本文旨在实践把mysql已有的数据同步到elasticsearch中,使用的版本是6.4.3,对于其它6.x版本理应是一样的处理方式。
本文目录:
本文3.2节所用到的jdbc连接mysql数据库相关的配置文件、jar包打包下载地址:点我去下载
用到的mysql-jdbc版本是:mysql-connector-java-8.0.13
mysql-server数据库版本是5.7
1.初始化ELASTICSEARCH 6.4.3
1.1 下载ELASTICSEARCH 6.4.3
这里使用最新的6.4.3版本,只是做一个实践,稳定性还不清楚,不建议在生产环境直接使用最新版。
下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch
1.2 配置ELASTICSEARCH 6.4.3
这里用单机搭建三个节点模拟集群(生产环境还是一机一节点,不要省,数据安全最重要):
解压elasticsearch-6.4.3.zip,并额外拷贝两份,三个目录分别命名为elasticsearch-6.4.3-node1、elasticsearch-6.4.3-node2、elasticsearch-6.4.3-node3模拟三个节点。然后分别修改解压目录里面config/elasticsearch.yml配置如下:
node1配置:
# ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: es # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-1 # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 192.168.1.222 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # http.port: 9210 transport.tcp.port: 9310 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.1.222:9310", "192.168.1.222:9311", "192.168.1.222:9312"] # # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # action.destructive_requires_name: true
node2配置跟上面差不多,不一样的是node节点名、http端口以及transport.tcp的端口
node2配置:
# ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: es # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-2 # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 192.168.1.222 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # http.port: 9211 transport.tcp.port: 9311 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.1.222:9310", "192.168.1.222:9311", "192.168.1.222:9312"] # # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # action.destructive_requires_name: true
node3配置:
# ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: es # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-3 # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 192.168.1.222 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # http.port: 9212 transport.tcp.port: 9312 # # For more information, consult the network module documentation. # # --------------------------------- Discovery ---------------------------------- # # Pass an initial list of hosts to perform discovery when new node is started: # The default list of hosts is ["127.0.0.1", "[::1]"] # discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.1.222:9310", "192.168.1.222:9311", "192.168.1.222:9312"] # # Prevent the "split brain" by configuring the majority of nodes (total number of master-eligible nodes / 2 + 1): discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 # ---------------------------------- Various ----------------------------------- # # Require explicit names when deleting indices: # action.destructive_requires_name: true
然后分别进入bin目录执行elasticsearch.bat启动相应的节点服务。
2.初始化KIBANA-6.4.3
2.1. 下载
kibana 6.4.3版本下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/downloads/kibana
下载zip版后解压
2.2. 配置
修改解压目录的config文件夹里面的kibana.yml配置文件,配置elasticsearch的url地址(其它的配置项根据需要自行修改):
# Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. server.port: 5601 # 配置elasticsearch的地址 elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.1.222:9210"
2.3. 启动
进入bin目录,执行kibana.bat 批处理文件启动kibana,
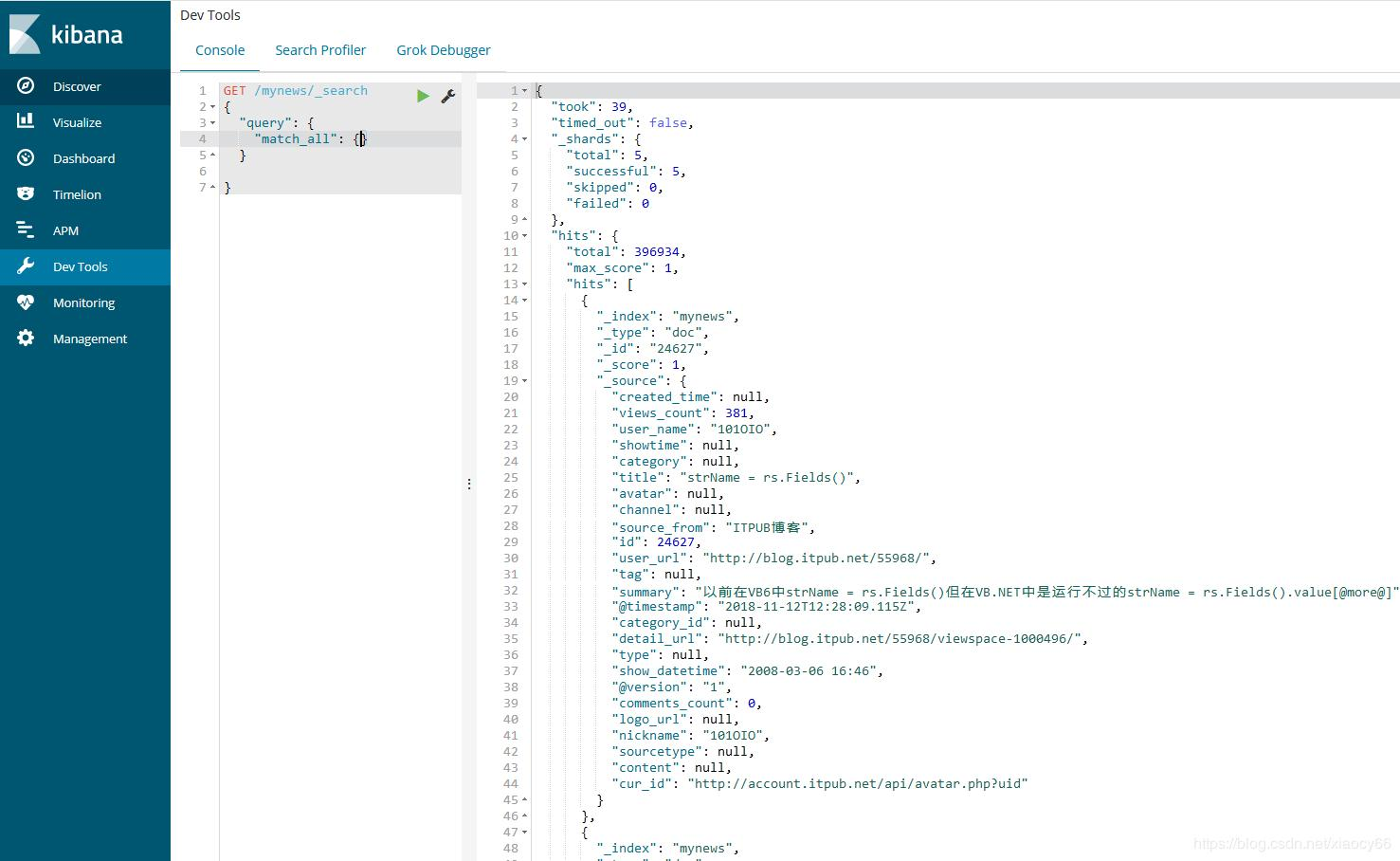
我们在左侧的Dev Tools开发工具输入查询集群状态的命令:GET /_cluster/state
可以看到集群的三个节点都正常运行中。
3.初始化LOGSTASH 6.4.3
3.1 下载LOGSTASH 6.4.3
logstash 6.4.3下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/downloads/logstash
解压下载后的zip文件
3.2 配置LOGSTASH
1.解压logstash-6.4.3 2.修改logstash-6.4.3目录下的Gemfile文件,将source由默认的"https://rubygems.org"改为:"https://gems.ruby-china.com" 3.进入logstash-6.4.3的bin目录,执行logstash-plugin install logstash-input-jdbc 出现如下信息表示安装成功。 在这里插入图片描述 4.在bin目录新建mysql文件夹,把mysql-connector-java-8.0.13.jar放到此文件夹 5.在mysql文件夹新建文件:jdbc.sql,输入以下内容并保存:select * from news 要注意:这里的内容就是logstash依赖执行的sql命令,所以这里的表名要跟你实际的数据库表名一致,否则会失败 6.修改logstash文件夹下config\logstash.conf文件,*(如果不存在,创建一个文件,文件编码为UTF-8)*改成如下配置(jdbc的url需要带时区信息,否则同步会出错,无法读取数据): 注意:以下配置内容,数据库连接相关的内容如数据库名字、用户名密码等需要修改为你当前环境相应的内容
input { stdin { } jdbc { # mysql jdbc connection 连接地址 jdbc_connection_string => "jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.212:3306/my_db?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8" # 登录数据库的用户名、密码 jdbc_user => "root" jdbc_password => "123456" # jdbc 驱动包路径(我们在步骤4处理的内容) jdbc_driver_library => "mysql\mysql-connector-java-8.0.13.jar" # 连接驱动类名 jdbc_driver_class => "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver" jdbc_paging_enabled => "true" jdbc_page_size => "50000" statement_filepath => "mysql\jdbc.sql" # 以下表示定时执行任务,使用cron表达式,本文只全量同步一次,所以不配置定时器,如果要实现增量更新,需要配合定时器以及上次查询的最后一个值,具体要根据你的业务来定。 #schedule => "* * * * *" type => "jdbc" } } filter { json { source => "message" remove_field => ["message"] } } output { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.1.212:9210"] index => "mynews" document_id => "%{id}" } stdout { codec => json_lines } }
7.进入bin目录,执行如下命令 logstash.bat -f ../config/logstash.conf 出现如下界面表示成功在同步数据了: 在这里插入图片描述
通过kibana查看下数据:OK,同步过来39W+ 记录数据了。
版权声明:本文为weixin_30576827原创文章,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接和本声明。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号