并行处理管道
当进行大规模的数据计算时
会将计算拆分进行并行计算以提升效率
我们这里以cpp进行一个并行计算的模拟 并且分析讲解流程 让大家对其有个了解认识
任务以排序和统计单词计数为例
数据排序例子
1 假设我们有许多数字需要排序(1T=1000G的数据),如果由一台执行排序处理,速度会非常缓慢.那么我们如何将数据划分成多台机器处理? 数据采集
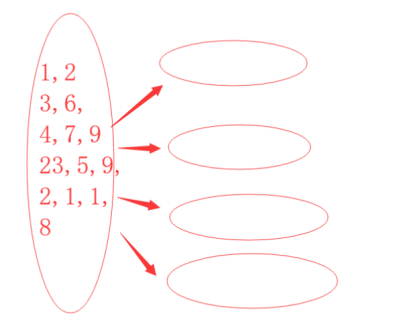
2 将数据根据情况划分成多块,分别排序.效率比一块数据排序肯定提升不少.

3 然后我们进行整合,由于每块都是有序数列,那么只有每块给出最小的数据,对给出 的数据进行比较就可以得出所有数据中最小的数字,将其放入汇总存放处
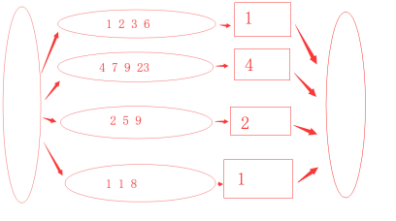


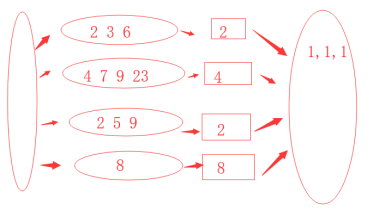

代码

1 #include <thread> 2 #include <deque> 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <algorithm> 5 #include <mutex> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 //定义处理模块的数量 10 const int thread_num = 4; 11 bool start_flag[thread_num]; 12 //数据存放处 13 std::deque<int> g_data_container[thread_num]; 14 15 //多线程处理的互斥锁 16 std::mutex mtx; 17 18 19 //数据收集函数 这里仅仅是简单的创建了示例中的数字 20 void DataCollect() { 21 g_data_container[0] = { 3,1,2,6 }; 22 g_data_container[1] = { 23,4,7,9 }; 23 g_data_container[2] = { 9,5,2 }; 24 g_data_container[3] = { 1,8,1}; 25 //依次开启标记 处理模块开始进行处理 26 for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; ++i) { 27 start_flag[i] = true; 28 } 29 } 30 31 32 void Handle(int i) { 33 int index = i; 34 while (true) { 35 if (start_flag[index]) { 36 //各个模块数据排序 37 std::sort(g_data_container[index].begin(), g_data_container[index].end()); 38 break; 39 } 40 std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100)); 41 } 42 43 } 44 45 bool GetMinData(int& minnum) { 46 bool bret = false; 47 int index = -1; 48 //先将模块中第一个最小的值复制给minnum 再与其他模块比较 获取最小值 49 for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; ++i) { 50 if (!g_data_container[i].empty()) { 51 minnum = g_data_container[i].front(); 52 index = i; 53 break; 54 } 55 } 56 //indx为-1 说明 所有模块中的数据都为空 处理完毕 57 if (index == -1) { 58 return bret; 59 } 60 for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; ++i) { 61 if (!g_data_container[i].empty() && 62 g_data_container[i].front() < minnum) { 63 minnum = g_data_container[i].front(); 64 index = i; 65 } 66 } 67 if (index != -1) { 68 //如果index 有正确的索引值 说明本轮比较获取到最小值 69 bret = true; 70 //最小值返回 则分处理模块中的该值 要弹出 71 g_data_container[index].pop_front(); 72 } 73 return bret; 74 } 75 76 int main() 77 { 78 //创建数据收集线程 79 std::thread data_collect(DataCollect); 80 std::thread t[thread_num]; 81 //创建数据处理线程 82 for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; ++i) { 83 t[i] = std::thread(Handle,i); 84 } 85 86 data_collect.join(); 87 for (int i = 0; i < thread_num; ++i) { 88 t[i].join(); 89 } 90 //汇聚各个模块数据 并显示 91 int i = 0; 92 std::deque<int> result; 93 int min; 94 bool b = true; 95 while (b) { 96 b = GetMinData(min); 97 if(b) 98 result.push_back(min); 99 } 100 101 std::cout << "result is :"; 102 for (auto& e : result) { 103 std::cout << e << " "; 104 } 105 std::cout << std::endl; 106 system("pause"); 107 108 return 0; 109 }
单词出现次数统计类似.示意图如下:
1 单词收集 见连接

作 者: itdef
欢迎转帖 请保持文本完整并注明出处
技术博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/itdef/
B站算法视频题解
https://space.bilibili.com/18508846
qq 151435887
gitee https://gitee.com/def/
欢迎c c++ 算法爱好者 windows驱动爱好者 服务器程序员沟通交流
如果觉得不错,欢迎点赞,你的鼓励就是我的动力


欢迎转帖 请保持文本完整并注明出处
技术博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/itdef/
B站算法视频题解
https://space.bilibili.com/18508846
qq 151435887
gitee https://gitee.com/def/
欢迎c c++ 算法爱好者 windows驱动爱好者 服务器程序员沟通交流
如果觉得不错,欢迎点赞,你的鼓励就是我的动力






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号