set _NT_SYMBOL_PATH = srv*F:\Yangl\DebuggingPaths\dbg*http://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols;
set _NT_SOURCE_PATH = p1;p2;
Summary of Steps Needed
- Install the Debugging Tools for Windows (if you don’t already have them)
- Create a directory in which to store your debugging symbols (e.g.,
c:\symbolsord:\symbols) - In Process Explorer, select
Options | Configure Symbols...and configure as below:
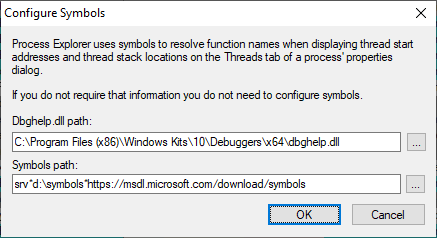
First, here is the Dbghelp.dll path:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x64\dbghelp.dll
Next, the Symbols path if you wish to use the C: drive:
srv*c:\symbols*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
Or, the Symbols path if you wish to use the D: drive.:
srv*d:\symbols*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
In the picture above, I show the path to the local symbols cache (between the asterisks in the Symbols path) on the D: drive. This is because my C: drive is short on space, and the the local symbols cache can get very big, many gigabytes. You can call it whatever you want, and put it wherever is expedient for you. A local drive is best for speed.
This is my setup, and works for me, with the Windows Driver Kit (WDK) installed as well as the Software Development Kit (SDK) with the Debugging Tools for Windows installed after the WDK too. NOTE: The Dbghelp.dll path is different from the paths I have seen in older articles, which do not work on my computer.
Introduction
I am following along in Windows Internals, Part 1, Edition 7 by Mark Russinovich, et. al. The book uses Sysinternals Process Explorer application heavily and discusses how to enable debugging symbols downloads via the Microsoft symbol server to enable resolution of raw address offsets in executables to symbolic names, for instance, in the Threads tab of a process’s Properties dialogue box or in stack traces.
However, I was not having much success getting it to work. His screenshot was correct, but the link he gave for information had an old windbg.dll path, and other articles on the web were also outdated or did not give the windbg.dll path at all. That is what threw me.
I did not see the screenshot, just the link. I finally made it work, and came to understand why it was not working, so I thought I would explain it here for the benefit of others and give some detailed insights into how to know whether it is truly working or not.
Detailed Instructions and Tips
First, open up the Options | Configure Symbols... dialogue box in Process Explorer:
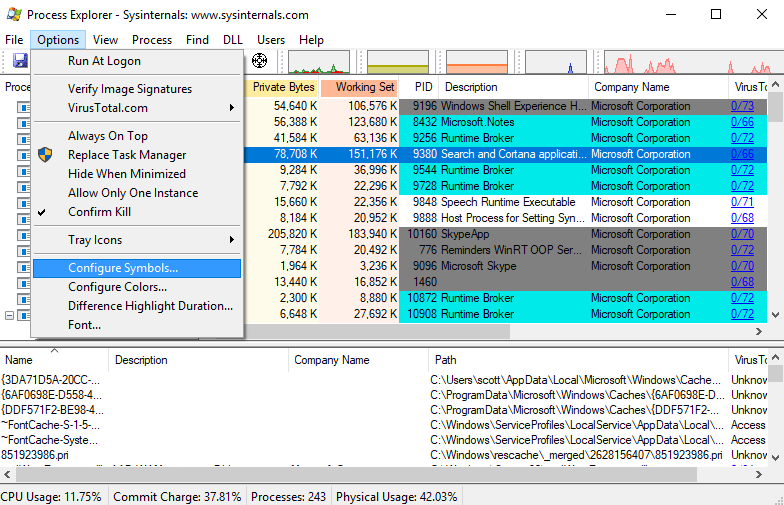
This is what the dialog box looks like the first time you use it:
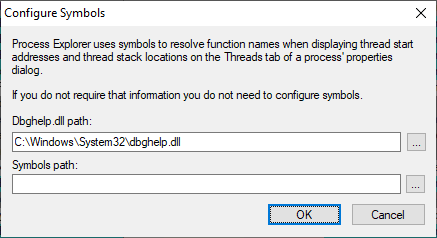
Note that the Symbols path is empty, and the default path to dbghelp.dll is in the C:\Windows\System32 subdirectory, which will not work.
Configuring the Dbghelp.dll Path
First, lets tackle the dgbhelp.dll path. The initial value for that path shown above points to a version of that dll that will not work. You will need to do some work to get the right version of the dll and point to it.
Debugging Tools for Windows
If you have not already, you will need to get a copy of the dgbhelp.dll that comes with the Debugging Tools for Windows. This immediately preceding link explains how to install those tools for Windows 10. Distilled, the steps are basically:
- Either install the Software Development Kit, including selecting the Debugging Tools for Windows
- Or, install only the Debugging Tools for Windows by installing the SDK but selecting Debugging Tools for Windows and deselecting everything else
- Or, install the Windows Driver Kit
The Right dgbhelp.dll Path
Now, you need to point to the right dbghelp.dll file. You can either paste the following path into its input box:
C:\Program Files (x86)\Windows Kits\10\Debuggers\x64\dbghelp.dll
Or click on the ellipsis button to the right of the Dbghelp.dll path input box and navigate to the above path and select dbghelp.dll:
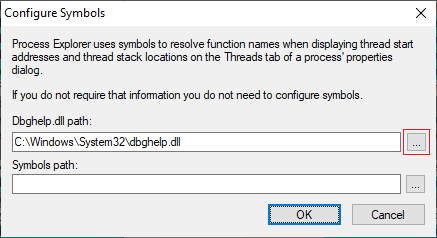
If you paste the path, I would still navigate to it to make sure it is correct for your machine (perhaps your OS drive is d:?). The dialogue box should now look like this:
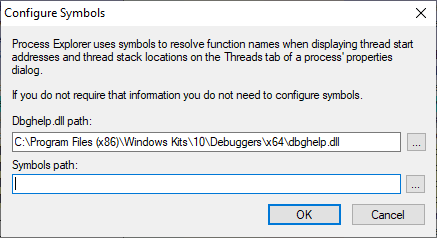
Update the Symbols Path
The Symbols path has the following form, taken from the Microsoft Docs Debugging with Symbols Page:
srv*[local cache]*[private symbol server]*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
I use the following Symbols path for my needs:
srv*d:\symbols*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
I do not use a private symbol server, and my d: drive is larger than my small c: drive, so the path to my local symbol cache (between the asterisks) is d:\symbols. You could use c:\symbols or wherever else is appropriate for you. For instance:
srv*c:\symbols*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
You will have to create the symbols directory yourself - Process Explorer will not make it for you. The symbol cache can get quite large (many gigabytes), so make sure you have plenty of space on the drive.
The Final Configuration
Fully configured, my setup looks like this (just like the screenshot in Windows Internals, Part 1, Edition 7 I missed!):

Articles with the Old Path
Note that I do not have the Dgbhelp.dll path which starts as below on my computer. Many older articles point to such a path for the location of debugging tools:
c:\Program Files\Debugging Tools for Windows\...
Articles that use that path for locating the dbghelp.dll seem to be out of date.
See if It All Works
Now, we need to see if everything is working as desired.
Check the Process’ Properties
Here is a screenshot of Process Explorer with the searchui.exe process highlighted (fourth from the top in dark blue). I will use it in my examples:
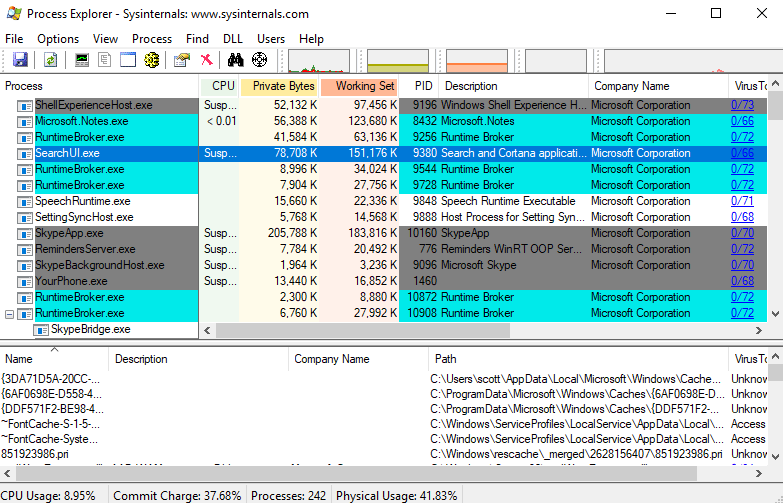
Right click on a Windows process, and select Properties:
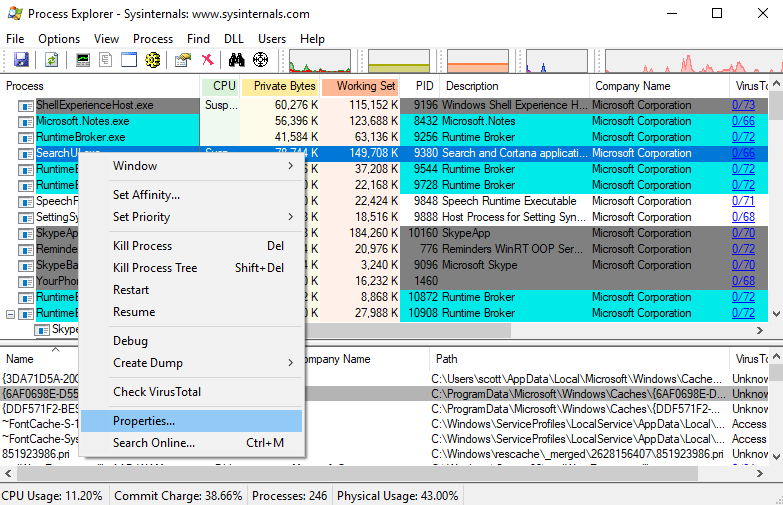
After the properties dialogue box comes up, select the Threads tab at the top:
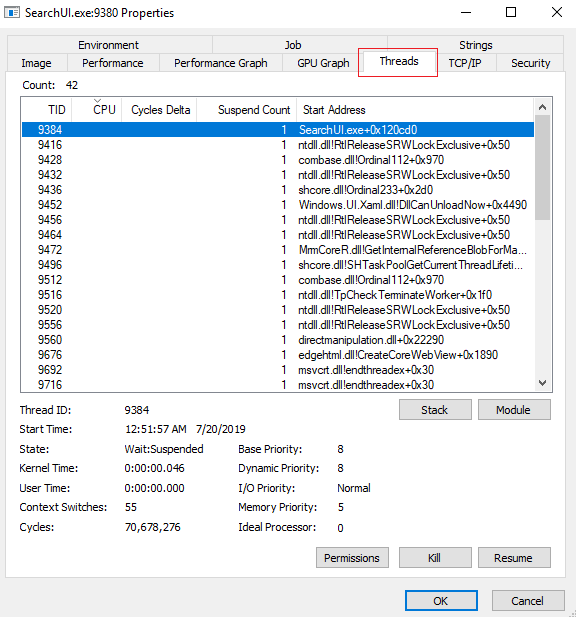
Not Yet Working
Before configuring symbols correctly, the output looks something like this:
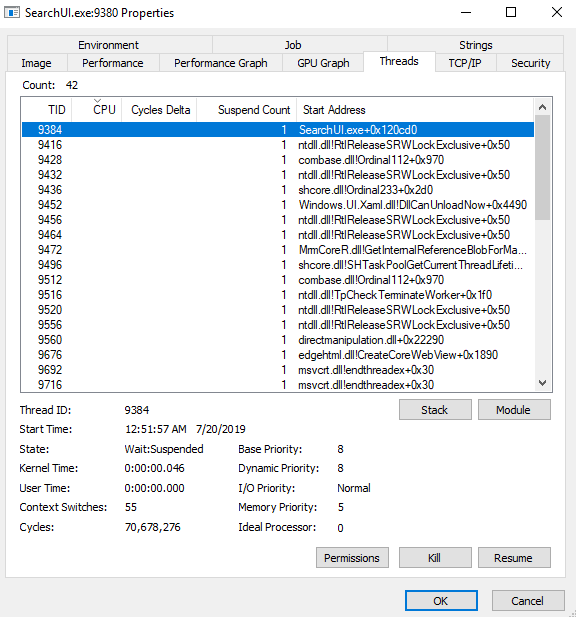
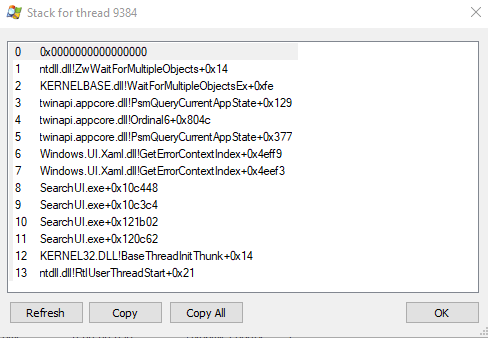
Note how the symbols are not resolved - in the highlighted line, you see the following for the start address of thread 9384:
SearchUI.exe+Ox120cd0
The symbol is not resolved - you just see the offset of the function as a hexadecimal number (0x120cd0) after a plus sign.
Symbols Working
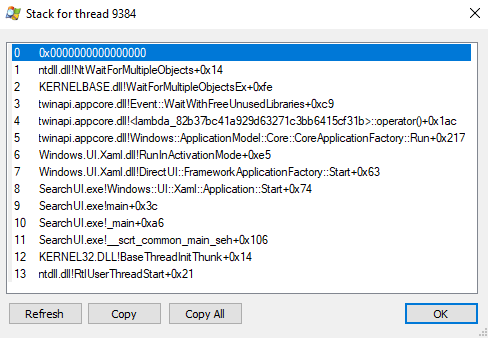
Below, you see the symbol server is working and the offset is resolved to a symbolic name (function name):
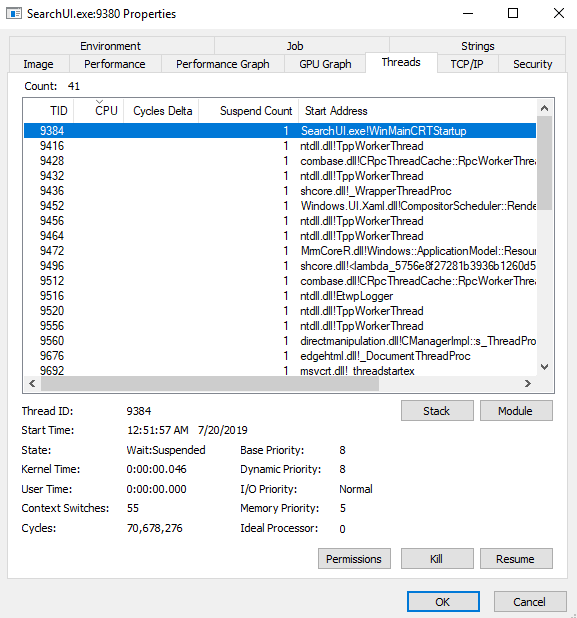
Now, we see not just the offset, but the actual function name:
SearchUI.exe!WinMainCRTStartup
Note that, especially at first, there may be a delay as the symbols are acquired from the Microsoft symbol server. Be patient. The symbols will automatically fill in as they are acquired. Let me emphasize that: be very patient! It may take a while until they start filling in, and you may think it is broken prematurely. In my experience, it has never taken more than 2-3 minutes to start going, but that can seem like a long time when just staring at the dialog box.
Check Stack Trace
You can also click the Stack button to see a stack trace:
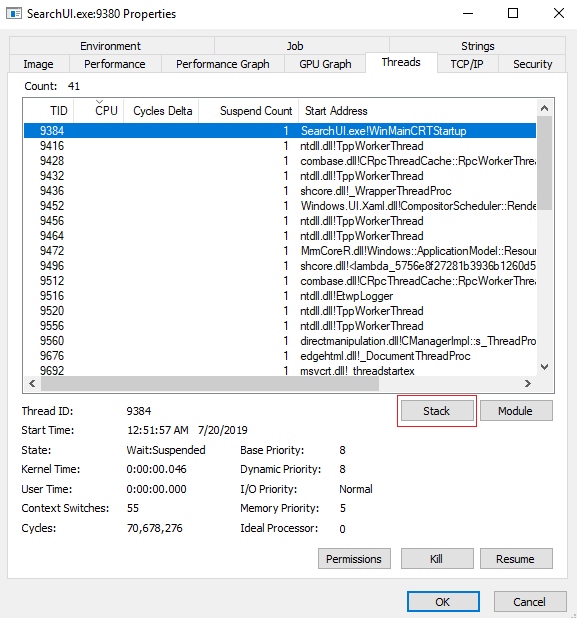
Stack trace without full symbols:
Stack trace with full symbols:
Check the Symbols Folder
Another way to verify explicitly that the symbol server functionality is working is to just go look at the local cache folder (d:\symbols in my case) with file explorer and see if it contains files and folders. If it is empty after viewing the threads in a process’ properties dialogue box for an appropriate amount of time, something is wrong.
Final Tips
As discussed here, setting up a Symbols Path environment variable _NT_SYMBOL_PATH, which uses the same format as above, can be very useful for Windows debuggers (WinDbg, Visual Studio, etc.) in certain situations.
However, the environment variable setup did not seem to work for Process Explorer, but when I opened a debug session in Visual Studio, it populated the symbol cache, so it was working for other programs.
Also, a gotcha: I noticed when I set up the Symbols Configuration in Process Explorer when not started with Administrator privileges, when I did start it with Administrator privileges, I had to reconfigure the Symbol Configuration - it had gone back to the initial configuration. So, that might be a potential problem to watch out for.
Conclusion
The Microsoft Symbol Server path and Symbols path format has not changed form in quite some time. That was not the problem. The problem was getting pointed to the right dbghelp.dll file. Because the place Microsoft puts it has changed, and many articles about Process Explorer symbols do not address the Dbghelp.dll path, it took me a while to get this right.
I hope this article helps people. It is pretty in-depth for this task, and I hope educational, showing many things all in one place that I found in various places on the Internet and in my hands-on testing. Stay tuned for other articles of interest as I work through the book. It is proving to be fascinating and extremely helpful, both from the viewpoint of a developer and an administrator.
See Also
Windows 调试器的符号路径
符号路径指定 Windows 调试器(如 WinDbg、KD、CDB 和 NTST)查找符号文件的位置。 有关符号和符号文件的详细信息,请参阅符号。
某些编译器(包括 Microsoft Visual Studio)将符号文件与二进制文件放在同一目录中。 符号文件和选中的二进制文件包含路径和文件名信息,使调试器能够自动查找符号文件。 如果在生成可执行文件的计算机上调试用户模式进程,并且符号文件位于其原始位置,则调试器可以在不设置符号路径的情况下找到符号文件。
在大多数其他情况下,需要将符号路径设置为指向符号文件位置。
提示
使用 .symfix 设置公共 Microsoft 公共符号服务器的默认路径,该服务器在许多情况下效果良好。
符号路径语法
调试器的符号路径是一个字符串,由多个目录路径组成,用分号分隔。 例如,C:\Dir1;C:\Dir2\DirA;C:\Dir2\DirB。
支持相对路径。 但是,应在每个路径之前添加驱动器号或网络共享,除非始终从同一目录启动调试器。 还支持网络共享。
对于符号路径中的每个目录,调试器将在三个目录中查找。 例如,如果符号路径包括 C:\Dir1 ,并且调试器正在查找 DLL 的符号信息,则调试器将在以下目录中查找符号信息(按顺序列出):
C:\Dir1\symbols\dllC:\Dir1\dllC:\Dir1
然后,调试器对符号路径中的每个目录重复此过程。 最后,调试器在当前目录中查找,然后在当前目录中附加 ..\dll。 调试器根据 ..\dll调试的二进制文件追加 、 ..\exe或 ..\sys。
符号文件具有日期和时间戳。 调试器始终查找与它所调试的二进制文件上的时间戳匹配的符号。 无需担心调试器使用在此序列中首先找到的错误符号。 有关符号文件不可用时响应的详细信息,请参阅 匹配符号名称。
设置符号路径的一种方法是输入 .sympath 命令。 有关设置符号路径的其他方法,请参阅本主题后面的 控制符号路径 。
在本地缓存符号
应在本地缓存符号。 在本地缓存符号的一种方法是在符号路径中包含 cache*; 或 cache*localsymbolcache;*。
如果在符号路径中包含字符串 cache*;,则从该字符串右侧的任何元素加载的符号都存储在本地计算机的默认符号缓存目录中。 例如,以下命令告知调试器从名为 \\someshare 的网络共享中获取符号,并将符号缓存在本地计算机上的默认位置。
.sympath cache*;\\someshare
如果在符号路径中包含字符串 cache*localsymbolcache;,则从该字符串右侧出现的任何元素加载的符号都存储在 localsymbolcache 目录中。
例如,以下命令通知调试器从网络共享 \\someshare 中获取符号,并将这些符号缓存在 c:\MySymbols 目录中。
.sympath cache*C:\MySymbols;\\someshare
使用符号服务器:srv*
如果你已连接到 Internet 或公司网络,则访问符号的最有效方法是使用符号服务器,例如公共 Microsoft 公共符号服务器。 可以通过在符号路径中使用以下字符串之一来使用符号服务器。
-
字符串
srv*如果在符号路径中包含字符串
srv*,调试器将使用符号服务器从默认符号存储中获取符号。 例如,以下命令告知调试器从默认符号存储中获取符号。 这些符号不会缓存在本地计算机上。.sympath srv* -
字符串
srv*symbolstore如果在符号路径中包含字符串
srv*symbolstore,调试器将使用符号服务器从 符号存储中获取符号。 例如,以下命令告知调试器从 Microsoft 符号服务器 存储中获取符号。 这些符号不会缓存在本地计算机上。.sympath srv*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols -
字符串
srv*localsymbolcache*symbolstore如果在符号路径中包含字符串
srv*localcache*symbolstore,调试器将使用符号服务器从 符号存储 中获取符号,并将其缓存在 localcache 目录中。 例如,以下命令告知调试器从 Microsoft 符号服务器 存储中获取符号并在 中c:\MyServerSymbols缓存符号。.sympath srv*C:\MyServerSymbols*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
如果计算机上有手动放置符号的目录,请不要使用该目录作为从符号服务器获取的符号的缓存。 相反,请使用两个不同的目录。 例如,可以手动将符号放在 c:\MyRegularSymbols 中,然后指定用 c:\MyServerSymbols 缓存从服务器获取的符号。 下面的示例演示如何在符号路径中指定这两个目录。
.sympath C:\MyRegularSymbols;srv*C:\MyServerSymbols*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
有关符号服务器和符号存储的详细信息,请参阅 自定义符号存储和符号服务器。
合并 cache* 和 srv*
如果在符号路径中包含字符串 cache*;,则从该字符串右侧的任何元素加载的符号都存储在本地计算机的默认符号缓存目录中。 例如,以下命令告知调试器从 Microsoft 符号服务器 存储中获取符号并将其缓存在默认符号缓存目录中。
.sympath cache*;srv*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
如果在符号路径中包含字符串 cache*localsymbolcache;,则从该字符串右侧出现的任何元素加载的符号都存储在 localsymbolcache 目录中。
例如,以下命令告知调试器从 Microsoft 符号服务器 存储中获取符号,并在目录中缓存符号 c:\MySymbols 。
.sympath cache*C:\MySymbols;srv*https://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
使用 AgeStore 减小缓存大小
可以使用 AgeStore 工具删除早于指定日期的缓存文件,或删除足够的旧文件,以便生成的缓存大小小于指定数量。 如果下游存储太大,这种缓存文件的清理非常有用。
延迟符号加载
调试器的默认行为是使用 延迟符号加载,也称为 延迟符号加载。 这种加载意味着在需要符号之前不会加载符号。
更改符号路径(例如,使用 .sympath 命令)时,将延迟重新加载具有导出符号的所有模块。
如果新路径不再包含用于加载 PDB 符号 的原始路径,则延迟重新加载具有完整 PDB 符号的模块的符号。 如果新路径仍包含 PDB 符号文件的原始路径,则不会延迟重新加载这些符号。
可以使用 -s 命令行选项关闭 CDB 和 KD 中的延迟符号加载。 还可以通过使用 ld load symbols 命令或 .reload 模块命令 和 /f 选项来强制加载符号。
Azure DevOps Services Artifacts
符号服务器可用于 Azure DevOps Services 中的 Azure Artifacts。 若要了解如何在 WinDbg 中使用 Azure Artifacts,请参阅使用 WinDbg 中的符号进行调试。 有关 Azure 生成的符号的一般信息,请参阅 符号概述。
控制符号路径
若要控制符号路径,可以选择以下方法之一:
-
使用 .symfix set 符号存储路径命令 设置公共 Microsoft 符号服务器的默认路径,该服务器在许多情况下都有效。 若要设置本地缓存,只需键入
.symfix C:\MyCache。 -
使用 .sympath 命令 可显示、设置、更改或追加到路径。
-
在启动调试器之前,请使用
_NT_SYMBOL_PATH和_NT_ALT_SYMBOL_PATH环境变量 来设置路径。 符号路径是通过在_NT_ALT_SYMBOL_PATH后附加_NT_SYMBOL_PATH创建的。 通常,路径通过 设置。_NT_SYMBOL_PATH但是,你可能希望在特殊情况下使用_NT_ALT_SYMBOL_PATH替代这些设置,例如,如果你有共享符号文件的专用版本。 如果尝试通过这些环境变量添加无效目录,调试器将忽略此目录。 -
启动调试器时,使用 -y 命令行选项 设置路径。
-
仅在 WinDbg 中,可以使用 文件|符号“文件路径”命令 或按
CTRL+S可显示、设置、更改或追加到路径。
如果使用 -sins 命令行选项,调试器将忽略符号路径环境变量。
疑难解答
使用 !sym noisy 或 -nWinDbg Command-Line 选项 在加载符号时显示其他详细信息。 有关其他故障排除策略,请参阅 验证符号。
另请参阅
南来地,北往的,上班的,下岗的,走过路过不要错过!
======================个性签名=====================
之前认为Apple 的iOS 设计的要比 Android 稳定,我错了吗?
下载的许多客户端程序/游戏程序,经常会Crash,是程序写的不好(内存泄漏?刚启动也会吗?)还是iOS本身的不稳定!!!
如果在Android手机中可以简单联接到ddms,就可以查看系统log,很容易看到程序为什么出错,在iPhone中如何得知呢?试试Organizer吧,分析一下Device logs,也许有用.


