数据缓存iOS
有时候,对同一个URL请求多次,返回的数据可能都是一样的,比如服务器上的某张图片,无论下载多少次,返回的数据都是一样的。

上面的情况会造成以下问题
(1)用户流量的浪费
(2)程序响应速度不够快
解决上面的问题,一般考虑对数据进行缓存。
数据缓存
为了提高程序的响应速度,可以考虑使用缓存(内存缓存\硬盘缓存)r

第一次请求数据时,内存缓存中没有数据,硬盘缓存中没有数据。
缓存数据的过程:
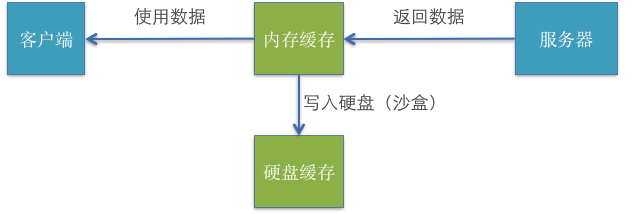
1 2 3 4 | 当服务器返回数据时,需要做以下步骤(1)使用服务器的数据(比如解析、显示)(2)将服务器的数据缓存到硬盘(沙盒) 此时缓存的情况是:内存缓存中有数据,硬盘缓存中有数据。<br><br> |
1 2 3 4 5 | 再次请求数据分为两种情况:(1)如果程序并没有被关闭,一直在运行 请求数据-> 内存数据(2)如果程序重新启动 请求数据->硬盘数据-> 再次请求数据-> 内存数据 |
提示:数据从硬盘读入内存-> 程序开启-> 内存中一直有数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 | 由于GET请求一般用来查询数据POST请求一般是发大量数据给服务器处理(变动性比较大)=>因此一般只对GET请求进行缓存,而不对POST请求进行缓存在iOS中,可以使用NSURLCache类缓存数据iOS 5之前:只支持内存缓存。从iOS 5开始:同时支持内存缓存和硬盘缓存 |
NSURLCache
1 2 3 4 | iOS中得缓存技术用到了NSURLCache类。缓存原理:一个NSURLRequest对应一个NSCachedURLResponse缓存技术:把缓存的数据都保存到数据库中。 |
NSURLCache的常见用法
(1)获得全局缓存对象(没必要手动创建)
1 | NSURLCache *cache = [NSURLCache sharedURLCache]; |
(2)设置内存缓存的最大容量(字节为单位,默认为512KB)
- (void)setMemoryCapacity:(NSUInteger)memoryCapacity;
(3)设置硬盘缓存的最大容量(字节为单位,默认为10M)
1 | - (void)setDiskCapacity:(NSUInteger)diskCapacity; |
(4)硬盘缓存的位置:
1 | 沙盒/Library/Caches |
(5)取得某个请求的缓存
1 | - (NSCachedURLResponse *)cachedResponseForRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request; |
(6)清除某个请求的缓存
1 | - (void)removeCachedResponseForRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request; |
(7)清除所有的缓存
1 | - (void)removeAllCachedResponses; |
缓存GET请求
1 | 要想对某个GET请求进行数据缓存,非常简单 |
1 2 3 4 | NSMutableURLRequest *request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url];// 设置缓存策略request.cachePolicy = NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataElseLoad; |
只要设置了缓存策略,系统会自动利用NSURLCache进行数据缓存
7种缓存策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 | NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy // 默认的缓存策略(取决于协议) NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalCacheData // 忽略缓存,重新请求 NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataElseLoad// 有缓存就用缓存,没有缓存就重新请求 NSURLRequestReturnCacheDataDontLoad// 有缓存就用缓存,没有缓存就不发请求,当做请求出错处理(用于离线模式)NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData // 未实现NSURLRequestReloadRevalidatingCacheData // 未实现NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData // 未实现 |
缓存的注意事项
缓存的设置需要根据具体的情况考虑,如果请求某个URL的返回数据:
1 2 3 | (1)经常更新:不能用缓存!比如股票、彩票数据(2)一成不变:果断用缓存(3)偶尔更新:可以定期更改缓存策略 或者 清除缓存 |
提示:如果大量使用缓存,会越积越大,建议定期清除缓存
GET缓存
在appDelegate中设置网络缓存大小 实现get 缓存:如果从服务器加载数据,通过etag 判断加载数据与缓存是否相同 从本地加载数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 | //// AppDelegate.m// A-get缓存请求//// Created by Mr.Sunday on 15/4/27.// Copyright (c) 2015年 Novogene. All rights reserved.//#import "AppDelegate.h"@interface AppDelegate ()@end@implementation AppDelegate- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions { /*===============设置网络缓存==============*/ /** 内存缓存->4M 磁盘缓存->20M diskPath 如果是 nil,会缓存到 cached 的 bundleId 目录下 只要在 AppDelegate 中加入以下两句话,今后所有的缓存处理,就不需要管了! */ NSURLCache *cathe = [[NSURLCache alloc] initWithMemoryCapacity:4*1024*1024 diskCapacity:20*1024*1024 diskPath:nil]; [NSURLCache setSharedURLCache:cathe]; /** SDWebImage 的缓存 1. 缓存时间:1周 2. 处理缓存文件,监听系统退出到后台的事件 - 遍历缓存文件夹,删除所有过期的文件 - 继续遍历缓存文件夹,将最大的文件删除,一直删除到缓存文件的大小和指定的“磁盘限额”一致,停止 */ return YES;} |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 | //// ViewController.m// A-get缓存请求//// Created by Mr.Sunday on 15/4/27.// Copyright (c) 2015年 Novogene. All rights reserved.//#import "ViewController.h"@interface ViewController ()@property (nonatomic, weak) IBOutlet UIImageView *iconView;//服务器返回的etag@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *etag;//清楚所有缓存- (void)removeAllCachedResponses;@end@implementation ViewController- (void)viewDidLoad { [super viewDidLoad];}/** 1. 请求的缓存策略使用 >NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringCacheData<,忽略本地缓存 2. 服务器响应结束后,要记录 Etag,服务器内容和本地缓存对比是否变化的重要依据! 3. 在发送请求时,设置 If-None-Match,并且传入 etag 4. 连接结束后,要判断响应头的状态码,如果是 304,说明本地缓存内容没有发生变化 *//*==================从本地缓存加载数据==============*//* NSCachedURLResponse *cachedResponse = [[NSURLCache sharedURLCache] cachedResponseForRequest:request]; self.iconView.image = [UIImage imageWithData:cachedResponse.data]; */- (void)touchesBegan:(NSSet *)touches withEvent:(UIEvent *)event{ NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:@"http://mrsunday.local/ml.png"]; NSMutableURLRequest *request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:url cachePolicy:NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringCacheData timeoutInterval:10.0]; /** *设置请求头->所有的请求头都是通过这种方法设置的 *如果etag length不为0,说明已经有缓存了 */ if (self.etag.length > 0) { NSLog(@"设置 etag: %@", self.etag); [request setValue:self.etag forHTTPHeaderField:@"IF-None-Match"]; } //请求的默认方法是get(高频使用) NSLog(@"%@",request.HTTPMethod); /** *Etag = "\"4a0b9-514a2d804bd40\""; *可以在请求中增加一个 etag 跟服务器返回的 etag 进行对比 *就能够判断服务器对应的资源是否发生变化,具体更新的时间,由request自行处理 */ [NSURLConnection sendAsynchronousRequest:request queue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue] completionHandler:^(NSURLResponse *response, NSData *data, NSError *connectionError) { NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *)response; /** *allHeaderFields 所有相应头子端 */ NSLog(@"%@ %@", httpResponse.allHeaderFields, httpResponse); /** *如果服务器的状态码是304,说明数据已经被缓存,服务器不再需要返回数据 *需要从本地缓存获取被缓存的数据 */ if (httpResponse.statusCode == 304) { NSLog(@"load local database"); /** *针对http访问的一个缓存类,提供了一个单例 *拿到被缓存的响应 */ NSCachedURLResponse *cachedResponse = [[NSURLCache sharedURLCache] cachedResponseForRequest:request]; self.iconView.image = [UIImage imageWithData:cachedResponse.data]; return; } //记录etag self.etag = httpResponse.allHeaderFields[@"etag"]; self.iconView.image = [UIImage imageWithData:data]; }];}//记得要清除缓存请求!- (void)removeAllCachedResponses{ [self removeAllCachedResponses];}@end |
posted on 2016-11-06 15:40 🌞Bob 阅读(346) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报



【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core GC压缩(compact_phase)底层原理浅谈
· 现代计算机视觉入门之:什么是图片特征编码
· .NET 9 new features-C#13新的锁类型和语义
· Linux系统下SQL Server数据库镜像配置全流程详解
· 现代计算机视觉入门之:什么是视频
· Sdcb Chats 技术博客:数据库 ID 选型的曲折之路 - 从 Guid 到自增 ID,再到
· .NET Core GC压缩(compact_phase)底层原理浅谈
· Winform-耗时操作导致界面渲染滞后
· Phi小模型开发教程:C#使用本地模型Phi视觉模型分析图像,实现图片分类、搜索等功能
· 语音处理 开源项目 EchoSharp