JAVA入门基础_SSM的学习
- Mybatis的学习
- Spring的学习
- SpringMVC的学习
- 整合SSM的步骤
Mybatis的学习
Mybaits快速入门案例
Mybatis开发环境搭建
-
下载Mybatis的jar包 或者 使用maven构建工具
-
使用Mybatis最基础需要引入如下jar包
- 连接数据库的驱动
- mybatis的jar包
- log4j日志(不使用mybaits也可以用,但是没有日志)
配置Mybaits的全局配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 引入外部配置文件,从根路径下找 -->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties" />
<!-- 配置数据库字段下划线与JAVA实体类的驼峰映射 -->
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<!-- 配置别名 -->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.codestarts.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<!-- 配置一个个的环境,其中主要配置了事务管理的方式和数据源 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!--
配置采用的事务管理方式,JDBC:编程式事务管理,
MANAGER:啥也不干,让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期
-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--
POOLED:采用数据库连接池的方式来获取连接
UNPOOLED:每一个连接都直接通过访问数据库获得
JNDI :上下文数据源引用(了解)
-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<!-- 可以配置多个,自行选择 -->
<environment id="test">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 配置*.xml映射文件-->
<mappers>
<!-- 配置单个的方式mappers/UserMapper.xml代表根路径下的mappers/UserMapper -->
<!--<mapper resource="mappers/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>-->
<!--
配置mapper接口与mapper.xml所在的包,
注意mapper接口和mapper.xml的名字必须一致
注意接口与mapper必须在同一个包下
-->
<package name="com.codestarts.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
配置一个Mapper接口文件
public interface UserMapper {
int insert();
}
配置一个Mapper接口对应的xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.codestarts.mapper.UserMapper">
<insert id="insert">
insert into user(name,gender,age) values('张三','女',15)
</insert>
</mapper>
编写一个测试类
public class SqlSessionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 获取到Mybatis配置文件
InputStream is = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
// 获取工厂
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder sqlSessionFactoryBuilder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
SqlSessionFactory build = sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(is);
// 获得对应的Mapper接口,注意,这里得到的UserMapper是一个动态代理生成的实现类。
SqlSession sqlSession = build.openSession();
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 插入一条数据
mapper.insert();
// 提交与关闭
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
}
目录结构
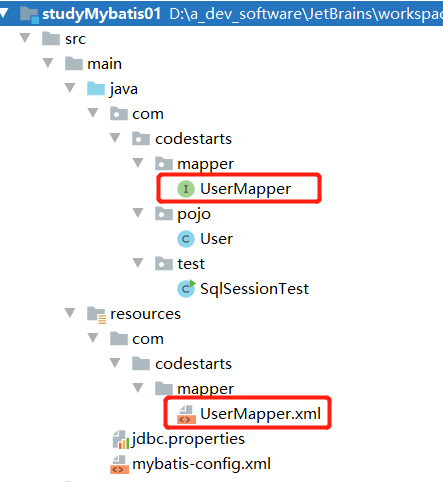
Mybatis获取参数的6种方式
#{}获取数据与${}获取数据的区别
-
#{}相当于之前写JDBC时用的
占位符,使用时传递参数会自动帮忙加上双引号 -
${}则相当于
字符串拼接。
当需要获取的参数列表只有一个参数时
- 在xml文件中可以通过 #{任意标识符}、${任意标识符}的方式获取
当需要获取的参数列表有多个参数时
- 在xml文件中可以通过
#{arg0 | param1}、#{arg1 | param2}或者${arg0 | param1}、${arg1 | param2}
当需要获取的参数列表为一个Map集合时
- 在xml文件中通过Map集合中的键值即可直接获取
#{键值} 或者 ${键值}
当需要获取的参数列表为一个实体类时(掌握)
- 在xml文件中使用#{}或者${}时,直接写属性名即可
- 注意:属性名并不是指实体对象中的一个个成员变量,而是指一个个setter、getter
通过@Param注解的方式获取参数(掌握)
-
在编写Mapper文件的接口时,在参数前加上注解:
@Param("key") -
那么xml文件中就可以通过#{}或者${} 中写上该键值的方式直接获取到
如果接口仅仅只传递一个List时的处理
<insert id="insertList" parameterType="java.util.List">
insert into student(name, age)
values
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" separator="," open=")" close= ")">
#{item.name} , #{item.age}
</foreach>
</insert>
添加日志功能
- 引入日志jar包
<!-- log4j日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
- 在根目录下添加log4j.xml文件,注意名称不能错
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE log4j:configuration SYSTEM "log4j.dtd">
<log4j:configuration xmlns:log4j="http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/">
<appender name="STDOUT" class="org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender">
<param name="Encoding" value="UTF-8" />
<layout class="org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout">
<param name="ConversionPattern" value="%-5p %d{MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS}
%m (%F:%L) \n" />
</layout>
</appender>
<logger name="java.sql">
<level value="debug" />
</logger>
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis">
<level value="info" />
</logger>
<root>
<level value="debug" />
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
</root>
</log4j:configuration>
Mybatis查询数据的各种情况
返回一个实体类对象和一个实体类对象的集合
-
xml文件中的select标签内将resultType写上需要映射的实体类全限定类名即可
-
Mapper接口
// 获取一条记录
User selectUserById(@Param("id") Integer id);
// 获取多条记录
List<User> selectList();
- Mapper.xml文件,比较重要的式这个
resultType
<select id="selectUserById" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.User">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
<select id="selectList" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.User">
select * from user
</select>
返回单行单列
- Mapper接口
// 获取单行单列记录
Integer selectCount();
- Mapper.xml文件
<select id="selectCount" resultType="java.lang.Integer">
select count(1) from user
</select>
查询的结果为Map时(2种情况)
返回一个List<Map<String, Object>>
- Mapper接口如下
List<Map<String, Object>> selectMap();
- Mapper.xml如下
<select id="selectMap" resultType="java.util.Map">
select * from user
</select>
- 查询结果如下
[{gender=女, name=11三, id=1, age=15}, {gender=女, name=张三, id=2, age=15}, {gender=女, name=张三, id=3, age=15}]
返回一个Map<String, Map<String, Object>>
- Mapper接口(使用了@MapKey注解,选择查询出的哪个字段作为外层Map的Key)
@MapKey("id")
Map<String, Object> selectMap02();
- Mapper.xml(跟查询一个List<Map>是一致的)
<select id="selectMap02" resultType="java.util.Map">
select * from user
</select>
- 查询的结果直接打印
{1={gender=女, name=11三, id=1, age=15}, 2={gender=女, name=张三, id=2, age=15}, 3={gender=女, name=张三, id=3, age=15}}
特殊的Sql执行(有些地方必须使用SQL拼接${}完成)
模糊查询的四种方式
- Mapper接口
// 模糊查询的4种方式
List<User> selectUserLikeName(@Param("name") String name);
List<User> selectUserLikeName01(@Param("name") String name);
List<User> selectUserLikeName02(@Param("name") String name);
List<User> selectUserLikeName03(@Param("name") String name);
- Mapper.xml文件
<!--
使用这种方式会报错,因为#{name}是个占位符,也就是我们之前JDBC所写的?,那么拼接后就变成了 '%?%'
这个?占位符就被当成了一个字符串解析,因此报错
-->
<select id="selectUserLikeName" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.User">
select * from user where name like '%#{name}%'
</select>
<!-- 使用字符串拼接方式 -->
<select id="selectUserLikeName01" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.User">
select * from user where name like '%${name}%'
</select>
<!-- 使用concat实现 -->
<select id="selectUserLikeName02" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.User">
select * from user where name like concat('%',#{name},'%')
</select>
<!-- 推荐使用~~~ -->
<select id="selectUserLikeName03" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.User">
select * from user where name like "%"#{name}"%"
</select>
批量删除
- Mapper接口
int deleteBatch(@Param("ids") String ids);
- Mapper.xml文件
传入类似于:"5,1,6"这样的字符串,使用#{}就不行了
<delete id="deleteBatch">
delete from user where id in (${ids})
</delete>
动态设置表名
- Mapper接口
List<Map<String, Object>> selectDynamicTableName(@Param("tableName") String tableName);
- Mapper.xml文件
<select id="selectDynamicTableName" resultType="java.util.Map">
select * from ${tableName}
</select>
新增记录时获取到自增的主键值
应用场景举例:添加一个班级,并且为该班级指定对应的学生。
前提该要:mybaits的增删改方法返回的结果都是影响到的行数。因此如果想要得到自增的ID需要将该值赋值到插入的实体类的一个属性当中。
- Mapper接口
void insertuseGeneratedKey(User user);
- Mapper.xml
<!--
useGeneratedKeys开启主键自增功能(JDBC的功能)
keyProperty:需要映射到实体类的哪个字段(注意是实体类)
-->
<insert id="insertuseGeneratedKey" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert into user(name,gender,age) values(#{name},#{gender},#{age})
</insert>
- 测试一下
User user = new User(null, "王五", "女", 18);
mapper.insertuseGeneratedKey(user);
System.out.println(user);
// 得到的结果为:User(id=5, name=王五, gender=女, age=18),可以看出自增的id已经得到了
自定义映射ResultMap
为什么需要自定义ResultMap呢
-
(1)我们实体类中的属性名与数据库中的字段名不一定是相互对应的
-
(2)当我们查询时,出现一对多、多对多的情况时,单纯的字段映射已经无法搞定
定义并使用一个ResultMap
<resultMap id="empResultMap" type="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="ename" property="eName"></result>
<result column="job" property="job"></result>
<result column="birth" property="birth"></result>
<result column="sal" property="sal"></result>
<result column="fk_dept_id" property="fkDeptId"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectList" resultMap="empResultMap">
select * from employee
</select>
ResultMap处理多对一映射的3种方式
级联方式
- Mapper接口
/**
* 多对一第一种方式,级联
*/
List<Employee> selectResultMapManyForOne01();
- Mapper.xml文件
<resultMap id="empResultMap01" type="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="ename" property="eName"></result>
<result column="job" property="job"></result>
<result column="birth" property="birth"></result>
<result column="sal" property="sal"></result>
<result column="fk_dept_id" property="fkDeptId"></result>
<result column="fk_dept_id" property="dept.id"></result>
<result column="ename" property="dept.dname"></result>
<result column="loc" property="dept.loc"></result>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectResultMapManyForOne01" resultMap="empResultMap01">
select e.*,d.*
from employee e left join dept d
on e.fk_dept_id = d.id
</select>
使用association处理映射关系
- Mapper接口
List<Employee> selectResultMapManyForOne02();
- Mapper.xml文件
<resultMap id="empResultMap02" type="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="ename" property="eName"></result>
<result column="job" property="job"></result>
<result column="birth" property="birth"></result>
<result column="sal" property="sal"></result>
<result column="fk_dept_id" property="fkDeptId"></result>
<association property="dept" javaType="com.codestarts.pojo.Dept">
<id property="id" column="fk_dept_id"></id>
<result property="dname" column="dname"></result>
<result property="loc" column="loc"></result>
</association>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectResultMapManyForOne02" resultMap="empResultMap02">
select e.*,d.*
from employee e left join dept d
on e.fk_dept_id = d.id
</select>
使用分布查询处理映射关系
- EmployeeMapper接口
List<Employee> selectResultMapManyForOne03();
- EmployeeMapper.xml文件
<resultMap id="empResultMap03" type="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
<id column="id" property="id"></id>
<result column="ename" property="eName"></result>
<result column="job" property="job"></result>
<result column="birth" property="birth"></result>
<result column="sal" property="sal"></result>
<result column="fk_dept_id" property="fkDeptId"></result>
<association property="dept"
select="com.codestarts.mapper.DeptMapper.selectDeptById"
column="fk_dept_id"
/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectResultMapManyForOne03" resultMap="empResultMap03">
select * from employee
</select>
- DeptMapper接口
Dept selectDeptById(@Param("deptId") Integer deptId);
- DeptMapper.xml文件
<select id="selectDeptById" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.Dept">
select * from dept where id = #{deptId}
</select>
ResulMap处理一对多映射的2种方式
使用collection处理映射关系
- Mapper接口
List<Dept> selectResultMapOneForMany01();
- Mapper.xml文件
<resultMap id="deptResultMap01" type="com.codestarts.pojo.Dept">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="dname" property="dname"/>
<result column="loc" property="loc"/>
<collection property="emps" ofType="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
<id column="eid" property="id" />
<result column="ename" property="eName"/>
<result column="job" property="job"/>
<result column="brith" property="brith"/>
<result column="sal" property="sal"/>
<result column="fk_dept_id" property="fkDeptId"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectResultMapOneForMany01" resultMap="deptResultMap01">
select d.*,e.id eid,e.*
from dept d left join employee e
on d.id = e.fk_dept_id
</select>
使用分布查询处理映射关系
- DeptMapper接口
List<Dept> selectResultMapOneForMany02();
- DeptMapper.xml文件
<resultMap id="deptResultMap02" type="com.codestarts.pojo.Dept">
<id column="id" property="id" />
<result column="dname" property="dname"/>
<result column="loc" property="loc"/>
<collection property="emps"
select="com.codestarts.mapper.EmployeeMapper.selectEmployeeByDeptId"
column="id">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectResultMapOneForMany02" resultMap="deptResultMap02">
select d.*,e.id eid,e.*
from dept d left join employee e
on d.id = e.fk_dept_id
</select>
- EmployeeMapper接口
List<Employee> selectEmployeeByDeptId(@Param("deptId") Integer deptId);
- EmployeeMapper.xml文件
<select id="selectEmployeeByDeptId" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee where fk_dept_id = #{deptId}
</select>
Result小总结
association的作用
当需要映射的属性是一个实体类时,就可以考虑使用该标签。
- 非分布查询时
- property 实体的属性名称
- javaType 该属性的全限定类名
- 分布查询时
- property 实体的属性名称
- select 需要分布查询方法的唯一路径
- column 需要传递给select的字段列
collection的作用
当需要映射的属性是一个集合时,可以考虑使用该标签
-
非分布查询时
- property 实体的属性名称
- ofType 集合中的元素类型
-
分布查询时(与association一致)
- property 实体的属性名称
- select 需要分布查询方法的唯一路径
- column 需要传递给select的字段列
ResultMap实现分布查询时的延迟加载配置
- 修改mybaits全局配置文件,添加如下setting
<!--开启延迟加载功能-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 关闭该功能后,才能进行按需加载,与lazyLoadingEnabled 配合使用-->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
- 如果一个查询功能不想使用延迟加载,则需要在Mapper.xml文件的该方法的resultMap中的collection或association标签上添加
fetchType="eager"
动态SQL
if进行模糊查询
<select id="selectByCondition" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee where 1=1
<if test="ename!=null and ename!=''">
and ename like "%"#{ename}"%"
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
and job like "%"#{job}"%"
</if>
<if test="sal!=null and sal!=''">
and sal like "%"#{sal}"%"
</if>
</select>
where配合if进行模糊查询
-
当where中的条件有任意匹配时,会自动拼接上where条件
-
会去除掉条件前多余的and(但是不会去掉条件后的and)
-
当where中没有条件匹配时,该标签无效
<select id="selectByCondition02" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee
<where>
<if test="ename!=null and ename!=''">
ename like "%"#{ename}"%"
</if>
<if test="job!=null and job!=''">
and job like "%"#{job}"%"
</if>
<if test="sal!=null and sal!=''">
and sal like "%"#{sal}"%"
</if>
</where>
</select>
trim
-
prefix/suffix 在SQL语句的前后添加上任意前缀或后缀
-
prefixOverrides / suffixOverrides 在SQL语句的前后删除任意前缀或后缀
choose、when、otherwise
-
相当于 if .. else if .. else
-
其中when至少需要出现一次
-
otherwise最多出现一次
-
测试代码
<select id="selectByCondition03" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
select * from employee
<where>
<choose>
<when test="ename!=null and ename!=''">
ename like "%"#{ename}"%"
</when>
<when test="job!=null and job!=''">
job like "%"#{job}"%"
</when>
</choose>
</where>
</select>
foreach(重要)
新增多条记录(使用了集合)
- Mapper接口
void insertBatchRecord(@Param("emps") List<Employee> emps);
- Mapper.xml文件
<insert id="insertBatchRecord">
insert into employee values
<foreach collection="emps" item="emp" separator=",">
(null, #{emp.ename}, #{emp.job}, #{emp.brith}, #{emp.sal}, #{emp.fkDeptId})
</foreach>
</insert>
删除多条记录(使用了数组)
- Mapper接口
void deleteBatchRecord(@Param("ids") Integer[] ids);
- Mapper.xml文件
<delete id="deleteBatchRecord">
delete from employee where id in
<foreach collection="ids" item="id" separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>
sql(片段)
作用:将重复的SQL代码统一的封装起来
<sql id="allFiled">
id, ename, job, brith, sal, fk_dept_id
</sql>
<select id="selectList" resultType="com.codestarts.pojo.Employee">
select <include refid="allFiled"/> from employee
</select>
MyBatis缓存
一级缓存
-
SqlSession级别,仅在同一个SqlSession有效,默认开启
-
失效条件
(1)使用同一条SQL语句查询时中间穿插了增删改操作
(2) 清空了SqlSession的缓存sqlSession.clearCache()
二级缓存
缓存的生效条件
-
在mybatis全局配置中开启二级缓存功能
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> -
二级缓存仅在同一个SqlSessionFactory创建的SqlSession中有效
-
开启二级缓存生效的四个条件
(1)在核心配置文件中,设置全局配置属性cacheEnabled="true",默认为true,不需要设置(2)在映射文件中设置标签
(3)只有当一个SqlSession提交或关闭时,才会将该SqlSession的一级缓存存储到二级缓存当中
(4)查询的数据所转换的实体类类型必须实现序列化的接口
注意:两次查询之间执行了任意的增删改,会使一级和二级缓存同时失效
二级缓存的相关配置
-
(1)在mapper配置文件中添加的cache标签可以设置一些属性:
-
(2)eviction属性:缓存回收策略
- LRU(Least Recently Used) – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象。
- FIFO(First in First out) – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。
- SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。
- WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。默认的是 LRU。
-
(3)flushInterval属性:刷新间隔,单位毫秒默认情况是不设置,也就是没有刷新间隔,缓存仅仅调用语句时刷新
-
(4)size属性:引用数目,正整数代表缓存最多可以存储多少个对象,太大容易导致内存溢出
-
(5)readOnly属性:只读,true/false
- true:只读缓存;会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些对象不能被修改。这提供了很重要的性能优势。
- false:读写缓存;会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化)。这会慢一些,但是安全,因此默认是false。
- 只读缓存,相当于把缓存中的引用直接交给了方法调用者。 读写缓存相当于每次都会拷贝一个对象交给调用者。
第三方二级缓存EHCache
引入依赖
<!-- Mybatis EHCache整合包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- slf4j日志门面的一个具体实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
各jar包的功能
-
(1)mybatis-ehcache Mybatis和EHCache的整合包
-
(2)ehcache EHCache核心包
-
(3)slf4j-api SLF4J日志门面包
-
(4)logback-classic 支持SLF4J门面接口的一个具体实现
在根路径下创建ehcache.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="../config/ehcache.xsd">
<!-- 磁盘保存路径 -->
<diskStore path="D:\mybatis_test\ehcache"/>
<defaultCache
maxElementsInMemory="1000"
maxElementsOnDisk="10000000"
eternal="false"
overflowToDisk="true"
timeToIdleSeconds="120"
timeToLiveSeconds="120"
diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds="120"
memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU">
</defaultCache>
</ehcache>
配置文件的参数作用
| 属性名 | 是否必须 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| maxElementsInMemory | 是 | 在内存中缓存的element的最大数目 |
| maxElementsOnDisk | 是 | 在磁盘上缓存的element的最大数目,若是0表示无穷大 |
| eternal | 是 | 设定缓存的elements是否永远不过期。 如果为true,则缓存的数据始终有效, 如果为false那么还要根据timeToIdleSeconds、timeToLiveSeconds判断 |
| overflowToDisk | 是 | 设定当内存缓存溢出的时候是否将过期的element缓存到磁盘上 |
| timeToIdleSeconds | 否 | 当缓存在EhCache中的数据前后两次访问的时间超过timeToIdleSeconds的属性取值时, 这些数据便会删除,默认值是0,也就是可闲置时间无穷大 |
| timeToLiveSeconds | 否 | 缓存element的有效生命期,默认是0.,也就是element存活时间无穷大 |
| diskSpoolBufferSizeMB | 否 | DiskStore(磁盘缓存)的缓存区大小。默认是30MB。每个Cache都应该有自己的一个缓冲区 |
| diskPersistent | 否 | 在VM重启的时候是否启用磁盘保存EhCache中的数据,默认是false。 |
| diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds | 否 | 磁盘缓存的清理线程运行间隔,默认是120秒。每隔120s, 相应的线程会进行一次EhCache中数据的清理工作 |
| memoryStoreEvictionPolicy | 否 | 当内存缓存达到最大,有新的element加入的时候, 移除缓存中element的策略。 默认是LRU(最近最少使用),可选的有LFU(最不常使用)和FIFO(先进先出) |
修改二级缓存的类型
<cache type="org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache"/>
创建logback.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration debug="true">
<!-- 指定日志输出的位置 -->
<appender name="STDOUT"
class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<!-- 日志输出的格式 -->
<!-- 按照顺序分别是:时间、日志级别、线程名称、打印日志的类、日志主体内容、换行 -->
<pattern>[%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS}] [%-5level] [%thread] [%logger]
[%msg]%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- 设置全局日志级别。日志级别按顺序分别是:DEBUG、INFO、WARN、ERROR -->
<!-- 指定任何一个日志级别都只打印当前级别和后面级别的日志。 -->
<root level="DEBUG">
<!-- 指定打印日志的appender,这里通过“STDOUT”引用了前面配置的appender -->
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
</root>
<!-- 根据特殊需求指定局部日志级别 -->
<logger name="com.codestarts.mapper" level="DEBUG"/>
</configuration>
缓存查询的先后顺序
-
(1)先查询二级缓存
-
(2)再查询一级缓存
-
(3)最后查询数据库
-
SqlSession关闭之后,一级缓存中的数据会写入二级缓存
MyBatis逆向工程
正向工程与逆向工程的区别
-
正向工程:先创建实体类,再根据实体类生成数据库表
-
逆向工程:先创建数据库表,再根据数据库表生成实体类,逆向生成的资源如下
- Java实体类
- Mapper接口
- Mapper映射文件
引入jar包及Maven插件
<!-- 依赖MyBatis核心包 -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- 控制Maven在构建过程中相关配置 -->
<build>
<!-- 构建过程中用到的插件 -->
<plugins>
<!-- 具体插件,逆向工程的操作是以构建过程中插件形式出现的 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
<!-- 插件的依赖 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- 逆向工程的核心依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.generator</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-generator-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mchange</groupId>
<artifactId>c3p0</artifactId>
<version>0.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.28</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
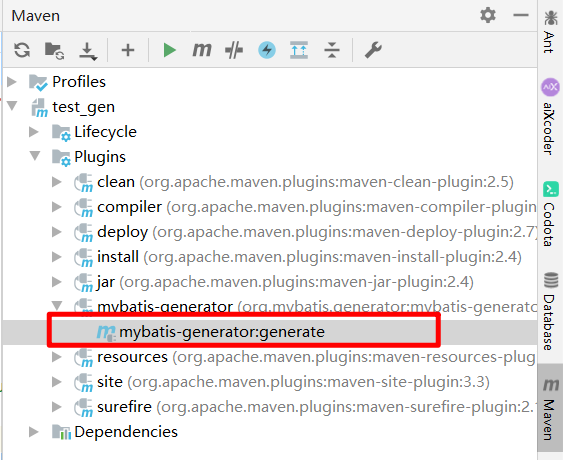
添加generatorConfig.xml配置文件并运行
- 添加了之后找到对应的插件运行即可
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd">
<generatorConfiguration>
<!--
targetRuntime: 执行生成的逆向工程的版本
MyBatis3Simple: 生成基本的CRUD(清新简洁版)
MyBatis3: 生成带条件的CRUD(奢华尊享版)
-->
<context id="DB2Tables" targetRuntime="MyBatis3">
<!-- 数据库的连接信息 -->
<jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"
connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_mybatis?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai"
userId="root"
password="abc123">
</jdbcConnection>
<!-- javaBean的生成策略-->
<javaModelGenerator targetPackage="com.codestats.mybatis.bean"
targetProject=".\src\main\java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/>
<property name="trimStrings" value="true"/>
</javaModelGenerator>
<!-- SQL映射文件的生成策略 -->
<sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="com.codestats.mybatis.mapper"
targetProject=".\src\main\resources">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/>
</sqlMapGenerator>
<!-- Mapper接口的生成策略 -->
<javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER"
targetPackage="com.codestats.mybatis.mapper" targetProject=".\src\main\java">
<property name="enableSubPackages" value="true"/>
</javaClientGenerator>
<!-- 逆向分析的表 -->
<!-- tableName设置为*号,可以对应所有表,此时不写domainObjectName -->
<!-- domainObjectName属性指定生成出来的实体类的类名 -->
<table tableName="dept" domainObjectName="Dept"/>
<table tableName="employee" domainObjectName="Employee"/>
</context>
</generatorConfiguration>
MyBatis分页插件
在pom.xml文件中引入插件
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.github.pagehelper/pagehelper -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.2.0</version>
</dependency>
在mybatis全局配置文件中配置
<plugins>
<!--设置分页插件-->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin>
</plugins>
PageInfo及参数解释
// 开启分页
PageHelper.startPage(2, 3);
List<Employee> employees = mapper.selectList();
// 获取PageInfo
PageInfo<Employee> pageInfo = new PageInfo<Employee>(employees);
// 导航分页的页码数量
PageInfo<Employee> pageInfo2 = new PageInfo<Employee>(employees, 3);
-
(1)pageNum:当前页的页码
-
(2)pageSize:每页显示的条数
-
(3)size:当前页显示的真实条数
-
(4)total:总记录数
-
(5)pages:总页数
-
(6)prePage:上一页的页码
-
(7)nextPage:下一页的页码
-
(8)isFirstPage/isLastPage:是否为第一页/最后一页
-
(9)hasPreviousPage/hasNextPage:是否存在上一页/下一页
-
(10)navigatePages:导航分页的页码数
-
(11)navigatepageNums:导航分页的页码,[1,2,3,4,5]
使用mybatis过程中出现的问题
在mapper.xml中,判断某个字段不是空字符串时,发现整数0会被当成空字符串..
判断的时候,要么先把int转换成string,要么不判断是否等于空字符串
Spring的学习
Spring的特性及五大功能模块
特性
-
(1)非侵入式:使用 Spring Framework 开发应用程序时,Spring 对应用程序本身的结构影响非常小。对领域模型可以做到零污染;对功能性组件也只需要使用几个简单的注解进行标记,完全不会破坏原有结构,反而能将组件结构进一步简化。这就使得基于 Spring Framework 开发应用程序时结构清晰、简洁优雅。
-
(2)控制反转:IOC——Inversion of Control,翻转资源获取方向。把自己创建资源、向环境索取资源变成环境将资源准备好,我们享受资源注入。
-
(3)面向切面编程:AOP——Aspect Oriented Programming,在不修改源代码的基础上增强代码功能。面向对象是纵向优化,优化的是从上往下执行的代码,而面向切面是横向优化,可以在不改变原有代码的基础上对原有的代码进行功能的扩展。
-
(4)容器:Spring IOC 是一个容器,因为它包含并且管理组件对象的生命周期。组件享受到了容器化的管理,替程序员屏蔽了组件创建过程中的大量细节,极大的降低了使用门槛,大幅度提高了开发效率。
-
(5)组件化:Spring 实现了使用简单的组件配置组合成一个复杂的应用。在 Spring 中可以使用 XML和 Java 注解组合这些对象。这使得我们可以基于一个个功能明确、边界清晰的组件有条不紊的搭建超大型复杂应用系统。
-
(6)声明式:很多以前需要编写代码才能实现的功能,现在只需要声明需求即可由框架代为实现。编程式指的是自己编写代码完成功能,例如以前的事务控制,都需要手动编写代码完成事务的开启、提交、回滚。而声明式则可以将这一工作交由框架来实现,换句话说,现在想要实现事务就只需要跟Spring声明一声即可。
-
(7)一站式:在 IOC 和 AOP 的基础上可以整合各种企业应用的开源框架和优秀的第三方类库。而且Spring 旗下的项目已经覆盖了广泛领域,很多方面的功能性需求可以在 Spring Framework 的基础上全部使用 Spring 来实现。
五大功能模块
-
(1)Core Container 核心容器,在 Spring 环境下使用任何功能都必须基于 IOC 容器。
-
(2)AOP&Aspects 面向切面编程
-
(3)Testing 提供了对 junit 或 TestNG 测试框架的整合。
-
(4)Data Access/Integration 提供了对数据访问/集成的功能。DI依赖注入,可以理解为IOC思想的一种具体实现,通俗易懂的作用就是为Spring容器中的属性进行赋值。
-
(5)Spring MVC 提供了面向Web应用程序的集成功能。
SpringIOC容器
Spring对于IOC容器的实现
-
(1)BeanFactory :这是 IOC 容器的基本实现,是 Spring 内部使用的接口。面向 Spring 本身,不提供给开发人员使用。
-
(2)ApplicationContext:BeanFactory 的子接口,提供了更多高级特性。面向 Spring 的使用者,几乎所有场合都使用ApplicationContext 而不是底层的 BeanFactory。主要实现类如下:
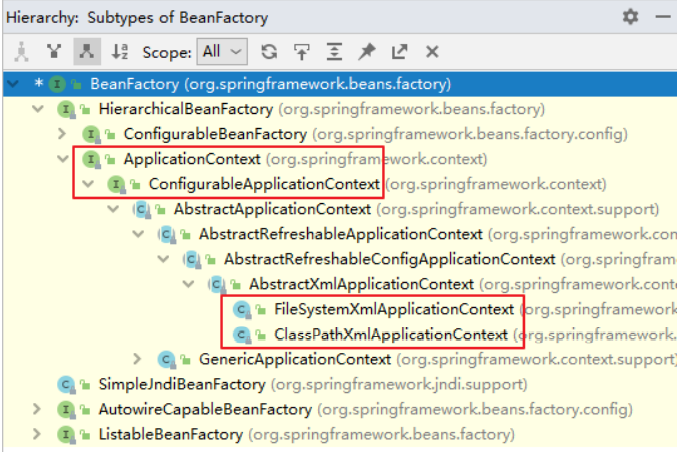
| 类型名 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| ClassPathXmlApplicationContext | 通过读取类路径下的 XML 格式的配置文件创建 IOC 容器对象 |
| FileSystemXmlApplicationContext | 通过文件系统路径读取 XML 格式的配置文件创建 IOC 容器对象(不常用) |
| ConfigurableApplicationContext | ApplicationContext 的子接口,包含一些扩展方法refresh() 和 close() ,让 ApplicationContext 具有启动、关闭和刷新上下文的能力。 |
| WebApplicationContext | 专门为 Web 应用准备,基于 Web 环境创建 IOC 容器对象,并将对象引入存入 ServletContext 域中。 |
基于XML管理Bean
获取Bean的三种方式
-
注意:被Spring IOC容器所管理的bean,可以通过其bena对象的父类或接口类型来获取
-
applicationContext.xml文件
<bean id="userController" class="com.codestars.controller.UserController"/>
- 测试类
// 通过bean的唯一标志id来获取
UserController userController1 = (UserController) ac.getBean("userController");
System.out.println("userController1 = " + userController1);
// 通过类型来获取(最常用)
UserController userController2 = ac.getBean(UserController.class);
System.out.println("userController2 = " + userController2);
// 通过id + 类型来获取
UserController userController3 = ac.getBean("userController", UserController.class);
System.out.println("userController3 = " + userController3);
DI依赖注入的2种方式
- set/get方式
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
<property name="age" value="15"></property>
</bean>
- 构造器方式
<bean id="user2" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="李四"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="18"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
字面量赋值
基本数据类型、包装数据类型、String类型这种看到什么就代表什么的值成为字面量。进行以来依赖注入时,字面量使用value赋值。
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="张三"></property>
</bean>
为属性赋值为null
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="name">
<null/>
</property>
</bean>
当遇到xml实体时的2种处理方案
-
使用xml实体对应的实体符号,例如大于号变成>,小于号变成<等
-
使用CDATA节
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="name">
<value><![CDATA[><><><><><><><]]></value>
</property>
</bean>
为类类型的属性赋值
引用外部已声明的bean
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="cat" ref="myCat"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="myCat" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
使用内部bean(内部bean无法在外部通过IOC容器获取)
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="cat">
<bean class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
</property>
</bean>
为数组类型赋值
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="catArr">
<array>
<!-- 注意:字面量使用value标签,类变量可以考虑内部bean,也可以考虑外部引用 -->
<!-- 赋值3个内部bean -->
<bean class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<!-- 外部引用3个bean -->
<ref bean="cat1"></ref>
<ref bean="cat2"></ref>
<ref bean="cat3"></ref>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="cat1" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="cat2" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="cat3" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
为List集合属性赋值
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="integerList">
<list>
<!-- 由于是存储字面量的List,所以使用value标签 -->
<value>12</value>
<value>33</value>
<value>22</value>
<value>141</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
为Map集合属性赋值
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="map">
<!-- 这个map是 <String, Cat> 类型的 -->
<map>
<entry key="catOne" value-ref="cat1"></entry>
<entry key="catTwo" value-ref="cat2"></entry>
<entry key="catThree" value-ref="cat3"></entry>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="cat1" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="cat2" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<bean id="cat3" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
创建集合、数组、Map类型的bean并引用
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="map" ref="catMap"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="cat1" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
<util:map id="catMap">
<entry key="catOne">
<!-- 使用内部bean -->
<bean class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
</entry>
<entry key="catTwo" value-ref="cat1"></entry>
</util:map>
命名空间p(了解)
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User" p:age="15" p:name="张三" p:integerList-ref="integerList"></bean>
<util:list id="integerList">
<value>13</value>
<value>11</value>
<value>44</value>
<value>66</value>
</util:list>
引入外部配置文件
<!-- 引入外部properties配置文件,引入后可通过${key}的方式获取 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User">
<property name="strArr">
<array>
<value>${jdbc.driver}</value>
<value>${jdbc.url}</value>
<value>${jdbc.username}</value>
<value>${jdbc.password}</value>
</array>
</property>
</bean>
bean的作用域
-
通过修改bean标签的scope属性调整
-
默认为singleton 单例模式,也可以修改为prototype多例模式
-
在Web容器当中,还会有另外2个作用域
- request 一个请求内有效
- session 一个会话内有效
bean的生命周期
-
(1)bean对象创建(调用无参构造器)、实例化
-
(2)给bean对象设置属性、依赖注入
-
(3)bean对象初始化之前操作(由bean的后置处理器负责)
-
(4)bean对象初始化(需在配置bean时指定初始化方法)、初始化
-
(5)bean对象初始化之后操作(由bean的后置处理器负责)
-
(6)bean对象就绪可以使用、使用状态
-
(7)bean对象销毁(需在配置bean时指定销毁方法)、只有当关闭IOC容器时才会销毁
-
(8)IOC容器关闭、使用ConfigurableApplicationContext调用close()方法可以关闭IOC容器
后置处理器BeanPostProcessor
-
可以在对象进行初始化之前以及初始化之后做一些事情(对所有Spring容器中的bean都有效)
-
创建一个类实现该接口
public class PostProcessorTest implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象实例化之前");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("对象实例化后");
return bean;
}
}
- 在xml文件中配置
<bean class="com.codestars.PostProcessorTest"></bean>
FactoryBean(以后spring整合mybatis时,Mybatis就提供了一个FactoryBean)
-
获取该FactoryBean 就相当于获取一个其getObject()方法返回值类型的实例
-
创建一个类,实现该接口
public class UserFactory implements FactoryBean<User> {
@Override
public User getObject() throws Exception {
return new User();
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return User.class;
}
/**
* 是否为单例,指的就是获取的实例是否为单例。
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
- 在配置文件中进行配置
<!-- 通过getBean("user1") 得到的Bean对象类型就是User类型 -->
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.factory.UserFactory"></bean>
自动装配
基于XML的自动装配byType 和 byName(不常用)
-
byType : 根据类型自动装配。byName:根据bean的唯一标志与属性名称自动装配
-
为一个bean配置了自动装配后,则会按照自动装配的规则将该bean中的所有非字面量
-
xml配置文件
<bean id="user1" class="com.codestars.pojo.User" autowire="byName"></bean>
<bean id="user2" class="com.codestars.pojo.User" autowire="byType"></bean>
<bean id="isNullCat" class="com.codestars.pojo.Cat"></bean>
基于注解管理Bean
基于注解管理bean的4个注解以及配置包扫描
- 用于标识需要被SpringIOC容器所管理的注解,这四个注解的作用都是一样的,只是不同的名称有利于我们程序员开发。
@Controller 标识为一个控制层的组件
@Service 标识为一个业务层的组件
@Repository 标识为一个持久层的组件
@Component 标识为一个组件(当如上3个都不是时)
- 通过注解扫描的方式,bean的id默认为类名的小驼峰。
扫描组件的3种方式
- 最基础的注解扫描
<!-- 这里表示扫描com.codestars这个包及其自包下的所有类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars" />
- 排除不需要扫描的注解
<!-- 这里表示扫描com.codestars这个包及其自包下的所有类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars">
<!-- type:annotation 按照注解排除不需要加载到IOC容器的类 -->
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
<!-- type:assignable 按照类型排除 -->
<context:exclude-filter type="assignable" expression="com.codestars.controller.UserController" />
</context:component-scan>
- 添加需要扫描的注解,需要配合use-default-filters="false"
<!-- 这里表示扫描com.codestars这个包及其自包下的所有类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars" use-default-filters="false">
<!-- type:annotation 按照注解添加需要加载到IOC容器的类 -->
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller" />
<!-- type:assignable 按照类型扫描 -->
<context:include-filter type="assignable" expression="com.codestars.service.impl.UserServiceImpl" />
</context:component-scan>
基于注解的自动装配
-
在被Spring管理的组件中使用
@Autowired作用于成员变量、set方法、构造器上均可以完成自动注入 -
@Autowired的注入原理:先使用byType的方式,若容器中包含有多个同类型的bean,则会使用byName的方式获取,若仍然没有获取到,则抛出异常。 -
有一个注解:
@Qualifier可以标识byType获取组件时使用的beanId
SpringAOP
什么是AOP,OOP
-
AOP : Aspect Oriented Programming 面向切面编程,采用的是横向拓展机制,可以在不影响原有功能实现的基础上,完成非入侵式的功能扩展。
-
OOP:Object Oriented Programming 面向对象编程,采用的是纵向继承极致,当我们需要进行代码的重用时,需要将被重用的代码纵向抽取,无法解决横向扩展的问题。例如一个计算器功能,我们想要在计算的前后添加上日志功能,通过面向对象的方法就无法解决。
静态代理、动态代理的区别
- 用生活中的例子来理解代理模式
例如我们的一个普通的饮水机,我们想要让饮水机具备水过滤的功能,因此我们将饮水机进行了改装,在不影响原有功能的情况下,添加了过滤功能。之后我们使用的时候就只能使用带过滤功能的饮水机。
使用计算器功能完成一个静态代理
Calculate 计算器接口
public interface Calculate {
Integer add(int a, int b);
Integer sub(int a, int b);
Integer mul(int a, int b);
Integer div(int a, int b);
}
CalculateImpl 计算器实现类
public class CalculateImpl implements Calculate {
@Override
public Integer add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
@Override
public Integer sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
@Override
public Integer mul(int a, int b) {
return a * b;
}
@Override
public Integer div(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}
}
思考一下,这个时候如果我们想要增加一些非核心代码应该怎么办?
-
难道在计算器实现类中的每个方法的前后都添加这些非核心代码吗?
-
这么做的弊端有如下几个:
(1)会影响程序员开发核心代码,应该在开发核心代码时,还要考虑非核心代码,比如日志应该如何添加等问题。
(2)会造成大量的重复代码,形成代码的冗余,不便于管理。
编写一个静态代理类来完成功能的扩展
public class CalculateImplProxy implements Calculate{
private CalculateImpl calculateImpl = new CalculateImpl();
@Override
public Integer add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:add" + "参数为:" + a + " ," + b) ;
Integer result = calculateImpl.add(a, b);
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:add,执行结果为: " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public Integer sub(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:sub" + "参数为:" + a + " ," + b) ;
Integer result = calculateImpl.sub(a, b);
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:sub,执行结果为: " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public Integer mul(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:mul" + "参数为:" + a + " ," + b) ;
Integer result = calculateImpl.mul(a, b);
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:mul,执行结果为: " + result);
return result;
}
@Override
public Integer div(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:div" + "参数为:" + a + " ," + b) ;
Integer result = calculateImpl.div(a, b);
System.out.println("日志功能,当前执行的方法是:div,执行结果为: " + result);
return result;
}
}
因此再使用的时候必须使用代理对象
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculate calculate = new CalculateImplProxy();
calculate.add(5, 2);
calculate.sub(3, 2);
calculate.mul(2, 2);
calculate.div(5, 2);
}
}
静态代理的弊端
-
静态代理时,一个代理类只能对应一个目标类,因此一旦有多个类都需要被代理时,那么就得编写多个代理类
-
并且如果有多个需要被代理的类,想要扩展的都是同样的功能,那不就依然造成代码的冗余了吗?
在如上计算器的基础上使用JDK动态代理完成计算器代理功能
public class ProxyFactory {
public static Object getProxyObject(Object target) {
/**
* ClassLoader loader, 由于代理类需要被动态生成,因此需要一个类加载器
* Class<?>[] interfaces, 想想我们刚刚写的静态代理,代理类需要跟目标类实现一样的接口
* InvocationHandler h , 进行对目标对象功能的增强处理
*/
ClassLoader classLoader = ProxyFactory.class.getClassLoader();
Class<?>[] interfaces = target.getClass().getInterfaces();
InvocationHandler invocationHandler = new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 前置通知
System.out.println("增强方法:前置通知,运行的方法为:" + method.getName() + " 参数列表为:" + Arrays.toString(args));
// 代理类,执行的依然是目标类的方法。为什么呢?代理类就是为了扩展目标类的方法,实际上还是使用的目标类的方法
Object resultObj = method.invoke(target, args);
// 方法有返回值的通知
System.out.println("方法正常运行完毕,运行的结果为:" + resultObj);
// 结果一定要返回去,为什么呢? 既然是扩展原有的目标类的方法,那么结果肯定不能变。
return resultObj;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 异常通知
System.out.println("增强方法:异常通知");
} finally {
// 后置通知
System.out.println("增强方法:后置通知");
}
return null;
}
};
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(classLoader, interfaces, invocationHandler);
}
}
AOP中的几个概念(7个,重要)
-
横切关注点(需要抽取的非核心代码,理解为刚刚计算器功能中的日志代码)
-
切面(将横切关注点中的代码进行抽取,抽取后放到一个类中,该类就是一个切面类)
-
通知(切面类中的一个个存放横切关注点代码的方法)
-
连接点(当前的通知需要连接到哪个类上的哪个方法?需要连接到的地方就称之为连接点)
-
切入点(其实就是连接点的具体表现形式,通过切入点表达式来表示需要连接的点)
-
代理(代理对象)
-
目标(需要扩展功能的被代理对象)
SpringAOP使用的步骤
将目标类和切面类都交由SpringIOC容器管理
-
可以通过注解、或者XML的方式交由IOC容器管理
-
一个类想要成为切面类,可以通过
@Aspect注解标识为一个切面类
将横切关注点的代码放在切面类中的通知方法中
// 定义一个全局切入点,大家可以一起使用
@Pointcut("execution(* com.codestars.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void pointCut(){}
// 定义不同的通知
@Before("pointCut()")
@After("pointCut()")
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()",returning = "result")
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "ex")
演示基于注解的AOP
添加SpringIOC、SpringAOP、spring-aspects的依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-aspects会帮我们传递过来aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/junit/junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
在resources路径下添加spring配置文件
<!-- 这里表示扫描com.codestars这个包及其自包下的所有类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 开启注解功能的AOP -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
创建一个切面类(除了切入点表达式,还能使用@annotation)
# 用@annotation,MyLog是一个注解,这样会从spring容器中拦截@MyLog注解
@AfterReturning(value = "@annotation(log)",returning = "res")
public void afterReturningAdvice(JoinPoint point, MyLog log, Object res){
@Component
@Aspect
public class LoggerAspect {
/**
* 定义全局切入点,用于找到连接点
* 完整格式为: public int com.codestars.service.impl.UserServiceImpl.save(这里可以写参数列表,写类型即可);
* public int 可以简化为 *
* 包名 可以简化为 *
* 方法名 可以简化为 *
* 参数列表 可以简化为 ..
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.codestars.service.impl.*.*(..))")
public void pointCut(){}
/**
* 前置通知,方法执行前执行
* @param joinPoint 连接点信息
*/
@Before("pointCut()")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("前置日志通知,方法执行前调用,当前执行的方法为:" + signature.getName());
}
/**
* 后置通知,在方法完毕后执行,相当于finally中的代码
* @param joinPoint 连接点信息
*/
@After("pointCut()")
public void after(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("后置通知,finally中执行的代码,当前执行的方法为:" + signature.getName());
}
/**
* 方法正常执行并为抛出异常时执行,可以获取到方法的返回值
* @param joinPoint
* @param result
*/
@AfterReturning(value = "pointCut()",returning = "result")
public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println("方法执行未抛出异常,执行的返回结果为:" + result);
}
/**
* 异常通知:方法抛出异常时执行
* @param joinPoint
* @param ex
*/
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointCut()",throwing = "ex")
public void AfterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("异常通知,当前的异常为: " + ex);
}
@Around(value = "pointCut()")
public Object aRound(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) {
Object resultObj = null;
try {
// 环绕:前置通知
System.out.println("环绕:前置通知");
// 方法执行
resultObj = proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
// 环绕:后置通知
System.out.println("环绕:后置通知");
} catch (Throwable e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("环绕:异常通知,当前异常为:" + e);
} finally {
System.out.println("环绕:后置通知,方法执行完毕");
}
// 一定要将目标对象执行方法的结果返回
return resultObj;
}
}
多个切面类的优先级
-
默认都为Integer的最大值
-
通过修改order属性(可以在切面类上使用@Order注解修改)
测试
ApplicationContext ioc = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-annoation.xml");
UserService userService = ioc.getBean(UserService.class);
userService.save();
基于XML的AOP配置(xml文件)
<!-- 这里表示扫描com.codestars这个包及其自包下的所有类 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars"></context:component-scan>
<aop:config>
<!-- 定义全局切入点表达式 -->
<aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.codestars.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<!-- 配置一个切面类 -->
<aop:aspect ref="loggerAspect">
<!-- 指定各个通知的方法名 -->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="pointCut"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="pointCut"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" returning="result" pointcut-ref="pointCut"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterReturning" throwing="ex" pointcut-ref="pointCut"/>
<aop:around method="aRound" pointcut-ref="pointCut"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
基于注解的AOP完成声明式事物处理
引入IOC、AOP、ORM、TX、数据源等依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- 基于Maven依赖传递性,导入spring-context依赖即可导入当前所需所有jar包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring 持久化层支持jar包 -->
<!-- Spring 在执行持久化层操作、与持久化层技术进行整合过程中,需要使用orm、jdbc、tx三个
jar包 -->
<!-- 导入 orm 包就可以通过 Maven 的依赖传递性把其他两个也导入 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-orm</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring 测试相关 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.16</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.0.31</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
在Spring的xml文件中进行配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 引入外部配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 扫描包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars"/>
<!-- 配置个数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- spring提供的封装jdbc的类 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 这是一个切面类,帮我们完成了事物管理功能 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 开启该功能后,会通过扫描@Transactional 注解来将类中的所有方法或单独的方法作为事物切面类的连接点 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
在需要进行事物管理的类或方法上加注解
-
在类上添加
@Transactional注解:标识该类中所有的方法都为连接点,会对该类中所有方法进行事物管理 -
在方法上添加
@Transactional注解:标识该方法为连接点,将会进行事物管理
事物的传播行为
思考:业务层的一个方法调用业务层的另外一个方法。那么事物应该怎么处理呢?
-
REQUIRED 被调用者与调用者使用同一个事物(默认)
-
REQUIRES_NEW 被调用者会开启一个新的事物(常用)
Spring提供的事物管理常用的配置
<!-- read-only属性:设置只读属性 -->
true:表示只读,false表示可读可写
<!-- rollback-for属性:设置回滚的异常 -->
<!-- no-rollback-for属性:设置不回滚的异常 -->
<!-- isolation属性:设置事务的隔离级别 -->
<!-- timeout属性:设置事务的超时属性 -->
<!-- propagation属性:设置事务的传播行为 -->
使用XML方式完成事物的管理
<!-- 这是一个切面类,帮我们完成了事物管理功能 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<!-- 指定连接点,为查询操作设置只读 -->
<tx:method name="query*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/>
<tx:method name="save*" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="buy*" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="update*" read-only="false"/>
<tx:method name="delete*" read-only="false" />
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.codestars.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointCut"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
SpringMVC的学习
SpringMVC是什么?
SpringMVC是Spring为我们提供的表现层的一站式解决方案。
开发WEB端的一些常见问题
服务器端的请求转发/重定向与浏览器解析路径: /的区别
-
在服务器端解析
/时,路径为:协议+端口号+上下文路径 -
浏览器解析
/时,路径为:协议+端口号
mvc:annotation-driven注解驱动的作用
-
在使用
view-controller标签时 -
在使用
@RequestBody与@RequestResponse时 -
在设置静态静态资源时需要配合
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>使用
RequestMapping注解
value属性
- 表示需要跳转到逻辑视图
method属性
- 表示能够接收到请求方式,RequestMethod枚举类中可以看到能够设置的值
params属性(了解)
-
"param":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数
-
"!param":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带param请求参数
-
"param=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数且param=value
-
"param!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带param请求参数但是param!=value
headers属性(了解)
-
"header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息
-
"!header":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须不能携带header请求头信息
-
"header=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header=value
-
"header!=value":要求请求映射所匹配的请求必须携带header请求头信息且header!=value
-
提示:若当前请求满足@RequestMapping注解的value和method属性,但是不满足headers属性,此时页面显示404错误,即资源未找到
SpringMVC支持ant风格的路径(了解)
-
?:表示任意的单个字符
-
*:表示任意的0个或多个字符
-
**:表示任意层数的任意目录
-
注意:在使用**时,只能使用/**/xxx的方式
支持路径中的占位符(重点),RestFul风格接口
@RequestMapping("/testRest/{id}/{username}")
public String testRest(@PathVariable("id") String id, @PathVariable("username")
String username) {
System.out.println("id:" + id + ",username:" + username);
return "success";
}
获取请求参数
通过原生ServletAPI获取
@RequestMapping("/testParam")
public String testParam(HttpServletRequest request) {
String username = request.getParameter("username");
String password = request.getParameter("password");
System.out.println("username:" + username + ",password:" + password);
return "success";
}
通过控制器方法的形参获取请求参数
@RequestMapping("/testParam")
public String testParam(String username, String password) {
System.out.println("username:" + username + ",password:" + password);
return "success";
}
@RequestParam注解
-
@RequestParam是将请求参数和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
-
@RequestParam注解一共有三个属性:
-
value:指定为形参赋值的请求参数的参数名
-
required:设置是否必须传输此请求参数,默认值为true
-
若设置为true时,则当前请求必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输该请求参数,且没有设置defaultValue属性,则页面报错400:Required String parameter 'xxx' is not present;若设置为false,则当前请求不是必须传输value所指定的请求参数,若没有传输,则注解所标识的形参的值为null
-
defaultValue:不管required属性值为true或false,当value所指定的请求参数没有传输或传输的值为""时,则使用默认值为形参赋值
-
@RequestHeader注解(了解)
-
@RequestHeader是将请求头信息和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
-
@RequestHeader注解一共有三个属性:value、required、defaultValue,用法同@RequestParam
@CookieValue(了解)
-
@CookieValue是将浏览器发送的Cookie信息和控制器方法的形参创建映射关系
-
用法同@RequestParam
通过POJO获取请求参数
- 在控制器的形参列表写上一个POJO类型时,SpringMVC会自动通过request.getParameter()获取参数后封装到该POJO类中
@RequestMapping("/testPojoParam")
public String testParam(User user) {
System.out.println(user);
return "success";
}
解决获取参数的乱码问题
-
一旦使用了reqeust.getParameter()获取了参数之后,再设置编码就没有效果了。而SpringMVC帮助我们封装了Servlet,我们只需要编写控制器,而进入到控制器方法之前,SpringMVC已经帮助我们获取过参数了,此时再设置编码就没有效果了。
-
因此我们需要在SpringMVC的Servlet执行之前进行编码的过滤,这个时候我们可以考虑使用过滤器,虽然我们自己写一个过滤器也可以,但是SpringMVC已经为我们提供了编码过滤器了
在web.xml中配置SpringMVC提供的编码过滤器
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<!-- 如果只配置encoding,则只会设置request.setCharacterEncoding的编码 ,但是不会设置response的响应编码 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<!-- 设置该参数后,还会设置response的响应编码 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
过滤器的过滤源码
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
String encoding = this.getEncoding();
if (encoding != null) {
if (this.isForceRequestEncoding() || request.getCharacterEncoding() == null) {
request.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
if (this.isForceResponseEncoding()) {
response.setCharacterEncoding(encoding);
}
}
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
域对象共享数据
使用ServletAPI向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute("username","张三");
return "index";
}
使用ModelAndView向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/modelAndView")
public ModelAndView testModelAndView() {
ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView();
mv.addObject("username","李四");
mv.setViewName("index");
return mv;
}
使用Model向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/model")
public String testModelAndView(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("username","王五");
return "index";
}
使用map向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/map")
public String testModelAndView(Map<String, Object> map) {
map.put("username","赵流");
return "index";
}
使用ModelMap向request域对象共享数据
@RequestMapping("/modelMap")
public String testModelAndView(ModelMap modelMap) {
// 两种方式都可以
modelMap.put("username","田七");
modelMap.addAttribute("username2","田七2");
return "index";
}
Model、ModelMap、Map的关系
-
SpringMVC在进行视图解析时,最终都会将这些类转换为ModelAndView
-
在DispatcherServlet的第1067行可以看到
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());,最终这些类型都会被转换为ModelAndView
向session域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/session")
public String session(HttpSession session) {
session.setAttribute("username","王八");
return "index";
}
向application域共享数据
@RequestMapping("/application")
public String application(HttpSession session) {
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
servletContext.setAttribute("username","九九");
return "index";
}
SpringMVC的视图
ThymeleafView
-
当控制器中所设置的视图名称没有任何前缀时,此时的视图名称会被SpringMVC中所配置的视图解析器解析,如果视图解析器配置了Thymeleaf解析器,那么将会使用ThymeleafView来解析。
-
可以通过debug DispatcherServlet的render方法查看,1377行
InternalResourceView转发视图
- 当控制器中所设置的视图名称前缀为:
forward:时,将会使用InternalResourceView视图解析器来解析,但是如果使用了该视图解析器跳转视图,会导致页面无法被Thymeleaf模板引擎所渲染。
RedirectView 重定向视图
- 当控制器中所设置的视图名称前缀为:
redirect:时,将会使用RedirectView视图解析器所解析,进行页面的重定向。
视图控制器view-controller
-
当有一些控制器,我们仅仅是用来进行页面跳转时,就可以使用view-controller
-
当SpringMVC中设置任何一个view-controller时,其他控制器中的请求映射将全部失效,此时需要在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中设置开启mvc注解驱动的标签
-
在springmvc.xml文件中进行配置
- 添加注解驱动
- 添加一个view-contoller
<!--当SpringMVC中设置任何一个view-controller时,其他控制器中的请求映射将全部失效
此时需要在SpringMVC的核心配置文件中设置开启mvc注解驱动的标签-->
<mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>
<mvc:view-controller path="/login" view-name="login"/>
RestFul风格
| 操作 | 传统方式 | RESTFul风格 |
|---|---|---|
| 查询单个用户 | getUserById?id=1 | user/1 --> get请求方式 |
| 查询所有用户 | getUserList | user --> get请求方式 |
| 新增用户 | saveUser | user --> post请求方式 |
| 删除用户 | delUser?id=1 | user/1 --> delete请求方式 |
| 更新用户 | updateUser | user --> put请求方式 |
| 更新用户界面 | updateUserPage | user/1 --> put请求方式 |
HiddenHttpMethodFilter过滤器
-
当我们的表单想要提交一个put或者delete请求时,可以使用该过滤器
-
使用方式:
(1)设置form表单的提交方式为post
(2)在form表单中添加一个隐藏的input,设置name为_method,其value值为需要请求的方式 -
配置HiddenHttpMethodFilter过滤器
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
- 页面的使用方式
<form th:action="@{/user/1}" method="post" >
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
<input type="submit" value="点击删除">
</form>
处理AJAX请求,使用axiso
@RequestBody(必须使用Post才有请求体)
-
会获取当前请求的请求体,为当前注解所标识的形参赋值(注意:类型为实体类或Map)
-
使用步骤
(1)导入Jackson依赖
(2)添加注解驱动
(3)在控制器的形参前标志即可
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.12.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--开启mvc的注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
@ResponseBody
-
将控制器方法的返回值作为响应报文直接响应给前端页面
-
使用步骤
(1)导入Jackson依赖
(2)添加注解驱动
(3)在控制器的方法上声明该注解即可
文件上传与下载
文件下载
@RequestMapping("/testDown")
public ResponseEntity<byte[]> testResponseEntity(HttpSession session) throws
IOException {
//获取ServletContext对象
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
//获取服务器中文件的真实路径
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("/static/img/2.jpg");
//创建输入流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(realPath);
//创建字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[is.available()];
//将流读到字节数组中
is.read(bytes);
//创建HttpHeaders对象设置响应头信息
MultiValueMap<String, String> headers = new HttpHeaders();
//设置要下载方式以及下载文件的名字
headers.add("Content-Disposition", "attachment;filename=1.jpg");
//设置响应状态码
HttpStatus statusCode = HttpStatus.OK;
//创建ResponseEntity对象
ResponseEntity<byte[]> responseEntity = new ResponseEntity<>(bytes, headers,
statusCode);
//关闭输入流
is.close();
return responseEntity;
}
文件上传
- 配置文件上传解析器
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"></bean>
- 添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
- 使用示例
### 前端代码
<form th:action="@{/testUpload}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="myFile">
<input type="submit" value="点击上传">
</form>
### 后端代码
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/testUpload")
public String testUpload(MultipartFile myFile, HttpSession session) throws IOException {
// 获取当前得到的文件名
String oldFileName = myFile.getOriginalFilename();
String newFileName = UUID.randomUUID() + oldFileName.substring(oldFileName.lastIndexOf("."));
// 获取到服务器的资源路径
ServletContext servletContext = session.getServletContext();
String realPath = servletContext.getRealPath("/static/img");
File file = new File(realPath);
if (!file.exists()) {
file.mkdirs();
}
// 将文件转存到服务器上
File realFile = new File(realPath + File.separator + newFileName);
myFile.transferTo(realFile);
return "上传成功";
}
拦截器
- 用于拦截控制器方法的执行,如果配置了多个拦截器,将会按照配置的顺序执行preHandle,然后按照逆序执行postHandle和afterCompletion
使用Java代码的方式完成配置
- 编写一个拦截器
public class FirstInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
System.out.println("控制器方法执行之前:FirstInterceptor --> preHandle");
return true;
}
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("控制器方法执行之后:FirstInterceptor --> postHandle");
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("控制器方法执行且视图渲染完毕后:afterCompletion --> afterCompletion");
}
}
- 完成配置
@Configuration
public class MvcExtraConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new FirstInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").excludePathPatterns("/index");
}
}
使用XML的方式进行配置
- 在SpringMVC中配置
<mvc:interceptors>
<mvc:interceptor>
<!-- 可以直接通过bean的方式配置拦截器 <bean></bean>-->
<!-- /* 代表一层上下文路径,/**代表所有路径 -->
<mvc:mapping path="/**"/>
<!-- 排除的路径 -->
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/testRequestEntity"/>
<!-- 通过引用的方式配置拦截器 -->
<ref bean="firstInterceptor"></ref>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>
异常处理器
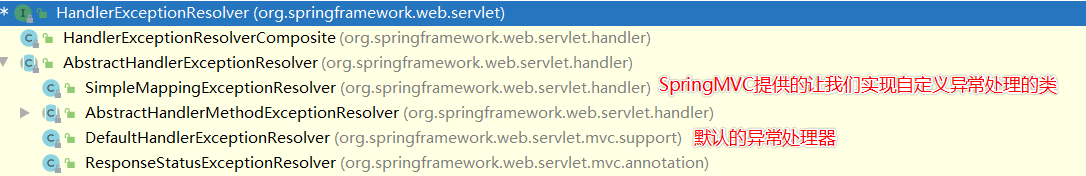
SpringMVC的异常处理机制
- 通过HandlerExceptionResolver进行项目中异常的处理,其大致的关系如下
基于XML的异常处理
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<props>
<!--
properties的键表示处理器方法执行过程中出现的异常
properties的值表示若出现指定异常时,设置一个新的视图名称,跳转到指定页面
-->
<prop key="java.lang.ArithmeticException">error</prop>
</props>
</property>
<!--
exceptionAttribute属性设置一个属性名,将出现的异常信息在请求域中进行共享
-->
<property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex"></property>
</bean>
基于注解的异常处理
//@ControllerAdvice将当前类标识为异常处理的组件
@ControllerAdvice
public class DIYExceptionResolver{
//@ExceptionHandler用于设置所标识方法处理的异常
@ExceptionHandler(ArithmeticException.class)
//ex表示当前请求处理中出现的异常对象
public String handleArithmeticException(Exception ex, Model model){
model.addAttribute("ex", ex);
// 返回逻辑视图
return "error";
}
}
使用纯注解的方式代替SpringMVC配置文件和web.xml文件
在Servlet3.0环境中,容器会在类路径中查找实现javax.servlet.ServletContainerInitializer接口的类,如果找到的话就用它来配置Servlet容器。 Spring提供了这个接口的实现,名为 SpringServletContainerInitializer,这个类反过来又会查找实现WebApplicationInitializer的类并将配置的任务交给它们来完成。Spring3.2引入了一个便利的WebApplicationInitializer基础实现,名为 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer,当我们的类扩展了 AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer并将其部署到Servlet3.0容器的时候,容器会自动发现它,并用它来配置Servlet上下文。
编写一个WebConfig用来代替web.xml文件
import org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter;
import org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
public class WebConfig extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
/**
* 获取Spring容器的配置
*
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringConfig.class};
}
/**
* 获取SpringMVC的配置
*
* @return
*/
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{SpringmvcConfig.class};
}
/**
* @return 指定DispatcherServlet的映射规则,也就是url-pattern
*/
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"};
}
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
CharacterEncodingFilter encodingFilter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
encodingFilter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
encodingFilter.setForceRequestEncoding(true);
HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter = new
HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
return new Filter[]{encodingFilter, hiddenHttpMethodFilter};
}
}
编写SpringmvcConfig代替springmvc配置文件
import com.codestars.interceptor.MyInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine;
import org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.templatemode.TemplateMode;
import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ITemplateResolver;
import org.thymeleaf.templateresolver.ServletContextTemplateResolver;
import java.util.List;
// 1、配置包扫描
@ComponentScan("com.codestars")
// 4、配置注解驱动
@EnableWebMvc
// 标志为一个Spring配置类
@Configuration
public class SpringmvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 3、配置视图控制器
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
}
/**
* 5、配置让tomcat处理静态资源
* @param configurer
*/
@Override
public void configureDefaultServletHandling(DefaultServletHandlerConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.enable();
}
/**
* 6、配置拦截器
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
MyInterceptor myInterceptor = new MyInterceptor();
registry.addInterceptor(myInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/**");
}
/**
* 7、配置异常处理器
* @param resolvers
*/
@Override
public void extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(List<HandlerExceptionResolver> resolvers) {
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver smer1 = new SimpleMappingExceptionResolver();
// 配置需要处理的异常、逻辑视图、共享异常的键
smer1.setMappedHandlerClasses(RuntimeException.class);
smer1.setDefaultErrorView("error");
smer1.setExceptionAttribute("ex");
resolvers.add(smer1);
}
/**
* 8、配置文件上传解析器
* @return
*/
@Bean
public CommonsMultipartResolver commonsMultipartResolver() {
return new CommonsMultipartResolver();
}
//配置生成模板解析器
@Bean
public ITemplateResolver templateResolver() {
WebApplicationContext webApplicationContext =
ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
// ServletContextTemplateResolver需要一个ServletContext作为构造参数,可通过WebApplicationContext 的方法获得
ServletContextTemplateResolver templateResolver = new
ServletContextTemplateResolver(
webApplicationContext.getServletContext());
templateResolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/templates/");
templateResolver.setSuffix(".html");
templateResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
templateResolver.setTemplateMode(TemplateMode.HTML);
return templateResolver;
}
//生成模板引擎并为模板引擎注入模板解析器
@Bean
public SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine(ITemplateResolver
templateResolver) {
SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine = new SpringTemplateEngine();
templateEngine.setTemplateResolver(templateResolver);
return templateEngine;
}
//生成视图解析器并未解析器注入模板引擎
@Bean
public ViewResolver viewResolver(SpringTemplateEngine templateEngine) {
ThymeleafViewResolver viewResolver = new ThymeleafViewResolver();
viewResolver.setCharacterEncoding("UTF-8");
viewResolver.setTemplateEngine(templateEngine);
return viewResolver;
}
}
配置SpringConfig代替spring的配置文件
/**
* 暂时没有内容
*/
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
}
整合SSM的步骤
需要思考的问题
SpringMVC容器的创建时机与Spring的创建时机,SpringMVC的控制层需要访问Spring的业务层该怎么办
-
SpringMVC的中央控制器在配置了
load-on-startup后是跟随Tomcat容器启动时进行启动的 -
SpringMVC的控制层会依赖Spring的管理的业务层,那么Spring的容器就一定要在SpringMVC创建之前进行创建。
-
根据WEB的三大组件我们可以知道他们的执行顺序为: Listener -> Filter -> Servlet
-
因此我们可以在Listener或Filter中来优先创建Spring的IOC容器,那么选择哪个更合适呢?
-
首先是可以通过Filter的初始化方法来完成对SpringIOC容器的初始化,但是过滤器本来应该做的事就是过滤请求,那之后的每一个请求都会经过该过滤器,而该过滤器就啥也不干就放行?这显然不太合理
-
因此我们考虑到了Listener,Listener一共有8个,首当其中我们选择的是ServletContextListener
-
-
因此我们只要配置一个ServletContextListener在我们的Web容器初始化时创建SpringIOC的容器,并且也可以使得创建的速度比SpringMVC的IOC容器更快
-
SpringIOC容器和SpringMVC的IOC容器在创建后都会存放到Application作用域当中,当SpringMVC的IOC容器在进行创建时,会将Spring的容器作为SpringMVC容器的父容器,可以访问父容器中的组件。但是父容器不能访问子容器中的组件。
正式开始整合SSM
创建一个Javaweb项目
(1)引入maven依赖(spring、springmvc、mybaits、thymeleaf、数据库驱动、连接池)
<packaging>war</packaging>
<properties>
<spring.version>5.3.18</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!--springmvc-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Mybatis核心 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis和spring的整合包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.0.9</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit测试 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL驱动,连接数据库 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.16</version>
</dependency>
<!-- log4j日志,mybatis需要 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis的分页插件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId>
<artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId>
<version>5.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志,thymeleaf依赖于slf4j,而logback是slf4j的实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.2.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- ServletAPI -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- ResponseBody与RequestBody依赖于jackson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.12.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 文件上传 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring5和Thymeleaf整合包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf</groupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5</artifactId>
<version>3.0.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- lombok插件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.24</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
配置web.xml文件(2个过滤器、一个Servlet、一个监听器)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!-- 1. 配置编码过滤器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
<init-param>
<param-name>forceEncoding</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- 2.配置表单提交过滤器 -->
<filter>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>HiddenHttpMethodFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- 3. 配置核心Servlet接收所有的请求,不包括.jsp结尾-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!-- 配置springmvc的配置文件 -->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- 在ContextServlet上下文启动时就加载SpringIOC容器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<!-- 配置SpringIOC容器的路径 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
</web-app>
配置springmvc.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 1. 扫描控制层组件 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars.controller"/>
<!-- 2. 配置视图解析器ThymeleafView -->
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver">
<property name="order" value="1"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<property name="templateEngine">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine">
<property name="templateResolver">
<bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver">
<!-- 视图前缀 -->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/>
<!-- 视图后缀 -->
<property name="suffix" value=".html"/>
<property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/>
<property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- 3. 配置注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!-- 4. 当springmvc处理不了时,让tomcat默认servlet来处理 -->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<!-- 5. 配置仅用于页面跳转到view-controller,如果不配置注解驱动,将会只能访问view-controller中配置的处理器(报红不影响) -->
<mvc:view-controller path="/" view-name="index"/>
<!-- 6. 配置文件上传解析器 -->
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver"></bean>
<!-- 7. 配置拦截器 -->
<!--<mvc:interceptors>-->
<!-- <bean class=""></bean>-->
<!-- <mvc:interceptor>-->
<!-- <!– /** 代表所有路径, /* 代表一层路径 –>-->
<!-- <mvc:mapping path="/user/**"/>-->
<!-- <!– 需要排除的路径–>-->
<!-- <mvc:exclude-mapping path=""/>-->
<!-- </mvc:interceptor>-->
<!--</mvc:interceptors>-->
<!-- 8. 配置异常处理器 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<!-- 异常的逻辑视图-->
<property name="defaultErrorView" value="error"></property>
<!-- 定义需要处理的异常 -->
<property name="mappedHandlerClasses">
<array>
<value>java.lang.Throwable</value>
</array>
</property>
<!-- 请求域中错误信息的key -->
<property name="exceptionAttribute" value="ex"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
配置spring.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/util https://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!-- 1. 配置需要加载的配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!-- 2. 扫描包,排除控制层的包,因为控制层需要交给SpringMVC的IOC容器管理 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.codestars">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<!-- 3. 配置数据源 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driver}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
<property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.initialSize}"></property>
<property name="maxActive" value="${jdbc.maxActive}"></property>
<property name="maxWait" value="${jdbc.maxWait}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 4. 整合mybatis第一步:配置SqlSessionFactoryBean,其中的getObject可以获取到SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<!-- 配置mybatis的全局配置文件,如果该配置文件中的属性都在该SqlSessionFactoryBean配置完毕,则该属性可以删除 -->
<!--<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"></property>-->
<!-- 配置数据源 -->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
<!-- 配置别名-->
<property name="typeAliasesPackage" value="com.codestars.pojo"></property>
<!-- 如果xml映射文件与mapper接口不在一个包下,需要配置该属性 -->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:mappers/*.xml"></property>
<!-- 配置分页插件 -->
<property name="plugins">
<array>
<bean class="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<!-- 配置合理化页码 -->
<prop key="reasonable">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</array>
</property>
<!-- 配置SessionSqlFactory的全局setting -->
<property name="configurationProperties">
<props>
<!-- 延迟加载 -->
<prop key="lazyLoadingEnabled">true</prop>
<prop key="aggressiveLazyLoading">false</prop>
<!-- 二级缓存 -->
<prop key="cacheEnabled">true</prop>
<!-- 数据库下划线与实体类驼峰转换 -->
<prop key="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase">true</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
<!--
4. 整合Mybatis第二步:获取第一步配置的SqlSessionFactory拿到所有Mapper接口映射的代理对象,
然后交给SpringIOC容器管理(非常重要)
-->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.codestars.mapper"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 5. 开启基于注解的aop功能 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<!-- 6. 配置声明式事物 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 7. 配置使@Transactional标识的类或方法成为连接点 -->
<tx:annotation-driven/>
<!-- 基于XML的AOP配置-->
<!--<aop:config>-->
<!-- <aop:pointcut id="pointCut" expression="execution(* com.codestars.service.impl.*.*(..))"/>-->
<!-- <aop:aspect ref="">-->
<!-- <aop:before method=""></aop:before>-->
<!-- <aop:after method=""></aop:after>-->
<!-- <aop:after-returning method=""></aop:after-returning>-->
<!-- <aop:after-throwing method=""></aop:after-throwing>-->
<!-- </aop:aspect>-->
<!--</aop:config>-->
</beans>
配置log4j.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE log4j:configuration SYSTEM "log4j.dtd">
<log4j:configuration xmlns:log4j="http://jakarta.apache.org/log4j/">
<appender name="STDOUT" class="org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender">
<param name="Encoding" value="UTF-8"/>
<layout class="org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout">
<param name="ConversionPattern" value="%-5p %d{MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS}
%m (%F:%L) \n"/>
</layout>
</appender>
<logger name="java.sql">
<level value="debug"/>
</logger>
<logger name="org.apache.ibatis">
<level value="info"/>
</logger>
<root>
<level value="debug"/>
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT"/>
</root>
</log4j:configuration>
配置jdbc.properties文件
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=abc123
# 初始连接数量
jdbc.initialSize=5
# 最大连接数量
jdbc.maxActive=10
# 最大等待时间,单位毫秒
jdbc.maxWait=3000
配置mybatis-config.xml文件(可以不需要)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 各个不同配置的顺序
properties?,settings?,typeAliases?,typeHandlers?,objectFactory?,objectWrapperFactory?,
reflectorFactory?,plugins?,environments?,databaseIdProvider?,mappers?
-->
<!-- 引入外部配置文件,从根路径下找 -->
<properties resource="jdbc.properties"/>
<settings>
<!--开启延迟加载功能-->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 关闭该功能后,才能进行按需加载,与lazyLoadingEnabled 配合使用-->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
<!-- 开启二级缓存,作用范围为一个SqssionFactory -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<!-- 配置数据库字段下划线与JAVA实体类的驼峰映射 -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
<!-- 配置别名 -->
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.codestarts.pojo"/>
</typeAliases>
<plugins>
<!--设置分页插件-->
<plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"></plugin>
</plugins>
<!-- 配置一个个的环境,其中主要配置了事务管理的方式和数据源 -->
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<!--
配置采用的事务管理方式,JDBC:编程式事务管理,
MANAGER:啥也不干,让容器来管理事务的整个生命周期
-->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!--
POOLED:采用数据库连接池的方式来获取连接
UNPOOLED:每一个连接都直接通过访问数据库获得
JNDI :上下文数据源引用(了解)
-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value=""/>
<property name="url" value=""/>
<property name="username" value=""/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
<!-- 可以配置多个,自行选择 -->
<environment id="test">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value=""/>
<property name="url" value=""/>
<property name="username" value=""/>
<property name="password" value=""/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<!-- 配置单个的方式mappers/UserMapper.xml代表根路径下的mappers/UserMapper -->
<!--<mapper resource="mappers/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>-->
<!--
配置mapper接口与mapper.xml所在的包,
注意mapper接口和mapper.xml的名字必须一致
注意接口与mapper必须在同一个包下
-->
<package name="com.codestarts.mapper"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
最终项目目录结构




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号