结合其他文章
http://weixiaolu.iteye.com/blog/1504898
https://www.cnblogs.com/dycg/p/3934394.html
https://blog.csdn.net/c929833623lvcha/article/details/49052845
和自己看的,记录下
如何用?
实现 VersionedProtocol 定义方法 Server server = new RPC.Builder(conf).setProtocol(TestProtocol.class) .setInstance(new TestProtocolImpl()).setBindAddress(ADDRESS).setPort(0) .build(); server.start();
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
TestProtocol proxy = RPC.getProxy(TestProtocol.class,TestProtocol.versionID,addr, conf);
proxy.调用定义的方法
如何实现?
Service:
先从启动看起,包含了Responder/Listener/Handler[],他们分别处理Nio过程中的不同步骤
public synchronized void start() { responder.start(); listener.start(); handlers = new Handler[handlerCount]; for (int i = 0; i < handlerCount; i++) { handlers[i] = new Handler(i); handlers[i].start(); } }
觉得别人写的不错,抄自:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhixingheyi2016/p/8781006.html
服务端使用了四组线程
Listener:
单个线程,用于监听连接,持有selector ,然后从 Reader[]线程组内挑选一个线程接受监听好的SelectionKey
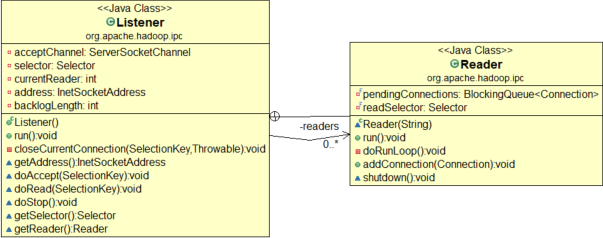
// create a selector; selector= Selector.open(); readers = new Reader[readThreads]; for (int i = 0; i < readThreads; i++) { Reader reader = new Reader( "Socket Reader #" + (i + 1) + " for port " + port); readers[i] = reader; reader.start(); }
Reader[]:
reader 线程组负责读取连接上的读请求,并传递给 Handler线程组,每个线程持有一个readSelector
void doRead(SelectionKey key) throws InterruptedException { int count; Connection c = (Connection)key.attachment();
......try {
//处理读 count = c.readAndProcess(); } catch (InterruptedException ieo) { }
private void processOneRpc(ByteBuffer bb) throws IOException, InterruptedException {try {
...... callId = header.getCallId();
......final RpcCall call = new RpcCall(this, callId, retry); setupResponse(call, rse.getRpcStatusProto(), rse.getRpcErrorCodeProto(), null, t.getClass().getName(), t.getMessage()); sendResponse(call); } }
Handler[]:
hander 线程组负责处理请求并返回响应,未能成功返回的响应交Responder
private class Handler extends Thread { public Handler(int instanceNumber) { this.setDaemon(true); this.setName("IPC Server handler "+ instanceNumber + " on " + port); } @Override public void run() { LOG.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": starting"); SERVER.set(Server.this); while (running) { TraceScope traceScope = null; try { final Call call = callQueue.take(); // pop the queue; maybe blocked here
...
call.run(); } } } }
Responder:
持有一个writeSelector,监听写事件

对于其中的Call对象 :该类封装了一个RPC请求,它主要包含唯一标识id,函数调用信息、函数执行返回值value,异常信息error和执行完成标识done。由于HadoopRPCServer采用了异步方式处理客户端请求,这使得远程过程调用的发生顺序与结果返回顺序无直接关系,而Client端正是通过id识别不同的函数调用。当客户端向服务端发送请求时,只需要填充id和param这两个变量,而剩下的三个变量:value,error,done,则由服务端根据函数执行情况填充.
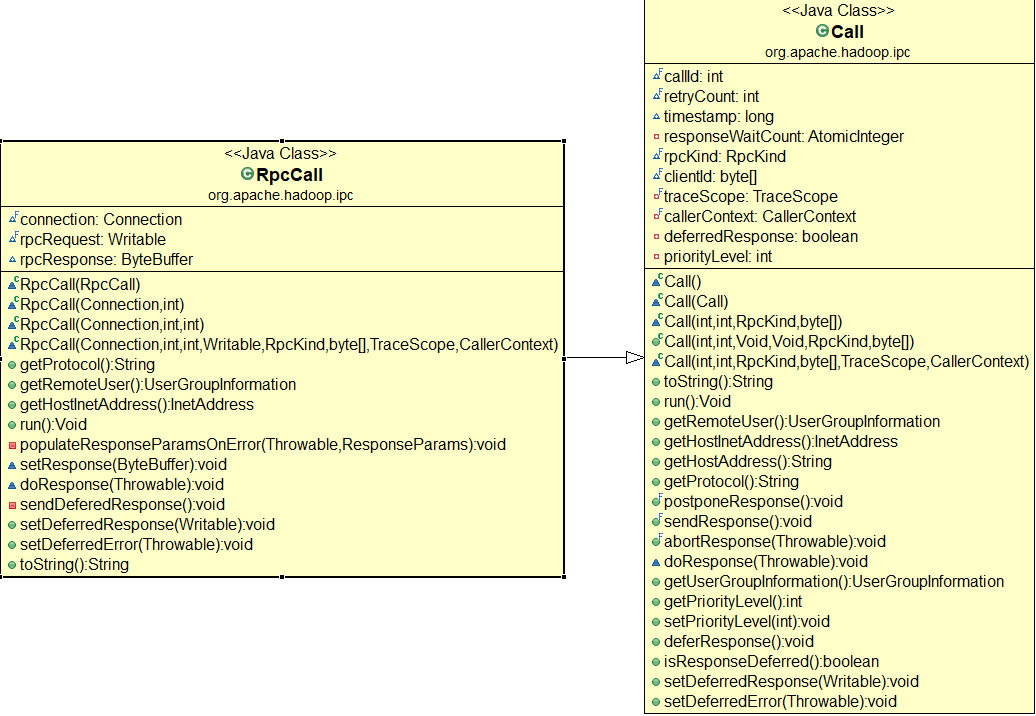
对于Connection, 用于Client与每个Server之间维护一个通信连接。该连接相关的基本信息及操作被封装到Connection类中,其中基本信息主要包括:通信连接唯一标识remoteId,与Server端通信的Socket,网络输入流in,网络输出流out,保存RPC请求的哈希表calls等.
public class Connection {
private Socket socket;private LinkedList<RpcCall> responseQueue;
......
Invoker的invoke方法
val = (RpcWritable.Buffer) client.call(RPC.RpcKind.RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER, new RpcProtobufRequest(rpcRequestHeader, theRequest), remoteId, fallbackToSimpleAuth);
客户端设计
client.call
Writable call(RPC.RpcKind rpcKind, Writable rpcRequest, ConnectionId remoteId, int serviceClass, AtomicBoolean fallbackToSimpleAuth) throws IOException { final Call call = createCall(rpcKind, rpcRequest); final Connection connection = getConnection(remoteId, call, serviceClass, fallbackToSimpleAuth); connection.sendRpcRequest(call); // send the rpc request
对于客户端和服务端的交互
Invoker :动态代理,起始就是为了在invoke中实现具体的客户端访问逻辑,实现网络调用
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { try { value = (ObjectWritable) client.call(RPC.RpcKind.RPC_WRITABLE, new Invocation(method, args), remoteId, fallbackToSimpleAuth); } finally { if (traceScope != null) traceScope.close(); }

Invocation :用于封装方法名和参数,作为数据传输层

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号