懒汉式
import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; public class ThreadPoolService { private static final int DEFAULT_CORE_SIZE=100; private static final int MAX_QUEUE_SIZE=500; private volatile static ThreadPoolExecutor executor; private ThreadPoolService() {}; // 获取单例的线程池对象 public static ThreadPoolExecutor getInstance() { if (executor == null) { synchronized (ThreadPoolService.class) { if (executor == null) { executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(DEFAULT_CORE_SIZE,// 核心线程数 MAX_QUEUE_SIZE, // 最大线程数 Integer.MAX_VALUE, // 闲置线程存活时间 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,// 时间单位 new LinkedBlockingDeque<Runnable>(Integer.MAX_VALUE),// 线程队列 Executors.defaultThreadFactory()// 线程工厂 ); } } } return executor; } public void execute(Runnable runnable) { if (runnable == null) { return; } executor.execute(runnable); } // 从线程队列中移除对象 public void cancel(Runnable runnable) { if (executor != null) { executor.getQueue().remove(runnable); } } }
静态参数(饿汉式)
import com.google.common.util.concurrent.ThreadFactoryBuilder; import java.util.concurrent.*; /** * 异步任务处理器 */ public class AsyncTaskExecutor { /** 线程池保持ALIVE状态线程数 */ public static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE = 10; /** 线程池最大线程数 */ public static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE = 40; /** 空闲线程回收时间 */ public static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME = 1000; /** 线程池等待队列 */ public static final int BLOCKING_QUEUE_SIZE = 1000; /** 业务请求异步处理线程池 */ private static final ThreadPoolExecutor processExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor( CORE_POOL_SIZE, MAX_POOL_SIZE, KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS, new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(BLOCKING_QUEUE_SIZE), new TreadFactoryBuilder.setNameFormat("boomoom-thread-pool-%d").build(), new TreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy()); private AsyncTaskExecutor() {}; /** * 异步任务处理 * * @param task 任务 */ public void execute(Runnable task) { processExecutor.submit(task); } }
在项目中,以上两种方式都使用过,主要看线程任务在项目里的位置。采用第二种的,项目的主要业务就是异步线程来实现。
比较:饿汉式是线程安全的,在类创建的同时就已经创建好一个静态的对象供系统使用,以后不再改变。
懒汉式如果在创建实例对象时不加上synchronized则会导致对对象的访问不是线程安全的,推荐使用第一种。
从实现方式来讲他们最大的区别就是懒汉式是延时加载,
懒汉式是在需要的时候才创建对象,而饿汉式在虚拟机启动的时候就会创建。
饿汉式无需关注多线程问题、写法简单明了、能用则用。但是它是加载类时创建实例、所以如果是一个工厂模式、缓存了很多实例、那么就得考虑效率问题,因为这个类一加载则把所有实例不管用不用一块创建。
懒汉式的优点是延时加载、缺点是应该用同步(比如double-check)、其实也可以不用同步、看你的需求了,多创建一两个无引用的废对象其实也没什么大不了。
实践:
@Test public void threadPool() { SimpleDateFormat sf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss:SSS"); Date startDate = new Date(); System.out.println("开始时间:"+sf.format(startDate)); for(int i=0;i<300000;i++){ System.out.println("i=" + i); //启动线程 ThreadPoolService.getInstance().execute(() -> { int total = 0; for(int k=0;k<1000;k++){ total = total + k; } System.out.println("total=" + total); }); System.out.println("结束了"); Date endDate = new Date(); System.out.println("结束时间:"+sf.format(endDate)); System.out.println("耗时,单位秒:"+ (endDate.getTime()-startDate.getTime())/1000); }
}
运行结果:
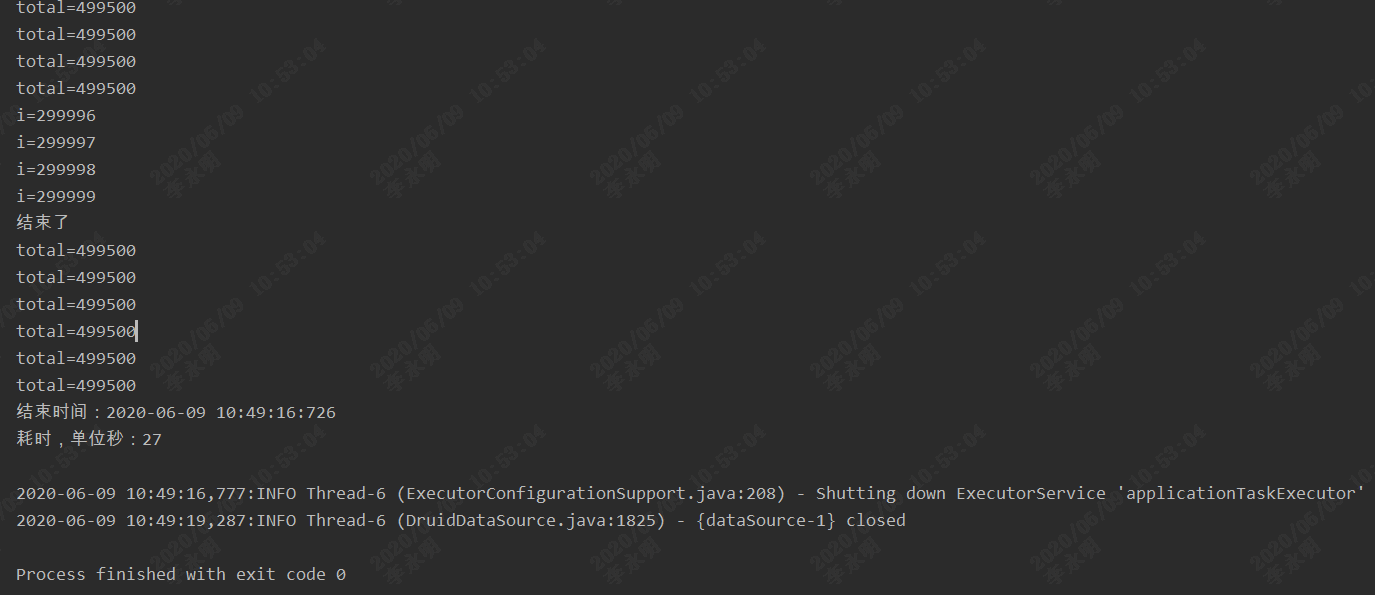
程序可以正常关闭