ASP.NET Core - 源码解析 - Startup.cs (一)
本篇已收录至 asp.net core 随笔系列
Reference
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/fundamentals/startup?view=aspnetcore-2.2
startup.cs
首先看看自动为我们创建的startup文件内容都有什么?
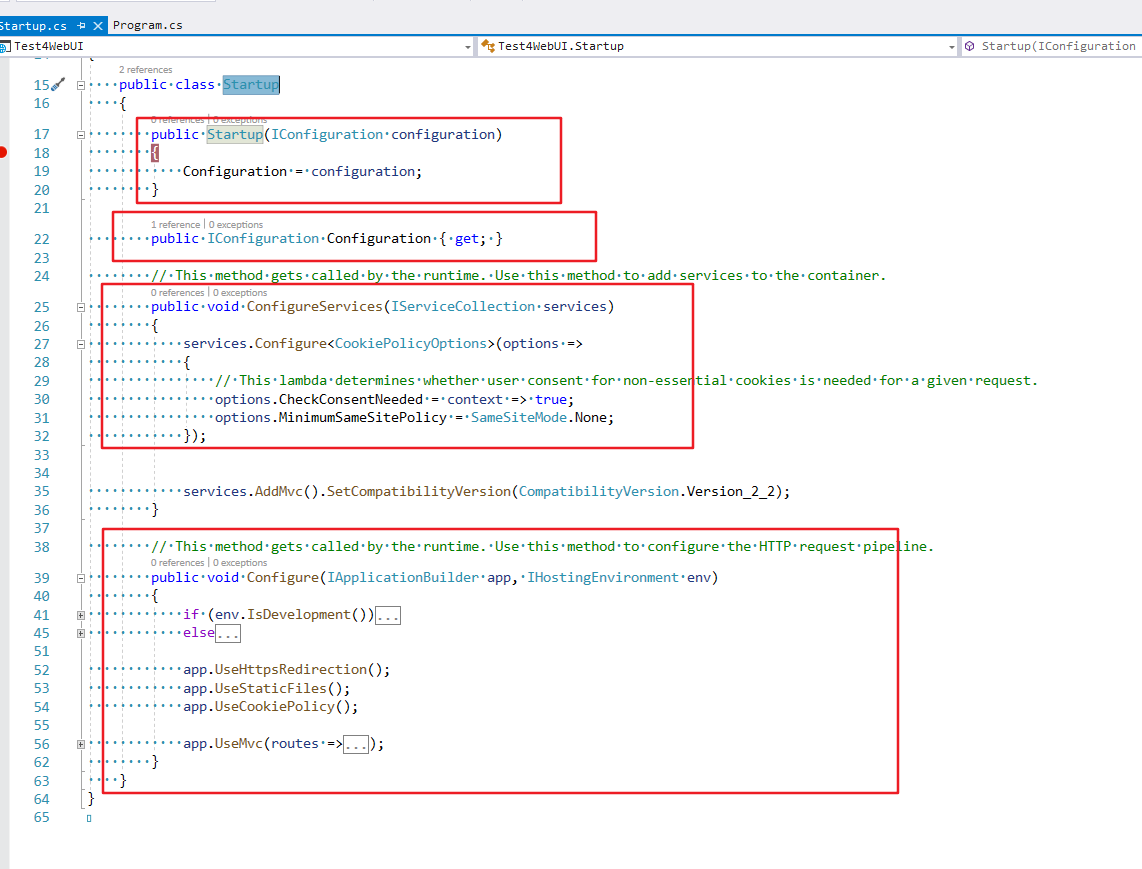
一共分为四部分, 分别是:构造函数, 属性, 和两个方法. 其中构造函数传递的参数将属性赋值, 这个就不详细说了. 我们主要看提供的两个方法, ConfigureServices 以及 Configure. 这两个方法俗称约定方法. 暴露给开发者的目的是让开发者自行构建方法体, 通过不同的构建达到一个非常灵活的配置的目的.
ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<CookiePolicyOptions>(options =>
{
// This lambda determines whether user consent for non-essential cookies is needed for a given request.
options.CheckConsentNeeded = context => true;
options.MinimumSameSitePolicy = SameSiteMode.None;
});
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
}
从方法的注释中可以知道, 这个方法是在运行的时候被调用的. 使用这个方法对 container 进行add service.
一般提到 Container 我们都知道是容器, 涉及到IOC的概念. 也就是说这个方法是指 在运行的时候被调用, 然后向IOC的容器中注入service. 那么既然是对容器进行注册, 我们不仅可以使用低层已有的一些service, 比如例子中给出的, AddMvc() , 或者我们自己写一些 service, 将它们'注册'到 services 中,
services.AddScoped<ITestService, TestService>();
或者使用低层提供的 service. 我列出我目前知道的, 以后还会逐渐补充:
IHostingEnvironment提供环境信息的 service.
IConfiguration提供读取config.
ILoggerFactory创建log对象.
例子我写到下面:
private readonly IHostingEnvironment _env;
private readonly IConfiguration _config;
private readonly ILoggerFactory _loggerFactory;
public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env, IConfiguration config,
ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
_env = env;
_config = config;
_loggerFactory = loggerFactory;
}
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.Configure<CookiePolicyOptions>(options =>
{
// This lambda determines whether user consent for non-essential cookies is needed for a given request.
options.CheckConsentNeeded = context => true;
options.MinimumSameSitePolicy = SameSiteMode.None;
});
services.AddMvc().SetCompatibilityVersion(CompatibilityVersion.Version_2_2);
var logger = _loggerFactory.CreateLogger<Startup>();
if (_env.IsDevelopment())
{
// Development service configuration
logger.LogInformation("Development environment");
}
else
{
// Non-development service configuration
logger.LogInformation($"Environment: {_env.EnvironmentName}");
}
}
当然除了向 Container 中注册 service, 还可以通过这个方法去配置低层的具体使用哪种 IOC 容器, 这也是可以的.
小结
思考一下. 如果将代码进行分层, services 是暴露给开发人员的对象, 开发人员使用这个对象进行操作(addMvc..), services 属于中间层, 但是底层是如何使用 services 呢? 这里是我之前写的一篇解析, 很浅显的介绍了一下底层是如何对 services 进行操作的. 有兴趣的话可以看看. program.cs解读. 在 .UseStartup<Startup>() 时解读了具体开发人员所配置的 service 是如何在底层被使用的.
Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
else
{
app.UseExceptionHandler("/Home/Error");
// The default HSTS value is 30 days. You may want to change this for production scenarios, see https://aka.ms/aspnetcore-hsts.
app.UseHsts();
}
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.UseStaticFiles();
app.UseCookiePolicy();
app.UseMvc(routes =>
{
routes.MapRoute(
name: "default",
template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}");
});
}
Configure 这个方法也是运行时才调用的.
IApplicationBuilder

IHostingEnvironment
总结
看完网上的各种材料以及官方文档后, 个人觉得, 怎么灵活使用 startup 真的是考验一个开发者对于 asp.net core 技术的掌握程度的一个很好的切入点. 因为太灵活, 所以能够讲清楚讲全面的就会很困难. 所以我会继续补充完善这篇文档.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号