DotNet并行计算的使用误区(二)
● 误区三 . 并行计算是运行时的事
的确,DotNet会在运行时决定是否使用并行库处理代码,但是早在你编译代码时,编译器就早已为这一时刻做好准备,换就话说:
1. 使用并行库处理代码与普通方式对比,IL的结构是不同的。
2. 即使你选择使用并行计算,并且你也确实拥有多核(线程)CPU,运行时你的代码也不一定是并行的。
使用TPL后CLR可能会分解任务,这一依据的其中之一是由IL支持的,IL将并行的任务代码分离,以便在将来的操作中并行,这一点可以从以下的示例中看出来,以下两段示例的核心C#代码都是Tostring()和Sleep(),Code A使用For包含Sleep,Code B使用Parallel.For处理:
Code Part A:
IL:
IL_000e: callvirt instance void [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::Start()
IL_0013: nop
IL_0014: ldc.i4.0
IL_0015: stloc.2
IL_0016: br.s IL_0031
IL_0018: nop
IL_0019: ldloca.s i
IL_001b: call instance string [mscorlib]System.Int32::ToString()
IL_0020: stloc.0
IL_0021: ldc.i4 0xc8
IL_0026: call void [mscorlib]System.Threading.Thread::Sleep(int32)
IL_002b: nop
IL_002c: nop
IL_002d: ldloc.2
IL_002e: ldc.i4.1
IL_002f: add
IL_0030: stloc.2
IL_0031: ldloc.2
IL_0032: ldc.i4.s 10
IL_0034: clt
IL_0036: stloc.3
IL_0037: ldloc.3
IL_0038: brtrue.s IL_0018
IL_003a: ldloc.1
IL_003b: callvirt instance void [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::Stop()
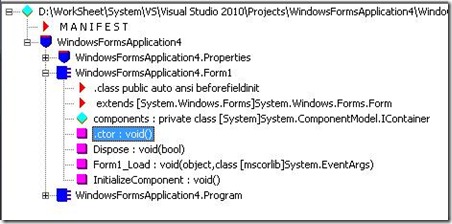
我们注意到,Code Part A的Sleep是直接出现在Load方法中的。
再来看看Parallel方式:
Code Part B:
Form1_Load:
IL_0019: callvirt instance void [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::Start()
IL_001e: nop
IL_001f: ldc.i4.0
IL_0020: ldc.i4.s 10
IL_0022: ldloc.1
IL_0023: ldftn instance void WindowsFormsApplication4.Form1/'<>c__DisplayClass1'::'<Form1_Load>b__0'(int32)
IL_0029: newobj instance void class [mscorlib]System.Action`1<int32>::.ctor(object,
native int)
IL_002e: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.Threading.Tasks.ParallelLoopResult [mscorlib]System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel::For(int32,
int32,
class [mscorlib]System.Action`1<int32>)
IL_0033: pop
IL_0034: ldloc.0
IL_0035: callvirt instance void [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::Stop()
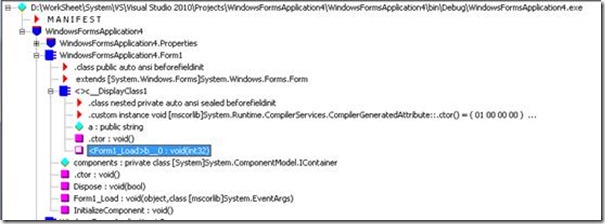
注意红色字体,Sleep已经不在Load方法中了,而是被一个“b__0”代替,并行代码与宿主代码分离,以下就是b__0的IL:
.method public hidebysig instance void '<Form1_Load>b__0'(int32 i) cil managed
{
// 代码大小 26 (0x1a)
.maxstack 8
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldarg.0
IL_0002: ldarga.s i
IL_0004: call instance string [mscorlib]System.Int32::ToString()
IL_0009: stfld string WindowsFormsApplication4.Form1/'<>c__DisplayClass1'::a
IL_000e: ldc.i4 0xc8
IL_0013: call void [mscorlib]System.Threading.Thread::Sleep(int32)
IL_0018: nop
IL_0019: ret
} // end of method '<>c__DisplayClass1'::'<Form1_Load>b__0'
结构图:
以上的红色代码就是在Code A中出现的主要代码。再让我们重温一下这张图,IL的代码任务已经很明显的指示了出来。
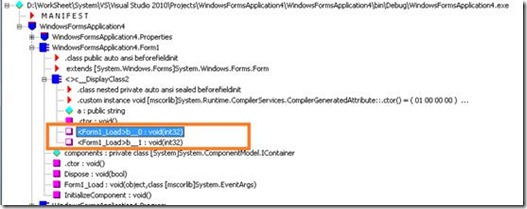
每当我们增加一个并行代码段,IL中就会增加一个b_N块:假如我们的代码中包含两个Parallel块,每块的主代码与上述一致,IL如下:
IL_0019: callvirt instance void [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::Start()
IL_001e: nop
IL_001f: ldc.i4.0
IL_0020: ldc.i4.s 10
IL_0022: ldloc.1
IL_0023: ldftn instance void WindowsFormsApplication4.Form1/'<>c__DisplayClass2'::'<Form1_Load>b__0'(int32)
IL_0029: newobj instance void class [mscorlib]System.Action`1<int32>::.ctor(object,
native int)
IL_002e: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.Threading.Tasks.ParallelLoopResult [mscorlib]System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel::For(int32,
int32,
class [mscorlib]System.Action`1<int32>)
IL_0033: pop
IL_0034: ldc.i4.0
IL_0035: ldc.i4.s 10
IL_0037: ldloc.1
IL_0038: ldftn instance void WindowsFormsApplication4.Form1/'<>c__DisplayClass2'::'<Form1_Load>b__1'(int32)
IL_003e: newobj instance void class [mscorlib]System.Action`1<int32>::.ctor(object,
native int)
IL_0043: call valuetype [mscorlib]System.Threading.Tasks.ParallelLoopResult [mscorlib]System.Threading.Tasks.Parallel::For(int32,
int32,
class [mscorlib]System.Action`1<int32>)
IL_0048: pop
IL_0049: ldloc.0
IL_004a: callvirt instance void [System]System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch::Stop()
下图中会有对应模块出现:
上面的例子说明,在IL阶段已经为运行时的并行执行任务做了准备,编译阶段将并行任务从宿主中分离出来,运行阶段决定是否采用并行方式执行任务。
李鸣(aicken)原创 转载注明










【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 单线程的Redis速度为什么快?
· 展开说说关于C#中ORM框架的用法!
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Pantheons:用 TypeScript 打造主流大模型对话的一站式集成库