学习Spring入门总结
什么是Spring
spring是一个轻量型的控制反转/依赖注入(IOC)和面向切面编程(AOP)的框架
-
spring在spring家族中起到了一个呈上启下的作用,有七大模块
spring想做的事情是什么?
-
spring想要管理整个项目中所有的类和接口,并对他们进行控制定义(赋值/创建),但是在spring项目的眼里项目是一个程序,里面的类和接口都是一个个的组件,然后根据具体的业务需求对类和接口进行一个组装配对
-
起到一个企业级管理的作用
Spring环境的一个搭建
-
导入搭建spring框架所必须要用到的jia包
-
配置spring的核心控制配置文(容器)
-
配置文件里面的每一个bean都是一个组件也可以称为是一个类或者接口
-
核心类:
-
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(“核心配置文件”)返回一个上下文对象
-
context.getBean("配置文件中配置的每个组件的唯一ID")方法 ,获取到配置文件中的类/组件
-
拿到类之后就可以操作类下的属性以及方法
案例:
<!--墨盒组装 -->
<bean id="BlackCartridge" class="com.cartridgeDao.cartridgeimpl.BlackCartridge"></bean>
<bean id="ColoursCartridge" class="com.cartridgeDao.cartridgeimpl.ColoursCartridge"></bean>
<!--纸张组装 -->
<bean id="A4page" class="com.PageDao.pagesizeimpl.A4page"></bean>
<bean id="B5page" class="com.PageDao.pagesizeimpl.B5page"></bean>
<!--打印机-->
<bean id="Print" class="com.print.Print">
<property name="cartridge" ref="BlackCartridge"></property>
<property name="pageSize" ref="A4page"></property>
</bean> -
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext classPathXmlApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-manager.xml");
CRUD crud = (CRUD)classPathXmlApplicationContext.getBean("CRUD");
crud.getA01BusinessDao().query();
SpringAOP
什么是springAop?
-
面向切面编程的一种方式
-
对方法进行增加,可以在执行核心方法前后执行不同的方法
-
底层核心是动态代理机制,可以参考代理模式
AOP的本质:
-
不改变原有业务逻辑的情况下增强横切逻辑,横切逻辑代码往往都是权限校验代码、日志代码、事务控制代码、性能监控代码
什么是面向切面编程?
-
是一种通过预编译和运行期动态代理的方式实现在不修改源代码的情况下给程序动态添加功能的技术
AOP切面配置
-
导入jia包
-
写一个增加类
-
配置前要导入头文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd"> -
-
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="LoggerAop">
<aop:pointcut id="Loggeraop" expression="execution(* com.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="Loggeraop"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="Loggeraop"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
IOC的注入方式
-
第一种方式:通过拿到Dao层的接口,GET/SET方法注入
-
第二种方式:通过构造方法注入
-
第三种方式:通过下标法注入,可以注入多个接口或者参数
-
第四种方式:通过类型方法注入
-
第五种方式:通过P的命名空间进行注入(底层也是通过GET,SET方法注入)
-
注入前必须引入头文件种
-
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"案例:
-
<bean id="StudentDaoImlp" class="com.dao.impl.StudentDaoImlp"></bean
<bean id="StudentServiceImpl" class="com.service.impl.StudentServiceImpl" p:studentDao-ref="StudentDaoImlp" >
-
注入参数的升级
-
基本数据类型
-
<property name="studentNo" value="1"></property>
<property name="resultScores" value="100"></property> -
数组注入方式
-
<!--数组的注入方式-->
<property name="ids">
<array>
<value>1</value>
<value>2</value>
<value>3</value>
<value>4</value>
</array>
</property> -
集合注入方式
-
<!--集合的注入方式-->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>3</value>
<value>4</value>
<value>5</value>
<value>6</value>
</list>
</property> -
-
<!--Map注入方式-->
<property name="map">
<map key-type="java.lang.String" value-type="java.lang.String">
<entry key="kkk" value="111"></entry>
<entry key="jjj" value="222"></entry>
</map>
</property>
Mybatis与Spring的一个简单整合
-
通过配置Mybatis配置文件
-
导入MybatisjiaBao
-
并配置映射文件,对应的Dao层实现类,并将其命名空间与Dao接口进行一个绑定
-
在映射文件种写动态SQL实现对象关系映射
-
在Dao接口中写方法。与映射文件id保持一致,并在Dao接口的实现类中利用Mybatis的核心类获取到接口类文件,并调下面的方法
-
在Service层创建对应的接口,并在接口的实现类调取Dao层的接口,注入方式选择创建GET/SET方法以及构造方法
-
此时在Spring的核心配置文件中,管理Dao层的实现类,管理Service层的实现类,并将Dao层的实现类注入进Service层实现类里的Dao接口。
-
在Service层的实现类中直接用dao层接口调下面的核心方法返回出去
-
在Test类中通过spring的核心类 new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-manage.xml") ,通过返回的对象调getBean("获取的类")然后调用其Service层实现类中的方法。
-
给每个程序加强
-
配置文件中引入springAop所需要的头文件
-
创建一个加强类
-
并将此加强类拿到springIoc容器中管理
-
给此类中的方法绑定在 XXX 包下,该包下的所有方法执行时此加强类中的方法都会执行
案例:
<!--AOP切面配置-->
<bean id="LoggerAop" class="com.util.LoggerAop"></bean>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="LoggerAop">
<aop:pointcut id="Loggeraop" expression="execution(* com.service.*.*(..))"/>
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="Loggeraop"></aop:before>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="Loggeraop"></aop:after>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
SpringAOP的几种增强方式:
Pointcut(切入点)它指的是那些已经把增强代码加入到业务主线进来之后的连接点。由上图中,我们看出表现层 transfer 方法就只是连接点,因为判断访问权限的功能并没有对其增强。
Advice(通知/增强)
前置通知 后置通知 异常通知 最终通知 环绕通知。
before、 after、after-throwing、<aop:around method="aroundPrintLog" pointcut-ref="pt1">/aop:around
Proxy(代理)
它指的是一个类被AOP织入增强后,产生的代理类。即代理对象。
Aspect(切面)
它指定是增强的代码所关注的方面,把这些相关的增强代码定义到一个类中,这个类就是切面类。例如,事务切面,它里面定义的方法就是和事务相关的,像开启事务,提交事务,回滚事务等等,不会定义其他与事务无关的方法。我们前面的案例中 TrasnactionManager 就是一个切面。
IOC 注解
-
IOC四种注解:
对象初始化注解:
-
@Component 通用注解
-
@Controller 控制层使用
-
@Service 服务层使用
-
@Repository 数据访问层的注解
依赖注入:
-
@Resource 这个注解属于J2EE的,默认按name注入,可以通过name和type属性进行选择性注入
-
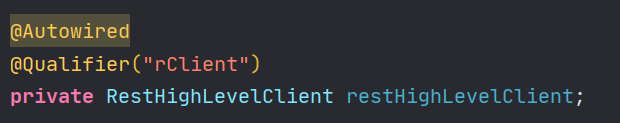
@Autowired spring的注解,默认按type注入
-
@Qualifier spring的注解,按名字注入 一般当出现两个及以上bean时,不知道要注入哪个,作为@Autowired()的修饰用
-
AOP注解
@Pointcut(“execution(public * *(…))”) private void anyPublicOperation() {} //如果方法执行连接点表示执行,anyPublicOperation将匹配任何公共方法。
案例:
总结:
-
使用注解需要在IOC容器中以扫描包的方式扫描这些注解
-
使用AOP注解必须在IOC容器中开启对AOP注解的支持
-
<!--扫描注解,以扫描包的方式-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com"/>
<!--开启对AOP配置注解的支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
以上是我学习Spring框架自我总结内容


