Zebra-VTYSH源码分析和改造
以下内容均为转载,内容来自:
http://blog.csdn.net/xuexingyang/article/details/6925487
http://blog.csdn.net/xuexingyang/article/details/7107221
http://blog.csdn.net/xuexingyang/article/details/7237935
感谢xuexingyang的辛勤劳动!
=======================================================
1. Zebra 功能认识
ZEBRA 提供了一个类Cisco命令行的分级多用户命令解析引擎--VTY(Virtual Terminal)。它是类似于Linux Shell的虚拟终端接口,负责对访问的安全验证、数据缓冲、命令解析、模式切换和命令调用。
用户通过VTYSH的每一次接口访问都会发起一个对应的VTY。VTY会根据用户优先级初始化并挂载相应的命令集Command Node。Command Node中以链表的形式包含了该用户可以访问和使用的Command。
用户通过各种接口访问VTY,VTY解析用户的每个命令,并且通过命令集链表找到并执行Command相应函数。这样,通过访问VTY实现基于命令集的管理功能。
2. Zebra 架构
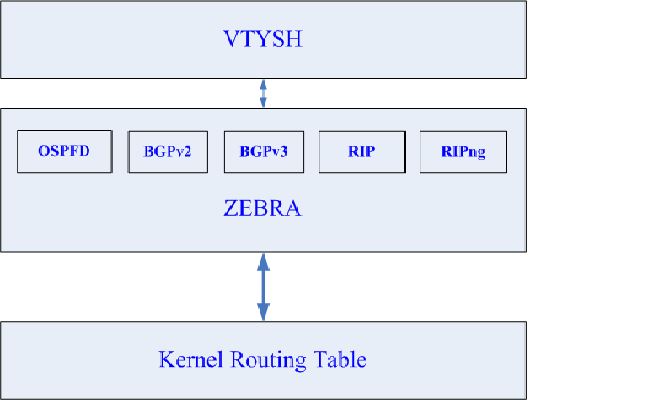
Zebra采用模块化的架构,,整个程序由一系列的守护进程构成,每个路由协议都有自己单独的路由处理进程,同时,它提供一个管理内核路由表的zebra 守护进程。路由处理程序通过zebra 守护程序管理内核路由表。
由图示可知,在Zebra中,总共有五个路由守护进程,和一个管理进程。这些路由进程可以和管理进程分布在不同的机器上,每一个进程可以分别监听从不同的端口来的VTY连接。
3. 编译Zebra为我所用
一般的路由产品都可以拿来Zebra稍加改动就可以使用了。如果你只需要VTY连接功能,通过接口增、改、删命令的话,Zebra是支持模块的删除和屏蔽的。
比如只需要VTY,那么你编译的时候可以在congfigure的时候加上如下参数就可以了。
...
cd ../zebra-vtysh && (test -e config.status ||(touch config.status && ./configure --disable-ipv6 --disable-bgpd --disable-ripngd --disable-ospf6d --disable-bgp-announce --enable-vtysh --disable-ospfd --disable-ripd --disable-zebra --prefix=/ --with-cflags="-O2 -Wall" --build=i386 --host=mips-linux --target=mips)) &&
...
(其中,config.status是configure的状态记录信息,以备下次使用)
这样,编译完zebra后,就可以运行vtysh了,查看它的各种模式(下篇文章会讲),就可以开始你的快乐之旅了。
参考:http://www.zebra.org
分析Zebra-VTYSH的源码,首先从main函数开始,在ztysh-main.c中找到main函数,来进一步分析流程执行如下图所示:

在平时的使用中我们会发现,配置的时候有很多的视图(View),每个视图中有不同的命令可供用户输入进行配置。
这里,根据源码,视图可以认为是Node,而每一个命令称为element,他们之间的结构如下图所示:
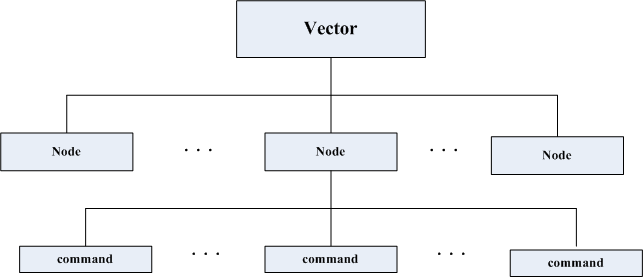
如图中所示,用到的数据结构如下:
- /* struct for vector */
- struct _vector
- {
- unsigned int max; /* max number of used slot */
- unsigned int alloced; /* number of allocated slot */
- void **index; /* index to data */
- };
- /* Node which has some commands and prompt string and configuration
- function pointer . */
- struct cmd_node
- {
- /* Node index. */
- enum node_type node;
- /* Prompt character at vty interface. */
- char *prompt;
- /* Is this node's configuration goes to vtysh ? */
- int vtysh;
- /* Node's configuration write function */
- int (*func) (struct vty *);
- /* Vector of this node's command list. */
- vector cmd_vector;
- };
- /* Structure of command element. */
- struct cmd_element
- {
- char *string; /* Command specification by string. */
- int (*func) (struct cmd_element *, struct vty *, int, char **);
- char *doc; /* Documentation of this command. */
- int daemon; /* Daemon to which this command belong. */
- vector strvec; /* Pointing out each description vector. */
- int cmdsize; /* Command index count. */
- char *config; /* Configuration string */
- vector subconfig; /* Sub configuration string */
- };
下面我们所要做的事情就是在node和element中添加我们自己的命令,如果一切顺利,稍加处理就可以在图一中的最后一步也就是loop循环中的vtysh_execute函数中来实现我们的执行过程了。
5. 添加定制命令
5.1 视图介绍
由上面几篇文章分析可见,所有的命令都是包含在node中的,根据Cisco或者H3常见路由器或者交换机的CLI格式可见,一个node就对应着一个视图(View)。常用的视图包括:普通视图,管理视图,文件系统视图,配置视图,以及接口配置视图和VLAN视图等。
在Zebra-VTYSH源码中,实现了的有Enable视图和配置视图。如下图所示:
- / # vtysh
- Copyright 2010-2011 IBM Co., Ltd.
- CLI> enable
- CLI#
- clear Reset functions
- configure Configuration from vty interface
- copy Copy from one file to another
- debug Debugging functions (see also 'undebug')
- disable Turn off privileged mode command
- end End current mode and down to previous mode
- exit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
- list Print command list
- no Negate a command or set its defaults
- ping send echo messages
- quit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
- show Show running system information
- start-shell Start UNIX shell
- telnet Open a telnet connection
- terminal Set terminal line parameters
- traceroute Trace route to destination
- undebug Disable debugging functions (see also 'debug')
- write Write running configuration to memory, network, or terminal
- CLI# configure terminal
- CLI(config)#
- access-list Add an access list entry
- bgp BGP information
- debug Debugging functions (see also 'undebug')
- device-config Device configuration
- dump Dump packet
- enable Modify enable password parameters
- end End current mode and down to previous mode
- exit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
- hostname Set system's network name
- interface Select an interface to configure
- ip IP information
- ipv6 IPv6 information
- key Authentication key management
- list Print command list
- log Logging control
- no Negate a command or set its defaults
- password Assign the terminal connection password
- route-map Create route-map or enter route-map command mode
- router Enable a routing process
- system-config System and management configuration
- username
- write Write running configuration to memory, network, or terminal
- CLI(config)# system-config
- CLI(config-system)#
- access Set CPE access ND flag
- admin-idle-time Set system idle time
- admin-psw Set system administrator password
- admin-username Set system administrator username
- connection-mode Set network connection mode : static and dynamic
- datetime Set date time (format:2000-01-01 00:00:00)
- default-gateway Set system's network default gateway
- dns-server-1 Set system network DNS server 1
- dns-server-2 Set system network DNS server 2
- exit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
- factory-defaults Restore ALL configure to factory default values( 0: reset all 1: reset with network parameters unchanged)
- hostname Set system's network name
- image-upgrade Upgrade image via ftp method
- ip Set system ip address and netmask
- list Print command list
- managment-ip-range Set management IP range and netmask
- managment-ip-range-flag Set management IP range service flag
- mgr-vlan-id Set management VLAN ID
- ntpserver Set NTP server
- quit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
- reset Reset system
- snmp-refresh-time Set SNMP service refresh time cycle
- snmp-rwcommunicty Set SNMP read/write community
- snmp-service Set SNMP service enable or disable
- snmp-trap-ip1 Set SNMP trap ip 1 address
- snmp-trap-ip2 Set SNMP trap ip 2 address
- snmp-trap1-ip-flag Set SNMP trap ip 1 service flag(enable/disable)
- snmp-trap2-ip-flag Set SNMP trap ip 2 service flag(enable/disable)
- ssh Set ssh service port and timeout values
- ssh-service Set ssh service flag
- telnet Set telnet PORT
- telnet-service Set telnet service flag
- timesync Set time sync service flag
- timezone Set time zone (0:ShangHai,1:ChongQing)
- CLI(config-system)# quit
- CLI(config)# device-config
- CLI(config-device)#
- exit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
- list Print command list
- port-mirror-analysis-port Device configuration: Set analysis port(1: eth1 2: eth2)
- port-mirror-flag Device configuration: Enable or disable port mirror service(0:disable,1:enable)
- port-mirror-packet Device configuration: Set packet type to be mirrored(1:Import & Export 2: Import 3: Export)
- port-mirror-port Device configuration:Set port to be mirrored
- port1-rate Device configuration: set duplex mode and import/export/broadcast/unkown/multicast rate limit.
- port2-rate Device configuration: set duplex mode and import/export/broadcast/unkown/multicast rate limit.
- quit Exit current mode and down to previous mode
- CLI(config-device)#
- CLI(config-device)#
如果想要添加自己的命令,可以在原有的视图上增加(也就是在原有的node中增加commands),或者新开自己的视图,然后在新视图中添加自己的commands。
5.2 添加命令
进入vtysh目录中,查看vtysh_main.c文件的main函数,也就是和vtysh初始化相关的一切都在这里,基本上在这里可以完成你需要的一些基本命令。
在函数vtysh_init_vty()中,有个
- /* Initialize command interface. Install basic nodes and commands. */
- Void cmd_init (int terminal)
的函数,就是负责初始化command接口,安装node和命令的。
比如你就可以添加自己的视图如下:
- /*Added by xyang*/
- install_element (CONFIG_NODE, &vtysh_sysconfig_cmd);
- install_element (CONFIG_NODE, &vtysh_devconfig_cmd);
(其中,安装的system和device配置的视图)
- /*Added by xyang
- * system config node*
- */
- DEFUN (system_config,
- vtysh_sysconfig_cmd,
- "system-config",
- SYS_CFG_STR
- "\n")
- {
- //vty_out (vty, "testing by xyang.%s", VTY_NEWLINE);
- vty->node = SYSCONFIG_NODE;
- return CMD_SUCCESS;
- }
- DEFUN (device_config,
- vtysh_devconfig_cmd,
- "device-config",
- DEV_CFG_STR
- "\n")
- {
- //vty_out (vty, "testing by xyang.%s", VTY_NEWLINE);
- vty->node = DEVCONFIG_NODE;
- return CMD_SUCCESS;
- }
- DEFUN定义为:
- /* DEFUN for vty command interafce. Little bit hacky ;-). */
- #define DEFUN(funcname, cmdname, cmdstr, helpstr) \
- int funcname (struct cmd_element *, struct vty *, int, char **); \
- struct cmd_element cmdname = \
- { \
- cmdstr, \
- funcname, \
- helpstr \
- }; \
- int funcname \
- (struct cmd_element *self, struct vty *vty, int argc, char **argv)
SYSCONFIG_NODE和DEVCONFIG_NODE要添加进enum node_type{}中去。
最后就要在init_cmd的最后加进自己的command了
比如
- /*add commands to system config node
- * added by xyang @ 2012-02-01*
- */
- /*management network settings*/
- install_element (SYSCONFIG_NODE, &vtysh_system_cfg_ip_cmd);//ip and subnet mask
其中,函数指针需要定义先:
- DEFUN (vtysh_system_cfg_ip,
- vtysh_system_cfg_ip_cmd,
- "ip ADDRESS NETMASK",
- "Set system ip address and netmask\n")
- {
- applyCfg(argv[0],"IPADDR");
- applyCfg(argv[1],"NETMASK");
- system(NETWORK_SETTING_SCRIPT);
- return CMD_SUCCESS;
- }
这样,基本上完成了添加node和命令的任务了。
其他Zebra-VTYH自带的命令如果不想要的话删除掉就行了。
(总完)


