iOS进阶笔记(二) 分类的加载过程及与类扩展的区别

一、通过runtime源码分析Category加载过程
1、runtime初始化入口函数(objc-os.mm)
void _objc_init(void)
{
static bool initialized = false;
if (initialized) return;
initialized = true;
// fixme defer initialization until an objc-using image is found?
environ_init();
tls_init();
static_init();
runtime_init();// 初始化runtime
exception_init();
#if __OBJC2__
cache_t::init();
#endif
_imp_implementationWithBlock_init();
// 动态链接器通知的注册
// 传入`objc-runtime-new.mm`中的`map_images`函数地址
_dyld_objc_notify_register(&map_images, load_images, unmap_image);
#if __OBJC2__
didCallDyldNotifyRegister = true;
#endif
}
void map_images_nolock(unsigned mhCount, const char * const mhPaths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
// some code
if (hCount > 0) {
// 这里读取模块,调用 objc-runtime-new.mm 中_read_images函数
_read_images(hList, hCount, totalClasses, unoptimizedTotalClasses);
}
// some code
}
2、 objc-runtime-new.mm中的map_images函数
// 来自objc-os.mm文件的 _dyld_objc_notify_register()函数调用
void map_images(unsigned count, const char * const paths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);// 加锁
// 调用objc-os.mm中map_images_nolock函数
return map_images_nolock(count, paths, mhdrs);
}
3、_read_images函数内部通过dyld搜索Category并加载分类
void _read_images(header_info **hList, uint32_t hCount, int totalClasses, int unoptimizedTotalClasses) {
// some code
#pragma mark- 通过dyld搜索Category
// Discover categories. Only do this after the initial category
// attachment has been done. For categories present at startup,
// discovery is deferred until the first load_images call after
// the call to _dyld_objc_notify_register completes. rdar://problem/53119145
if (didInitialAttachCategories) {
for (EACH_HEADER) {
// 加载分类
load_categories_nolock(hi);
}
}
// some code
}
4、 来自objc-os.mm文件的 _dyld_objc_notify_register()函数调用
void map_images(unsigned count, const char * const paths[],
const struct mach_header * const mhdrs[])
{
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
return map_images_nolock(count, paths, mhdrs);
}
// 加载分类
static void load_categories_nolock(header_info *hi) {
bool hasClassProperties = hi->info()->hasCategoryClassProperties();
size_t count;
#pragma mark- C++ 闭包 [&](category_t * const *catlist) {};
auto processCatlist = [&](category_t * const *catlist)
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < count; i++) {
category_t *cat = catlist[i];
Class cls = remapClass(cat->cls);
locstamped_category_t lc{cat, hi};
if (!cls) {
// Category's target class is missing (probably weak-linked).
// Ignore the category.
if (PrintConnecting) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: IGNORING category \?\?\?(%s) %p with "
"missing weak-linked target class",
cat->name, cat);
}
continue;
}
// Process this category.
if (cls->isStubClass()) {// 若当前类为rootClass
// Stub classes are never realized. Stub classes
// don't know their metaclass until they're
// initialized, so we have to add categories with
// class methods or properties to the stub itself.
// methodizeClass() will find them and add them to
// the metaclass as appropriate.
if (cat->instanceMethods ||
cat->protocols ||
cat->instanceProperties ||
cat->classMethods ||
cat->protocols ||
(hasClassProperties && cat->_classProperties))
{
objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(lc, cls);
}
} else {
// First, register the category with its target class.
// Then, rebuild the class's method lists (etc) if
// the class is realized.
// 若是实例对象
if (cat->instanceMethods || cat->protocols
|| cat->instanceProperties)
{
if (cls->isRealized()) {// 若cls已经初始化了,则重新编译该类的方法列表
attachCategories(cls, &lc, 1, ATTACH_EXISTING);
} else {
// 调用unattachedCategories 类的addForClass方法
// 注册分类并将其加入到当前class
objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(lc, cls);
}
}
// 若是类对象
if (cat->classMethods || cat->protocols
|| (hasClassProperties && cat->_classProperties))
{
if (cls->ISA()->isRealized()) {
attachCategories(cls->ISA(), &lc, 1, ATTACH_EXISTING | ATTACH_METACLASS);
} else {
objc::unattachedCategories.addForClass(lc, cls->ISA());
}
}
}
}
};
// 执行闭包函数,参数为catlist和catlist2
processCatlist(hi->catlist(&count));
processCatlist(hi->catlist2(&count));
}
5、通过attachCategories函数将合并后的分类数据(方法、属性、协议),插入到类原来数据的前面
static void attachCategories(Class cls, const locstamped_category_t *cats_list, uint32_t cats_count, int flags)
{
if (slowpath(PrintReplacedMethods)) {
printReplacements(cls, cats_list, cats_count);
}
if (slowpath(PrintConnecting)) {
_objc_inform("CLASS: attaching %d categories to%s class '%s'%s",
cats_count, (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) ? " existing" : "",
cls->nameForLogging(), (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS) ? " (meta)" : "");
}
/*
* Only a few classes have more than 64 categories during launch.
* This uses a little stack, and avoids malloc.
*
* Categories must be added in the proper order, which is back
* to front. To do that with the chunking, we iterate cats_list
* from front to back, build up the local buffers backwards,
* and call attachLists on the chunks. attachLists prepends the
* lists, so the final result is in the expected order.
*/
constexpr uint32_t ATTACH_BUFSIZ = 64;
method_list_t *mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];// 方法列表
property_list_t *proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];// 属性列表
protocol_list_t *protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ];// 协议列表
uint32_t mcount = 0;
uint32_t propcount = 0;
uint32_t protocount = 0;
bool fromBundle = NO;
bool isMeta = (flags & ATTACH_METACLASS);
auto rwe = cls->data()->extAllocIfNeeded();
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < cats_count; i++) {
auto& entry = cats_list[i];
// 取出方法列表
method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);
if (mlist) {
if (mcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle, __func__);
rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);
mcount = 0;
}
// 将前面的mlist覆盖到mlists数组的后边,保证Xcode->Build Phases -> Compil Sources 列表中下面的Category文件比其上边的Category文件先参与编译,即下面的Category文件中的方法先执行。
mlists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++mcount] = mlist;
fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle();
}
// 取出属性列表
property_list_t *proplist =
entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi);
if (proplist) {
if (propcount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {
rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount);
propcount = 0;
}
proplists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++propcount] = proplist;
}
// 取出协议列表
protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocolsForMeta(isMeta);
if (protolist) {
if (protocount == ATTACH_BUFSIZ) {
rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount);
protocount = 0;
}
protolists[ATTACH_BUFSIZ - ++protocount] = protolist;
}
}
if (mcount > 0) {
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount,
NO, fromBundle, __func__);
//
rwe->methods.attachLists(mlists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - mcount, mcount);
if (flags & ATTACH_EXISTING) {
flushCaches(cls, __func__, [](Class c){
// constant caches have been dealt with in prepareMethodLists
// if the class still is constant here, it's fine to keep
return !c->cache.isConstantOptimizedCache();
});
}
}
// 最后依次装载属性列表和协议列表
rwe->properties.attachLists(proplists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - propcount, propcount);
rwe->protocols.attachLists(protolists + ATTACH_BUFSIZ - protocount, protocount);
}
小结:
通过runtime加载某个类的所有Category信息
-
多个分类编译顺序(队列方式):Build Phases -> Compil Sources 列表中下面的Category文件比其上边的Category文件先加载运行
-
分类中的instance方法合并到class对象中,类方法合并到meta-class对象中
-
属性、instance方法、协议合并到类对象struct class_rw_t中
-
通过attachCategories函数将合并后的分类数据(方法、属性、协议),插入到类原来数据的前面
二、Category与Extension区别
1、类扩展分析
下面以Person类扩展为例
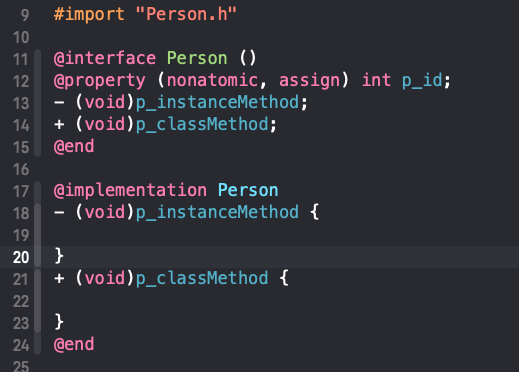
通过clang,可以看出在编译时,类扩展的信息已经加载到类中。
-
编译过程中,类的实现中已加载成员属性
_p_id
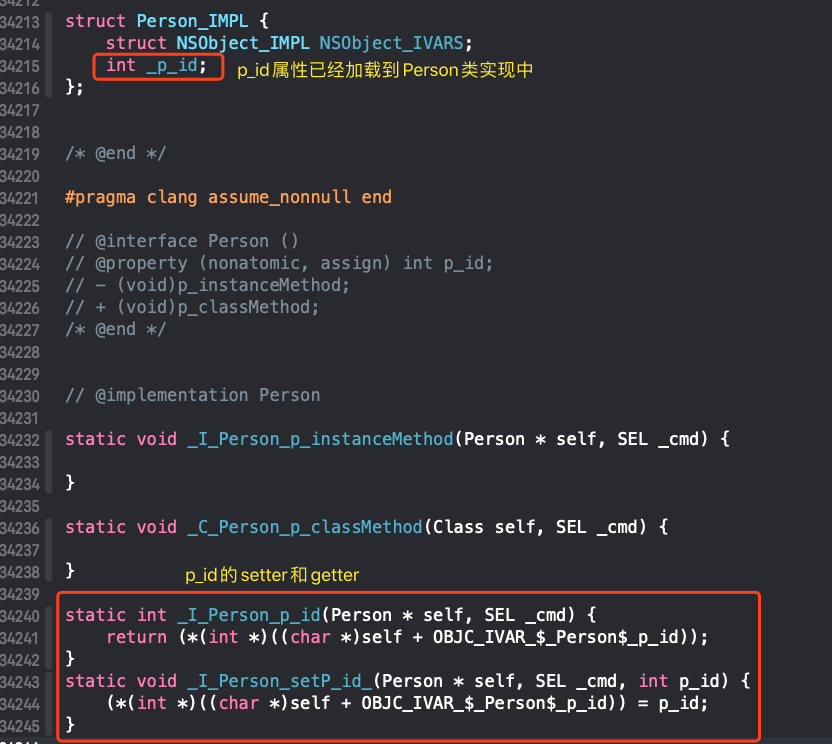
-
编译过程中,在实例方法列表初始化时已加载到类的instanceMethod列表中
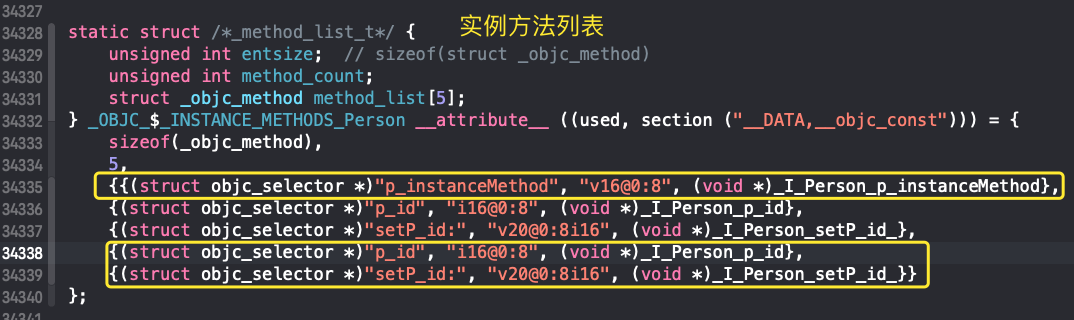
-
编译过程中,在对象方法列表初始化时已加载到类的classMethod列表中
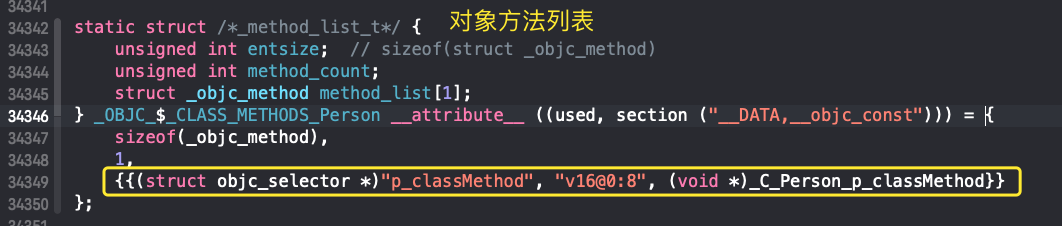
2、分类分析
下面以Person+Method 分类为例
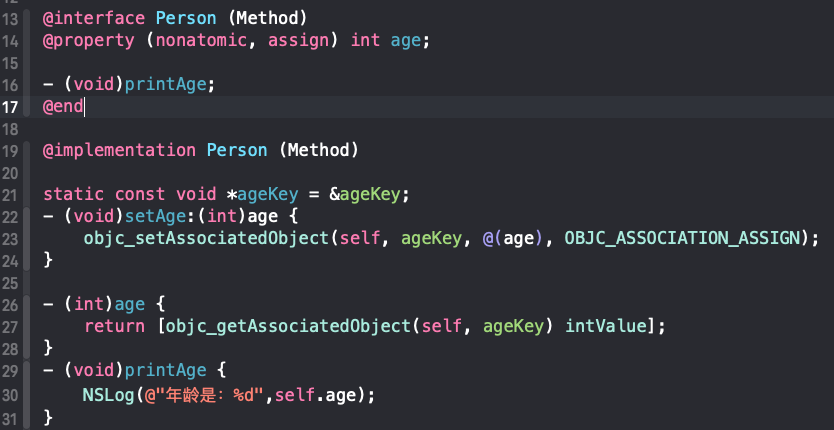
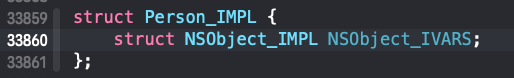
- Person类的实现中并没有
age属性信息,而是通过关联对象AssociationsManager维护在一张全局的AssociationsHashMap中
- 在runtime初始化时,加载分类的信息(详见:
1、通过runtime源码分析Category加载过程)
小结:
-
Class Extension(即匿名分类)类的扩展只是声明,依赖于当前类,没有.m文件;在编译时,作为类的一部分,和类一起编译,它的数据包含在类信息中。
-
Category是在运行时,才会将数据合并到类信息中。
以上(完)
----------End------------
(限于水平,本文可能存在瑕疵甚至错误的地方。如有发现,还请留言指正,相互学习。thx! )
KEEP LOOKING, DON`T SETTLE!

