使用@EnableAsync注解
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement; import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2; @SpringBootApplication @MapperScan({"com.company.test.api.repository.mysql.mapper"}) @EnableCaching @EnableSwagger2 @EnableAsync @EnableTransactionManagement public class MyApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args); } }
Serivce中的方法用@Async进行注解,如果所有的方法都是异步的,可以在类上面注解即可。
package com.company.test.api.base.service.impl; import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Slf4j @Service public class AsyncTestServiceImpl { @Async public void sayHello(){ try { int total = 0; for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){ total = total + i; } log.info("Hello " + total); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
进行测试
@Slf4j @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) @SpringBootTest(classes = MyApplication.class,webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT) public class JoyApiApplicationTest { @Autowired private AsyncTestServiceImpl asyncTestService; @Test public void async(){ asyncTestService.sayHello(); log.info("end"); } }
执行结果
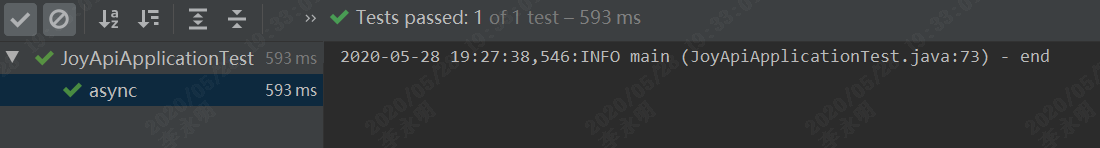
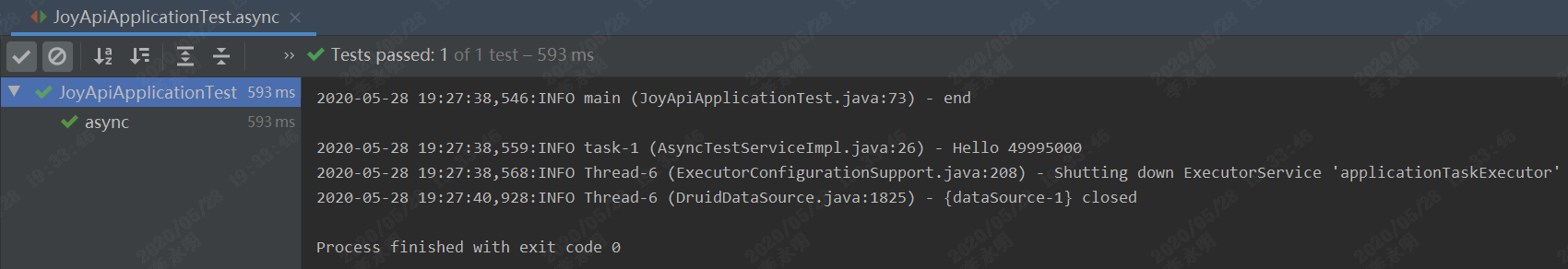
结束


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号