AcWing 1067. 精确覆盖问题 DLX
地址 https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/1069/
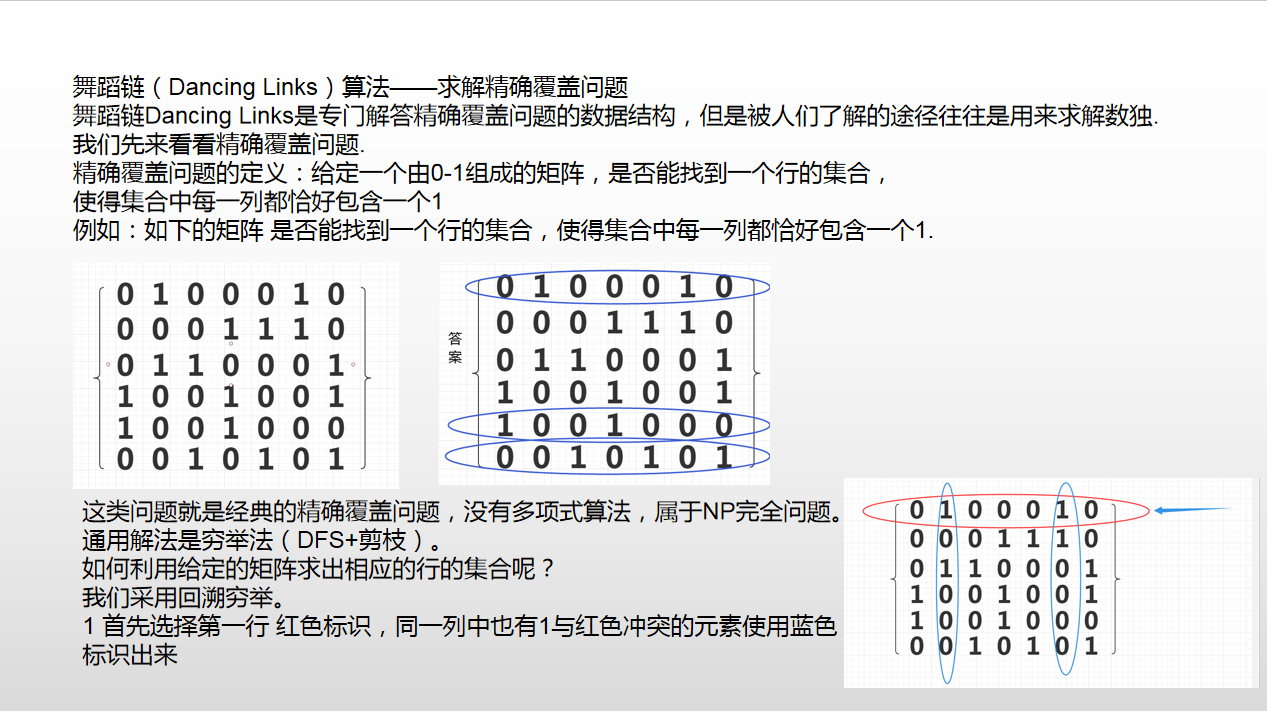
给定一个 N×M 的数字矩阵 A,矩阵中的元素 Ai,j∈{0,1}。
请问,你能否在矩阵中找到一个行的集合,使得这些行中,每一列都有且仅有一个数字 1。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 N 和 M。
接下来 N 行,每行包含 M 个整数(0 或 1),表示完整的数字矩阵。
输出格式
如果能找到满足条件的行的集合,则在一行中依次输出这些行的编号(行编号 1∼N)。
如果方案不唯一,则以任意顺序输出任意方案即可。
否则,输出 No Solution!。
数据范围
1≤N,M≤500,
数据保证矩阵中 1 的数量不超过 5000。
输入样例1:
3 3
0 1 0
0 0 1
1 0 0
输出样例1:
1 2 3
输入样例2:
4 4
0 0 0 1
1 0 0 0
1 1 0 1
0 1 0 0
输出样例2:
No Solution!
自写指针版本 DLX
这里是自己整理重新画图的V2版本 DLX学习心得


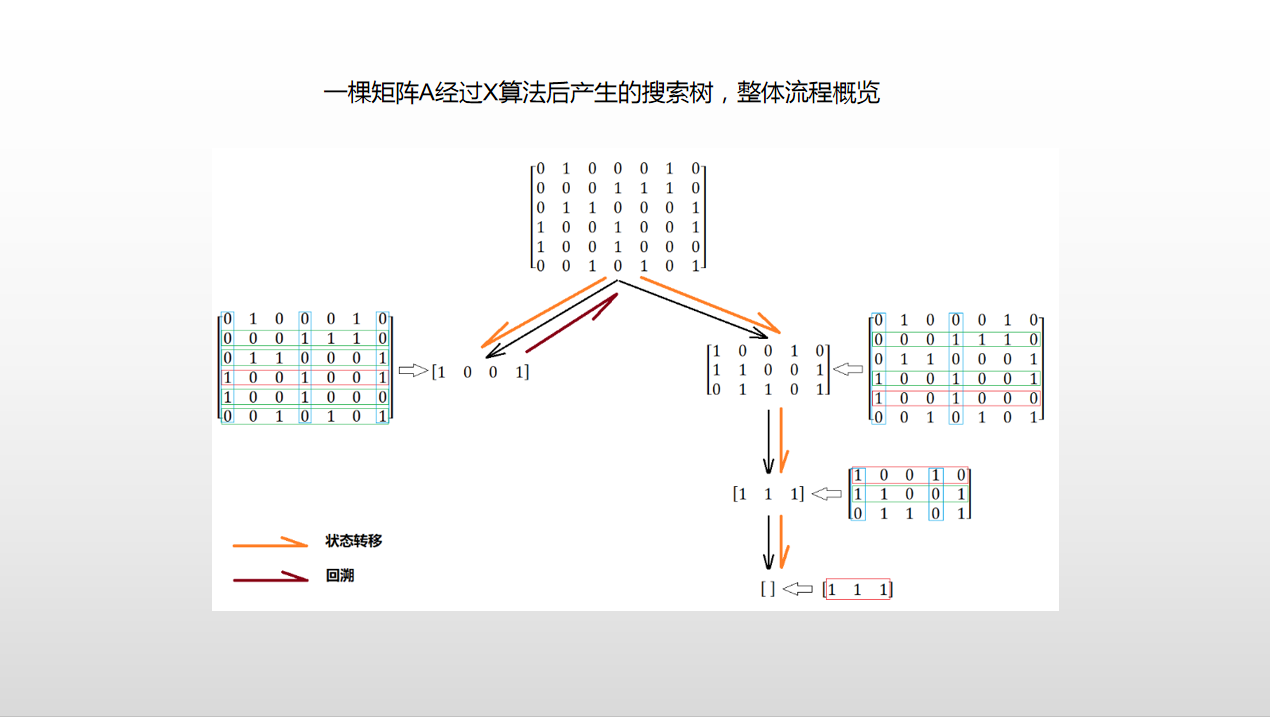
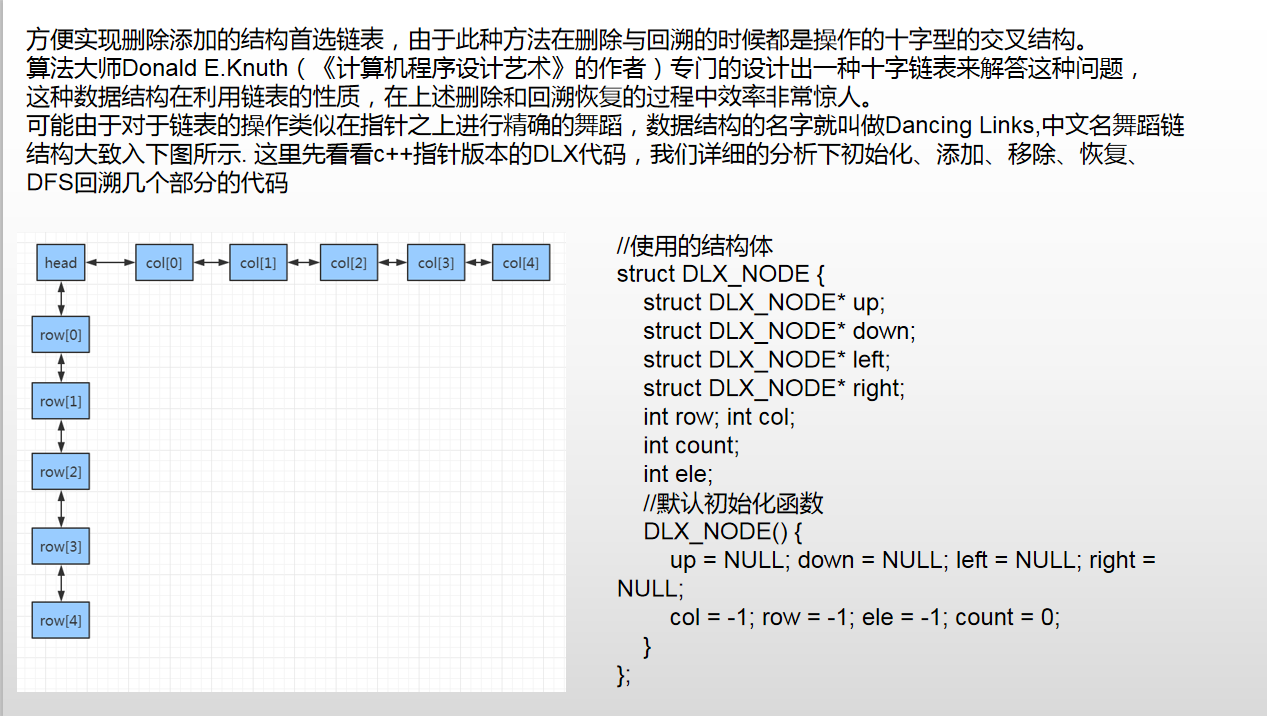
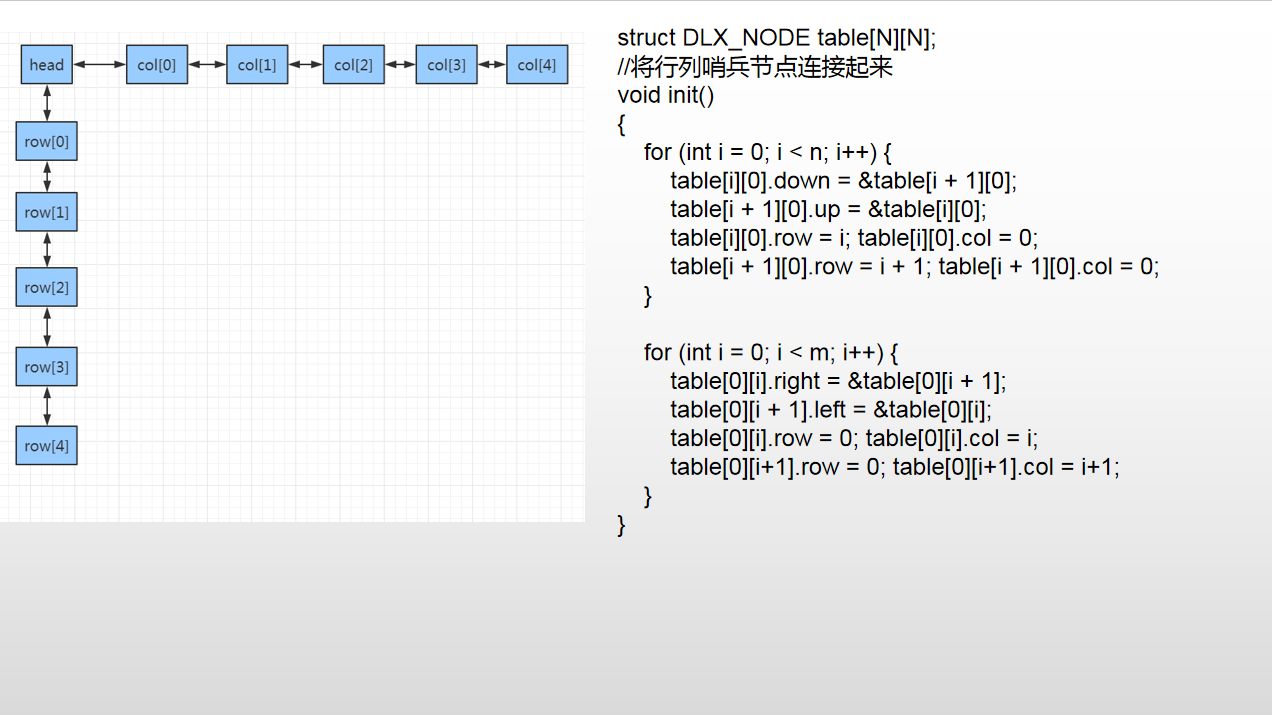
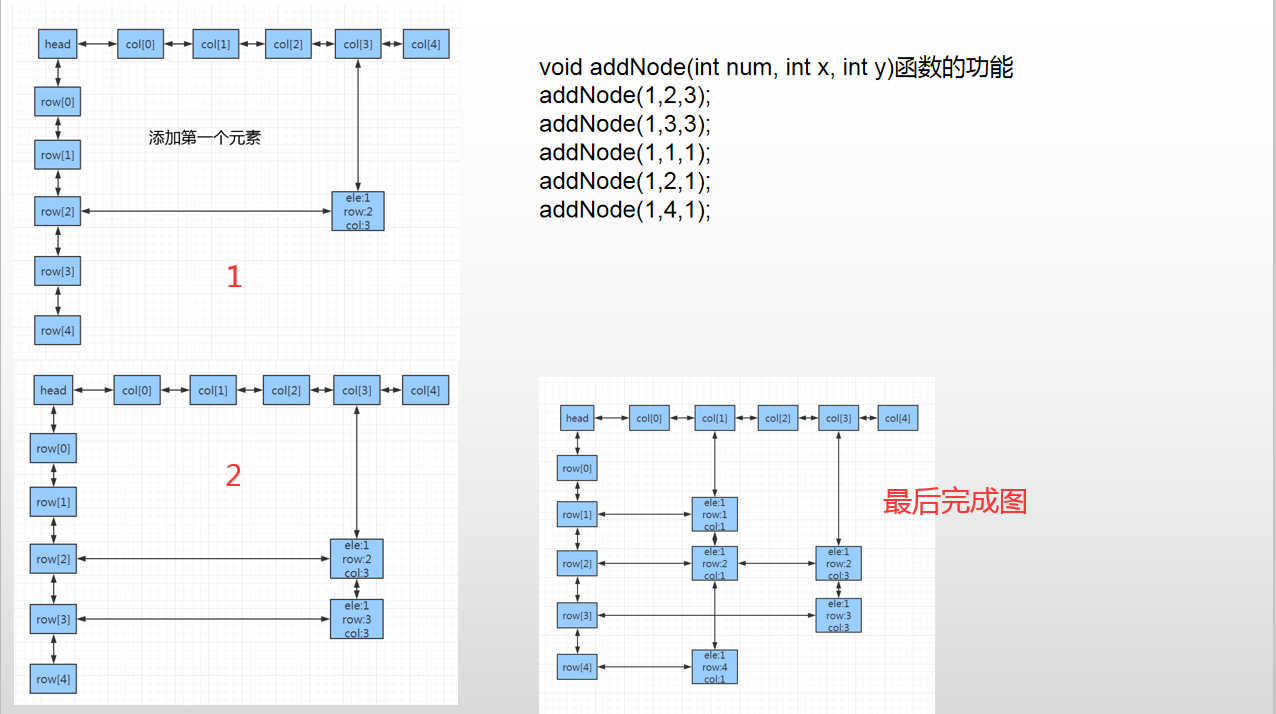
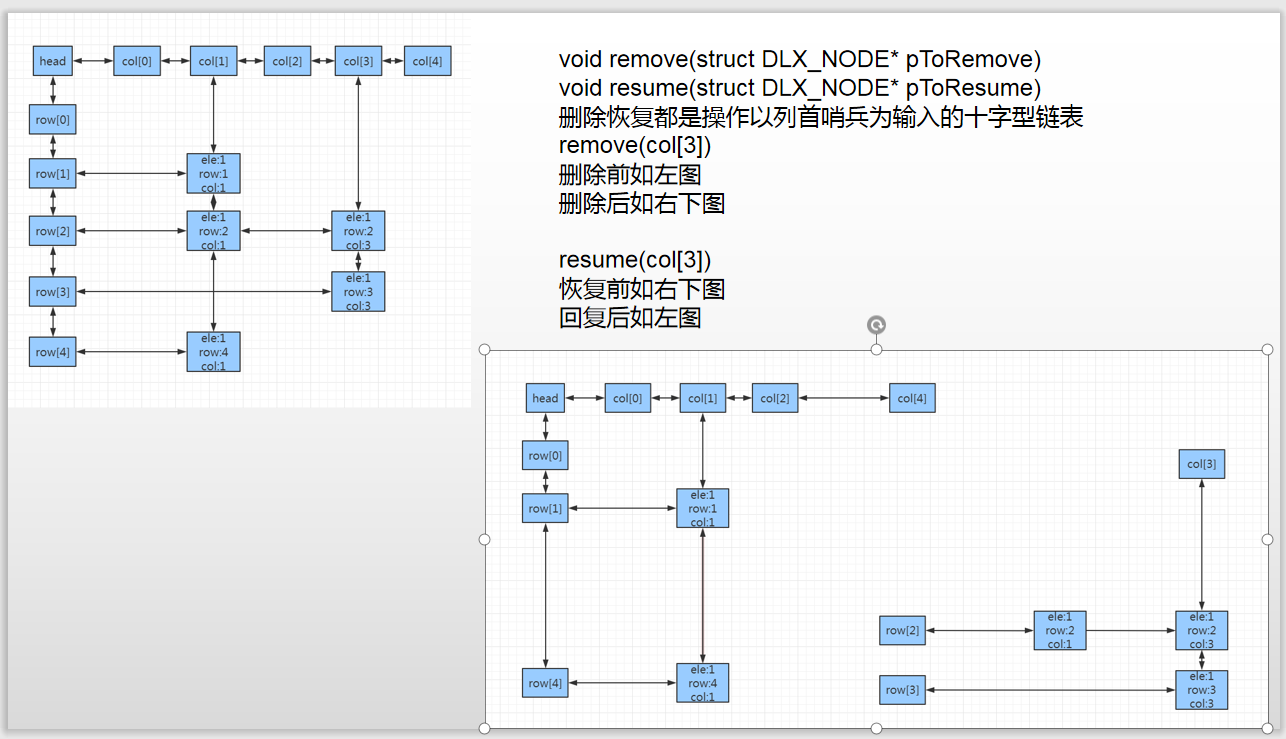

// DLX_2.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。 // #include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <assert.h> using namespace std; const int N = 510; /* 3 3 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 4 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 No Solution! */ struct DLX_NODE { struct DLX_NODE* up; struct DLX_NODE* down; struct DLX_NODE* left; struct DLX_NODE* right; int row; int col; int count; int ele; DLX_NODE() { up = NULL; down = NULL; left = NULL; right = NULL; col = -1; row = -1; ele = -1; count = 0; } }; struct DLX_NODE table[N][N]; int n, m; void init() { for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { table[i][0].down = &table[i + 1][0]; table[i + 1][0].up = &table[i][0]; table[i][0].row = i; table[i][0].col = 0; table[i + 1][0].row = i + 1; table[i + 1][0].col = 0; } for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { table[0][i].right = &table[0][i + 1]; table[0][i + 1].left = &table[0][i]; table[0][i].row = 0; table[0][i].col = i; table[0][i+1].row = 0; table[0][i+1].col = i+1; } } void printDLX() { struct DLX_NODE* p = &table[0][0]; cout << "=================================================>\n"; p = p->right; while (p != NULL) { struct DLX_NODE* pp = p; if (pp->count != 0) { cout << "colBase.count = " << pp->count << endl; } while (pp != NULL) { if (pp->ele == 1) cout << "pp->col = " << pp->col << ". pp->row = " << pp->row << ".pp->ele = " << pp->ele << endl; pp = pp->down; } p = p->right; } cout << endl << endl; p = &table[0][0]; p = p->down; while (p != NULL) { struct DLX_NODE* pp = p; while (pp != NULL) { if (pp->ele == 1) cout << "pp->col = " << pp->col << ". pp>row = " << pp->row << ".pp->ele = " << pp->ele << endl; pp = pp->right; } p = p->down; } cout << endl ; } void FindColInsert(int row,int col) { struct DLX_NODE* p = &table[0][col]; while (p != NULL) { struct DLX_NODE* next = p->down; //找到链表结尾或者 next比当前元素行数更大 P的下面即是插入的位置 if (next == NULL) break; else if (next->row > row) break; else if (next->row == row) { //行列都相同则说明重复插入了 assert(0); } p = next; } assert(p != NULL); //插入 struct DLX_NODE* node = &table[row][col]; node->down = p->down; if (p->down != NULL) p->down->up = node; node->up = p; p->down = node; table[0][col].count++; } void FindRowInsert(int row, int col) { struct DLX_NODE* p = &table[row][0]; while (p != NULL) { struct DLX_NODE* next = p->right; //找到链表结尾或者 next比当前元素列数更大 P的右面即是插入的位置 if (next == NULL) break; else if (next->col > col) break; else if (next->col == col) { //行列都相同则说明重复插入了 assert(0); } p = next; } assert(p != NULL); //插入 struct DLX_NODE* node = &table[row][col]; node->right = p->right; if (p->right != NULL) p->right->left = node; node->left = p; p->right = node; } void addNode(int num, int x, int y) { table[x][y].row = x; table[x][y].col = y; table[x][y].ele = num; //插入列中 FindColInsert(x,y); //插入行中 FindRowInsert(x,y); } void resume(struct DLX_NODE* pToResume) { struct DLX_NODE* pdown = pToResume->down; while (pdown != NULL) { int row = pdown->row; assert(row != -1); struct DLX_NODE* nextResume = &table[row][0]; while (nextResume != NULL) { if (nextResume->col > 0) table[0][nextResume->col].count++; nextResume->up->down = nextResume; if (nextResume->down != NULL) nextResume->down->up = nextResume; nextResume = nextResume->right; } pdown = pdown->down; } if (pToResume->right != NULL) pToResume->right->left = pToResume; pToResume->left->right = pToResume; } void remove(struct DLX_NODE* pToRemove) { if (pToRemove->right != NULL) { pToRemove->right->left = pToRemove->left; } pToRemove->left->right = pToRemove->right; struct DLX_NODE* pdown = pToRemove->down; while (pdown != NULL) { int row = pdown->row; assert(row != -1); struct DLX_NODE* nextRemove = &table[row][0]; while (nextRemove != NULL) { if(nextRemove->col != 0) table[0][nextRemove->col].count--; assert(table[0][nextRemove->col].count >= 0); if (nextRemove->col == pToRemove->col) { nextRemove = nextRemove->right; continue; } if (nextRemove->down != NULL) nextRemove->down->up = nextRemove->up; nextRemove->up->down = nextRemove->down; nextRemove = nextRemove->right; } pdown = pdown->down; } } vector<int> ans; bool dfs() { int noEle = 1; int minCount = 99999; struct DLX_NODE* selectP = NULL; struct DLX_NODE* p = table[0][0].right; if (p == NULL) return true; while (p != NULL) { if (p->count != -1 && p->count < minCount) { minCount = p->count; selectP = p; } p = p->right; } remove(selectP); { p = selectP->down; while (p != NULL) { ans.push_back(p->row); struct DLX_NODE* tmp = table[p->row][0].right; while (tmp != NULL) { if(tmp->col != selectP->col) remove(&table[0][tmp->col]); tmp = tmp->right; } if (dfs()) return true; tmp = table[p->row][0].right; while (tmp != NULL) { if (tmp->col != selectP->col) resume(&table[0][tmp->col]); tmp = tmp->right; } ans.pop_back(); p = p->down; } } resume(selectP); return false; } int main() { cin >> n >> m; init(); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) { int x; cin >> x; if (x) { addNode(x, i, j); } } } //printDLX(); if (dfs()) { for(auto& e:ans) printf("%d ", e); puts(""); } else puts("No Solution!"); return 0; } 作者:itdef 链接:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/26693/ 来源:AcWing 著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
实际使用建议使用Y总模板
使用了链式前向星的十字链表DLX
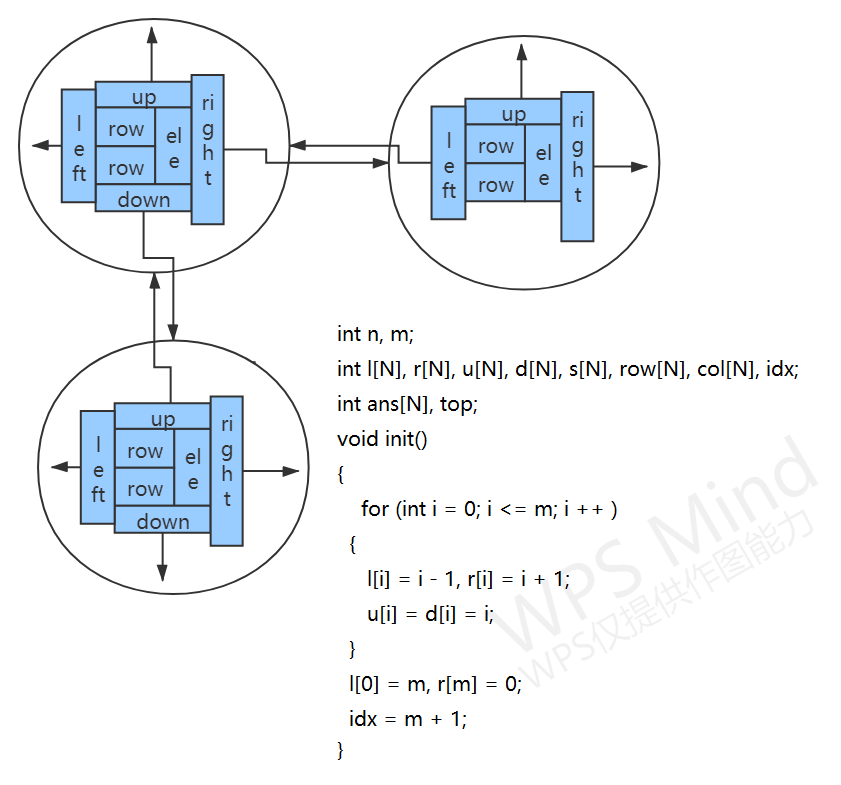

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 const int N = 5510; 8 9 int n, m; 10 int l[N], r[N], u[N], d[N], s[N], row[N], col[N], idx; 11 int ans[N], top; 12 13 void init() 14 { 15 for (int i = 0; i <= m; i ++ ) 16 { 17 l[i] = i - 1, r[i] = i + 1; 18 u[i] = d[i] = i; 19 } 20 l[0] = m, r[m] = 0; 21 idx = m + 1; 22 } 23 24 void add(int& hh, int& tt, int x, int y) 25 { 26 row[idx] = x, col[idx] = y, s[y] ++ ; 27 u[idx] = y, d[idx] = d[y], u[d[y]] = idx, d[y] = idx; 28 r[hh] = l[tt] = idx, r[idx] = tt, l[idx] = hh; 29 tt = idx ++ ; 30 } 31 32 void remove(int p) 33 { 34 r[l[p]] = r[p], l[r[p]] = l[p]; 35 for (int i = d[p]; i != p; i = d[i]) 36 for (int j = r[i]; j != i; j = r[j]) 37 { 38 s[col[j]] -- ; 39 u[d[j]] = u[j], d[u[j]] = d[j]; 40 } 41 } 42 43 void resume(int p) 44 { 45 for (int i = u[p]; i != p; i = u[i]) 46 for (int j = l[i]; j != i; j = l[j]) 47 { 48 u[d[j]] = j, d[u[j]] = j; 49 s[col[j]] ++ ; 50 } 51 r[l[p]] = p, l[r[p]] = p; 52 } 53 54 bool dfs() 55 { 56 if (!r[0]) return true; 57 int p = r[0]; 58 for (int i = r[0]; i; i = r[i]) 59 if (s[i] < s[p]) 60 p = i; 61 remove(p); 62 for (int i = d[p]; i != p; i = d[i]) 63 { 64 ans[ ++ top] = row[i]; 65 for (int j = r[i]; j != i; j = r[j]) remove(col[j]); 66 if (dfs()) return true; 67 for (int j = l[i]; j != i; j = l[j]) resume(col[j]); 68 top -- ; 69 } 70 resume(p); 71 return false; 72 } 73 74 int main() 75 { 76 scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); 77 init(); 78 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) 79 { 80 int hh = idx, tt = idx; 81 for (int j = 1; j <= m; j ++ ) 82 { 83 int x; 84 scanf("%d", &x); 85 if (x) add(hh, tt, i, j); 86 } 87 } 88 89 if (dfs()) 90 { 91 for (int i = 1; i <= top; i ++ ) printf("%d ", ans[i]); 92 puts(""); 93 } 94 else puts("No Solution!"); 95 96 return 0; 97 }
//====================================================
//数独的DLX解答代码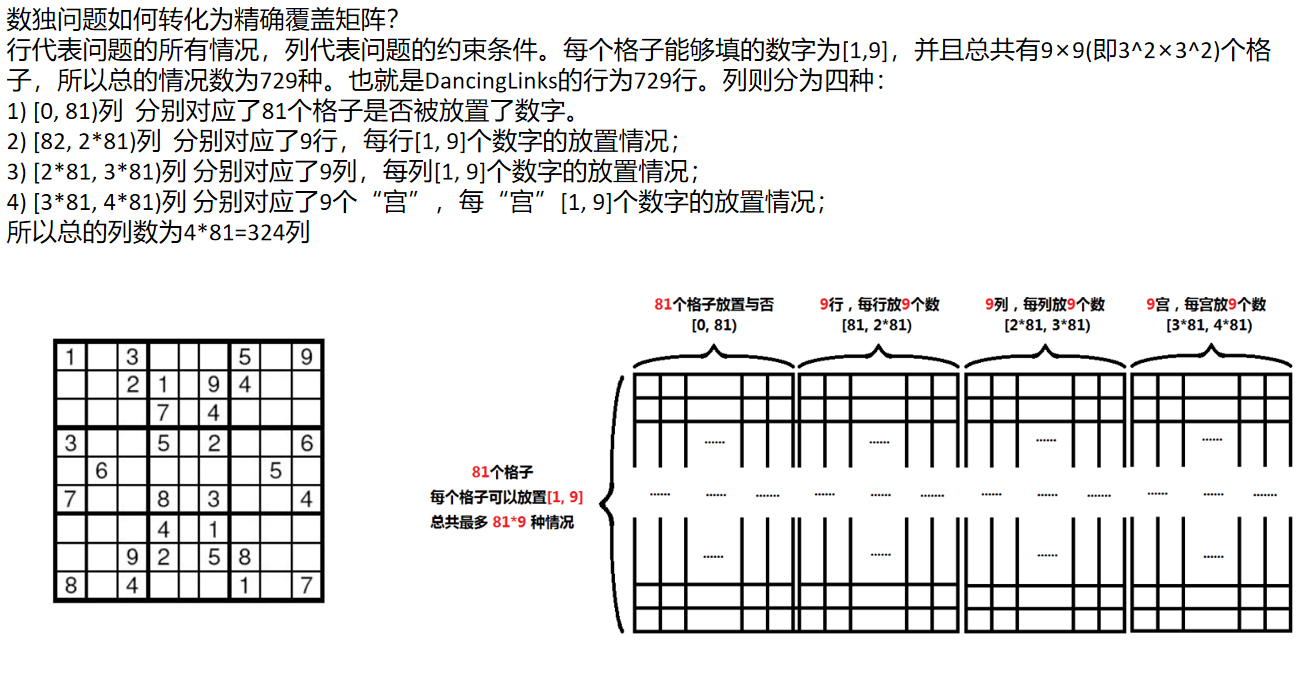
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 20000; int m = 9 * 9 * 4; int u[N], d[N], l[N], r[N], s[N], col[N], row[N], idx; int ans[N], top; struct Op { int x, y; char z; }op[N]; char g[20][9]; char input[90]; void init() { for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++) { l[i] = i - 1, r[i] = i + 1; s[i] = 0; d[i] = u[i] = i; } l[0] = m, r[m] = 0; idx = m + 1; } void add(int& hh, int& tt, int x, int y) { row[idx] = x, col[idx] = y, s[y] ++; u[idx] = y, d[idx] = d[y], u[d[y]] = idx, d[y] = idx; r[hh] = l[tt] = idx, r[idx] = tt, l[idx] = hh; tt = idx++; } void remove(int p) { r[l[p]] = r[p], l[r[p]] = l[p]; for (int i = d[p]; i != p; i = d[i]) for (int j = r[i]; j != i; j = r[j]) { s[col[j]] --; u[d[j]] = u[j], d[u[j]] = d[j]; } } void resume(int p) { for (int i = u[p]; i != p; i = u[i]) for (int j = l[i]; j != i; j = l[j]) { u[d[j]] = j, d[u[j]] = j; s[col[j]] ++; } r[l[p]] = p, l[r[p]] = p; } bool dfs() { if (!r[0]) return true; int p = r[0]; for (int i = r[0]; i; i = r[i]) if (s[i] < s[p]) p = i; remove(p); for (int i = d[p]; i != p; i = d[i]) { ans[++top] = row[i]; for (int j = r[i]; j != i; j = r[j]) remove(col[j]); if (dfs()) return true; for (int j = l[i]; j != i; j = l[j]) resume(col[j]); top--; } resume(p); return false; } int main() { while (~scanf("%s", input)) { if (input[0] == 'e') break; memset(g, 0, sizeof(g[0][0]) * 20 * 9); int ii = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { g[i][j] = input[ii++]; } } init(); for (int i = 0, n = 1; i < 9; i++) for (int j = 0; j < 9; j++) { int a = 0, b = 8; if (g[i][j] != '.') a = b = g[i][j] - '1'; for (int k = a; k <= b; k++, n++) { int hh = idx, tt = idx; op[n] = { i, j, (char)(k + '1') }; add(hh, tt, n, i * 9 + j + 1); add(hh, tt, n, 81 + i * 9 + k + 1); add(hh, tt, n, 81 * 2 + j * 9 + k + 1); add(hh, tt, n, 81 * 3 + (i / 3 * 3 + j / 3) * 9 + k + 1); } } dfs(); for (int i = 1; i <= top; i++) { auto t = op[ans[i]]; g[t.x][t.y] = t.z; } puts(g[0]); //puts(""); } return 0; }
参考链接
https://www.cnblogs.com/ivan-count/p/7355431.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/grenet/p/3145800.html
https://blog.csdn.net/whereisherofrom/article/details/79220897
https://www.luogu.org/blog/ONE-PIECE/qian-tan-dlx 【模板】舞蹈链(DLX)
作 者: itdef
欢迎转帖 请保持文本完整并注明出处
技术博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/itdef/
B站算法视频题解
https://space.bilibili.com/18508846
qq 151435887
gitee https://gitee.com/def/
欢迎c c++ 算法爱好者 windows驱动爱好者 服务器程序员沟通交流
如果觉得不错,欢迎点赞,你的鼓励就是我的动力


欢迎转帖 请保持文本完整并注明出处
技术博客 http://www.cnblogs.com/itdef/
B站算法视频题解
https://space.bilibili.com/18508846
qq 151435887
gitee https://gitee.com/def/
欢迎c c++ 算法爱好者 windows驱动爱好者 服务器程序员沟通交流
如果觉得不错,欢迎点赞,你的鼓励就是我的动力






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号