Go 语言学习系列(三): 学习 handle an error
我们写代码肯定要做异常处理的. 所以本文介绍 Go 中如何做.
还是找到之前的 code, 粘贴下面的代码到 greetings.go 文件里面去:
package greetings
import (
"errors"
"fmt"
)
// Hello returns a greeting for the named person.
func Hello(name string) (string, error) {
// If no name was given, return an error with a message.
if name == "" {
return "", errors.New("empty name")
}
// If a name was received, return a value that embeds the name
// in a greeting message.
message := fmt.Sprintf("Hi, %v. Welcome!", name)
return message, nil
}
这段代码挺简单的,就不解析了.
然后得修改 hello.go 文件.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"example.com/greetings"
)
func main() {
// Set properties of the predefined Logger, including
// the log entry prefix and a flag to disable printing
// the time, source file, and line number.
log.SetPrefix("greetings: ")
log.SetFlags(0)
// Request a greeting message.
message, err := greetings.Hello("")
// If an error was returned, print it to the console and
// exit the program.
if err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
// If no error was returned, print the returned message
// to the console.
fmt.Println(message)
}
这段代码也比较简单, 只不过是加入了 log, 在出错时输出一些 log 用于 debug.
运行结果如下:
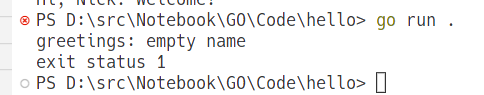
异常处理今天学到这, 下一篇介绍 go 中的数组, Go slice.


