BeanShell取样器
使用BeanShell取样器自动生成测试所使用的数据,后用json提取器提取生成的数据到变量中,在后续的参数化过程中使用,也可以使用BeanShell后置处理程序保存在参数化文件中,在后续的测试过程中使用。
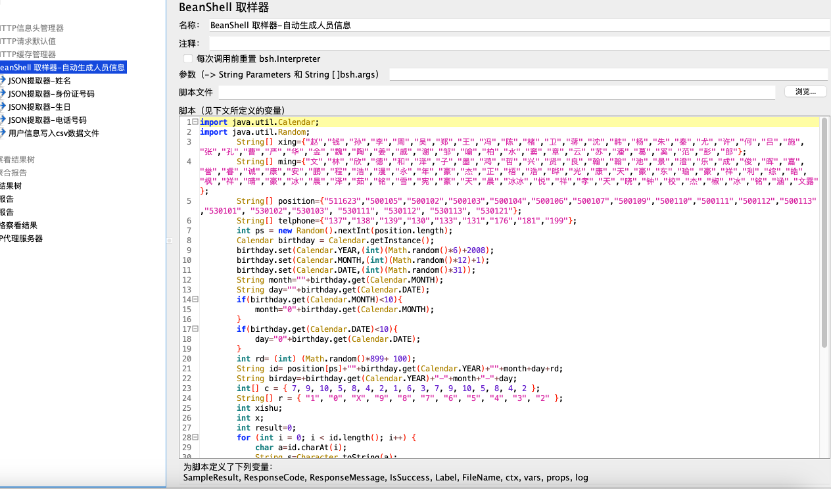
代码示例
import java.util.Calendar; import java.util.Random; String[] xing={"赵","钱","孙","李","周","吴","郑","王","冯","陈","楮","卫","蒋","沈","韩","杨","朱","秦","尤","许","何","吕","施","张","孔","曹","严","华","金","魏","陶","姜","戚","谢","邹","喻","柏","水","窦","章","云","苏","潘","葛","奚","范","彭","郎"}; String[] ming={"文","林","欣","德","和","泽","子","墨","鸿","哲","兴","贤","良","翰","翰","池","景","澄","乐","成","俊","晖","嘉","誉","睿","诚","康","安","鹏","程","浩","漫","永","年","豪","杰","正","梧","浩","晔","光","康","天","豪","东","瑜","豪","祥","利","综","皓","枫","祥","晴","豪","冰","晨","泽","茹","铭","雪","宪","豪","天","晨","冰冰","悦","祥","孝","天","晓","钟","校","杰","椒","冰","铭","涵","文露"}; String[] position={"511623","500105","500102","500103","500104","500106","500107","500109","500110","500111","500112","500113","530101", "530102","530103", "530111", "530112", "530113", "530121"}; String[] telphone={"137","138","139","130","133","131","176","181","199"}; int ps = new Random().nextInt(position.length); Calendar birthday = Calendar.getInstance(); birthday.set(Calendar.YEAR,(int)(Math.random()*6)+2008); birthday.set(Calendar.MONTH,(int)(Math.random()*12)+1); birthday.set(Calendar.DATE,(int)(Math.random()*31)); String month=""+birthday.get(Calendar.MONTH); String day=""+birthday.get(Calendar.DATE); if(birthday.get(Calendar.MONTH)<10){ month="0"+birthday.get(Calendar.MONTH); } if(birthday.get(Calendar.DATE)<10){ day="0"+birthday.get(Calendar.DATE); } int rd= (int) (Math.random()*899+ 100); String id= position[ps]+""+birthday.get(Calendar.YEAR)+""+month+day+rd; String birday=+birthday.get(Calendar.YEAR)+"-"+month+"-"+day; int[] c = { 7, 9, 10, 5, 8, 4, 2, 1, 6, 3, 7, 9, 10, 5, 8, 4, 2 }; String[] r = { "1", "0", "X", "9", "8", "7", "6", "5", "4", "3", "2" }; int xishu; int x; int result=0; for (int i = 0; i < id.length(); i++) { char a=id.charAt(i); String s=Character.toString(a); xishu=Integer.parseInt(s)*c[i]; result+=xishu; } x=result%11; int rdphone= (int) (Math.random()*89999+ 10000); String getid=id+r[x]; int i = (int) (Math.random() * xing.length); int j = (int) (Math.random() * ming.length); int k = (int) (Math.random() * telphone.length); String name=xing[i]+ming[j]; String telphoneid=telphone[k]+rd+rdphone; //SampleResult.setResponseData("{\"name\":\""+name+"\",\"id\":\""+getid+"\",\"getbirday\":\""+birday+"\"}"); //SampleResult.setResponseData("{\"name\":\""+name+"\",\"id\":\""+getid+"\",\"getbirday\":\""+birday+"\"}");// SampleResult.setResponseData("{\"name\":\""+name+"\",\"id\":\""+getid+"\",\"getbirday\":\""+birday+"\",\"telphoneid\":\""+telphoneid+"\"}");
JSON提取器的获取姓名
‘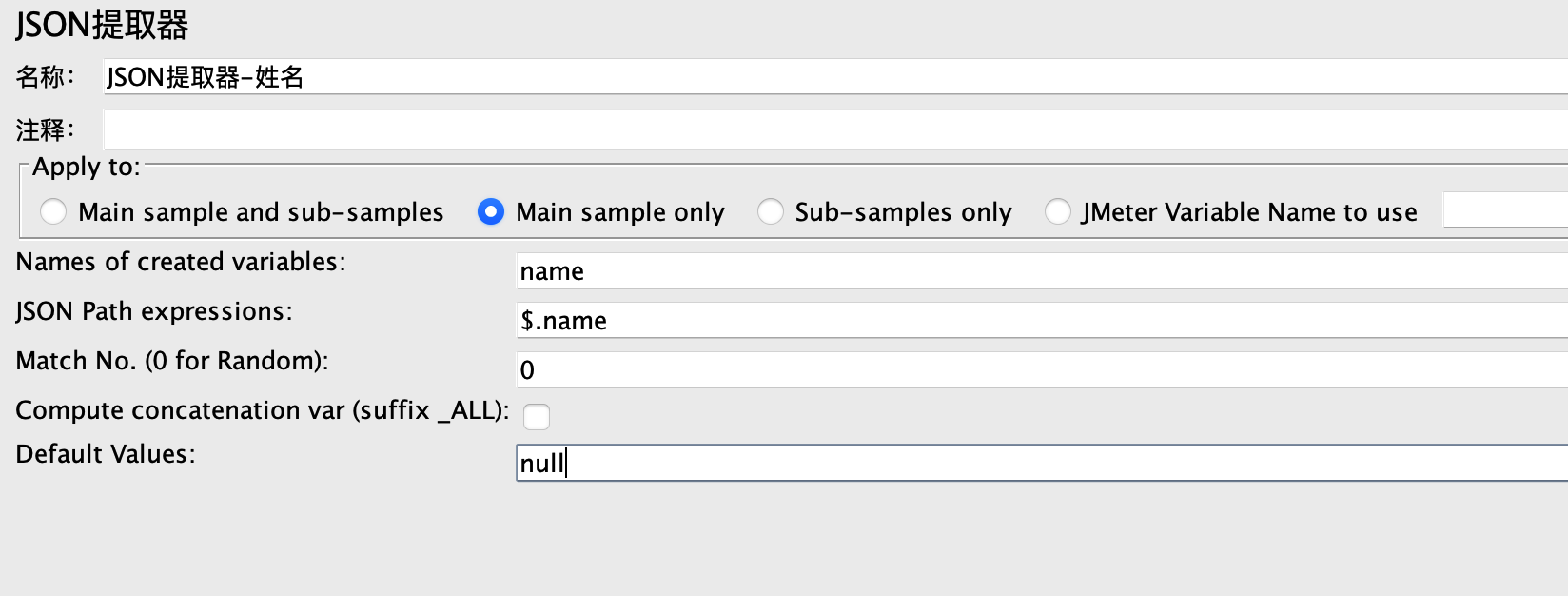
name为变量名名称,后续调用的便利名称
$.name为前置处理程序返回的变量参数名称,为下面代码中返回的第一个参数的名称,下面代码共返回4个参数,分别为姓名name,身份证能号码Id,生日birday,电话号码telphoneid
SampleResult.setResponseData("{\"name\":\""+name+"\",\"id\":\""+getid+"\",\"getbirday\":\""+birday+"\",\"telphoneid\":\""+telphoneid+"\"}");
BeanShell后置处理程序
以下代码就是把jmeter运行过程中的变量值写入D:\\jmx\\app\\userinfo.csv的文件中,代码中的name、namecard,telphoneid分别为三个变量,同时存入参数文件中的,用,号分割开来。
FileWriter fstream = new FileWriter("D:\\jmx\\app\\userinfo.csv",true); BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(fstream); out.write(vars.get("name")+',');//","为了提取多列数据时换列, out.write(vars.get("namecard")+',') out.write(vars.get("telphoneid")+"\n"); out.close(); fstream.close();



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号