import re import random import torch import torch.nn as nn from torch import optim import torch.nn.functional as F device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") SOS_token = 0 EOS_token = 1 class Lang: def __init__(self, name): self.name = name self.word2index = {} self.word2count = {} self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"} self.n_words = 2 # Count SOS and EOS def addSentence(self, sentence): for word in sentence.split(' '): self.addWord(word) def addWord(self, word): if word not in self.word2index: self.word2index[word] = self.n_words self.word2count[word] = 1 self.index2word[self.n_words] = word self.n_words += 1 else: self.word2count[word] += 1 # https://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427 def unicodeToAscii(s): return ''.join( c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s) if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn' ) # Lowercase, trim, and remove non-letter characters def normalizeString(s): s = unicodeToAscii(s.lower().strip()) s = re.sub(r"([.!?])", r" \1", s) s = re.sub(r"[^a-zA-Z.!?]+", r" ", s) return s def readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse=False): print("Reading lines...") # Read the file and split into lines lines = open('data/%s-%s.txt' % (lang1, lang2), encoding='utf-8').\ read().strip().split('\n') # Split every line into pairs and normalize pairs = [[normalizeString(s) for s in l.split('\t')] for l in lines] # Reverse pairs, make Lang instances if reverse: pairs = [list(reversed(p)) for p in pairs] input_lang = Lang(lang2) output_lang = Lang(lang1) else: input_lang = Lang(lang1) output_lang = Lang(lang2) return input_lang, output_lang, pairs MAX_LENGTH = 10 eng_prefixes = ( "i am ", "i m ", "he is", "he s ", "she is", "she s ", "you are", "you re ", "we are", "we re ", "they are", "they re " ) def filterPair(p): return len(p[0].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \ len(p[1].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \ p[1].startswith(eng_prefixes) def filterPairs(pairs): return [pair for pair in pairs if filterPair(pair)] def prepareData(lang1, lang2, reverse=False): input_lang, output_lang, pairs = readLangs(lang1, lang2, reverse) print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs)) pairs = filterPairs(pairs) print("Trimmed to %s sentence pairs" % len(pairs)) print("Counting words...") for pair in pairs: input_lang.addSentence(pair[0]) output_lang.addSentence(pair[1]) print("Counted words:") print(input_lang.name, input_lang.n_words) print(output_lang.name, output_lang.n_words) return input_lang, output_lang, pairs input_lang, output_lang, pairs = prepareData('eng', 'fra', True) print(random.choice(pairs)) class EncoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size): super(EncoderRNN, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_size, hidden_size) self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size) def forward(self, input, hidden): embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1) output = embedded output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) return output, hidden def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device) class DecoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size): super(DecoderRNN, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_size, hidden_size) self.gru = nn.GRU(hidden_size, hidden_size) self.out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size) self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) def forward(self, input, hidden): output = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1) output = F.relu(output) output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) output = self.softmax(self.out(output[0])) return output, hidden def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device) class AttnDecoderRNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, hidden_size, output_size, dropout_p=0.1, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): super(AttnDecoderRNN, self).__init__() self.hidden_size = hidden_size self.output_size = output_size self.dropout_p = dropout_p self.max_length = max_length self.embedding = nn.Embedding(self.output_size, self.hidden_size) self.attn = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.max_length) self.attn_combine = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size * 2, self.hidden_size) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(self.dropout_p) self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_size, self.hidden_size) self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.output_size) def forward(self, input, hidden, encoder_outputs): embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1, 1, -1) embedded = self.dropout(embedded) attn_weights = F.softmax( self.attn(torch.cat((embedded[0], hidden[0]), 1)), dim=1) attn_applied = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0), encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0)) output = torch.cat((embedded[0], attn_applied[0]), 1) output = self.attn_combine(output).unsqueeze(0) output = F.relu(output) output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden) output = F.log_softmax(self.out(output[0]), dim=1) return output, hidden, attn_weights def initHidden(self): return torch.zeros(1, 1, self.hidden_size, device=device) def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence): return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')] def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence): indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence) indexes.append(EOS_token) return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1) def tensorsFromPair(pair): input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0]) target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1]) return (input_tensor, target_tensor) teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5 def train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden() encoder_optimizer.zero_grad() decoder_optimizer.zero_grad() input_length = input_tensor.size(0) target_length = target_tensor.size(0) encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device) loss = 0 # from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter # writer = SummaryWriter('../runs/fashion_mnist_experiment_1') # writer.add_graph(encoder, (input_tensor[0], encoder_hidden,)) # writer.close() # 9/0 for ei in range(input_length): encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder( input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden) encoder_outputs[ei] = encoder_output[0, 0] decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden use_teacher_forcing = True if random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio else False if use_teacher_forcing: # Teacher forcing: Feed the target as the next input for di in range(target_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder( decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs) loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di]) decoder_input = target_tensor[di] # Teacher forcing else: # Without teacher forcing: use its own predictions as the next input for di in range(target_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder( decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs) topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1) decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() # detach from history as input loss += criterion(decoder_output, target_tensor[di]) if decoder_input.item() == EOS_token: break loss.backward() encoder_optimizer.step() decoder_optimizer.step() w2 = np.array(encoder.embedding.weight.data) b = np.sum(w2) print(b) return loss.item() / target_length import time import math def asMinutes(s): m = math.floor(s / 60) s -= m * 60 return '%dm %ds' % (m, s) def timeSince(since, percent): now = time.time() s = now - since es = s / (percent) rs = es - s return '%s (- %s)' % (asMinutes(s), asMinutes(rs)) def trainIters(encoder, decoder, n_iters, print_every=1000, plot_every=100, learning_rate=1.01): start = time.time() plot_losses = [] print_loss_total = 0 # Reset every print_every plot_loss_total = 0 # Reset every plot_every encoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(encoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) decoder_optimizer = optim.SGD(decoder.parameters(), lr=learning_rate) training_pairs = [tensorsFromPair(random.choice(pairs)) for i in range(n_iters)] criterion = nn.NLLLoss() for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1): training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1] input_tensor = training_pair[0] target_tensor = training_pair[1] loss = train(input_tensor, target_tensor, encoder, decoder, encoder_optimizer, decoder_optimizer, criterion) print_loss_total += loss plot_loss_total += loss if iter % print_every == 0: print_loss_avg = print_loss_total / print_every print_loss_total = 0 print('%s (%d %d%%) %.4f' % (timeSince(start, iter / n_iters), iter, iter / n_iters * 100, print_loss_avg)) if iter % plot_every == 0: plot_loss_avg = plot_loss_total / plot_every plot_losses.append(plot_loss_avg) plot_loss_total = 0 showPlot(plot_losses) import matplotlib.pyplot as plt plt.switch_backend('agg') import matplotlib.ticker as ticker import numpy as np def showPlot(points): plt.figure() fig, ax = plt.subplots() # this locator puts ticks at regular intervals loc = ticker.MultipleLocator(base=0.2) ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(loc) plt.plot(points) def evaluate(encoder, decoder, sentence, max_length=MAX_LENGTH): with torch.no_grad(): input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentence) input_length = input_tensor.size()[0] encoder_hidden = encoder.initHidden() encoder_outputs = torch.zeros(max_length, encoder.hidden_size, device=device) for ei in range(input_length): encoder_output, encoder_hidden = encoder(input_tensor[ei], encoder_hidden) encoder_outputs[ei] += encoder_output[0, 0] decoder_input = torch.tensor([[SOS_token]], device=device) # SOS decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden decoded_words = [] decoder_attentions = torch.zeros(max_length, max_length) for di in range(max_length): decoder_output, decoder_hidden, decoder_attention = decoder( decoder_input, decoder_hidden, encoder_outputs) decoder_attentions[di] = decoder_attention.data topv, topi = decoder_output.data.topk(1) if topi.item() == EOS_token: decoded_words.append('<EOS>') break else: decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi.item()]) decoder_input = topi.squeeze().detach() return decoded_words, decoder_attentions[:di + 1] def evaluateRandomly(encoder, decoder, n=10): for i in range(n): pair = random.choice(pairs) print('>', pair[0]) print('=', pair[1]) output_words, attentions = evaluate(encoder, decoder, pair[0]) output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words) print('<', output_sentence) print('') hidden_size = 256 encoder1 = EncoderRNN(input_lang.n_words, hidden_size).to(device) attn_decoder1 = AttnDecoderRNN(hidden_size, output_lang.n_words, dropout_p=0.1).to(device) trainIters(encoder1, attn_decoder1, 1000, print_every=5) evaluateRandomly(encoder1, attn_decoder1) output_words, attentions = evaluate( encoder1, attn_decoder1, "je suis trop froid .") plt.matshow(attentions.numpy()) def showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions): # Set up figure with colorbar fig = plt.figure() ax = fig.add_subplot(111) cax = ax.matshow(attentions.numpy(), cmap='bone') fig.colorbar(cax) # Set up axes ax.set_xticklabels([''] + input_sentence.split(' ') + ['<EOS>'], rotation=90) ax.set_yticklabels([''] + output_words) # Show label at every tick ax.xaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1)) ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(ticker.MultipleLocator(1)) plt.show() def evaluateAndShowAttention(input_sentence): output_words, attentions = evaluate( encoder1, attn_decoder1, input_sentence) print('input =', input_sentence) print('output =', ' '.join(output_words)) showAttention(input_sentence, output_words, attentions) evaluateAndShowAttention("elle a cinq ans de moins que moi .") evaluateAndShowAttention("elle est trop petit .") evaluateAndShowAttention("je ne crains pas de mourir .") evaluateAndShowAttention("c est un jeune directeur plein de talent .")
|
使用预训练模型 |
由于LSTM也不可能完全克服梯度消失问题,那么穿透LSTM更新Embedding层的参数就比较困难。
与此同时模型的参数总量就相当于LSTM的参数总量,加上Embedding层的参数总量。假设词表长度是10W,词向量维度是100的话,这种做法就意味着你的模型凭空多出了10W * 100 = 1000W的参数,显然你那点标注数据根本就喂不饱这么多参数,真这么玩的话直接就过拟合到姥姥家了。这也就是为什么我们要使用预训练词向量——训练模型同时训练词向量,就意味着要使用宝贵的标注数据去填Embedding层这个大窟窿。而预训练词向量就完全不一样了——主流的词向量训练方法,比如早年间的word2vec,GloVe,或者近年来的各种Context-aware Embedding,都可以通过自监督(Self-Supervised)方法进行训练。也就是说,语料的词与词间共现关系(word2vec)或者上下文顺序(ELMo和BERT等)本身就是给模型的标注信息——这就意味着我们可以轻而易举地使用大量的无监督文本语料进行词向量训练。要知道,互联网时代,无监督文本语料本身的获取成本是很低的,基本上只要你往上堆算力堆模型就可以了。通过预训练词向量,不仅可以通过大量的文本获得质量更高的词向量,还可以在训练的时候直接把Embedding层当成常数(requires_grad=False),这样的话需要训练的参数就只有LSTM本身的参数了,让宝贵的标注数据可以好钢用在刀刃上。
|
参考资料 |
https://www.zhihu.com/question/316535024
https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/seq2seq_translation_tutorial.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号