Python格式化字符串f-string f"{}{}{}"详细介绍
简介
f-string,亦称为格式化字符串常量(formatted string literals),是Python3.6新引入的一种字符串格式化方法,该方法源于PEP 498 – Literal String Interpolation,主要目的是使格式化字符串的操作更加简便。f-string在形式上是以 f 或 F 修饰符引领的字符串(f'xxx'或 F'xxx'),以大括号 {} 标明被替换的字段;f-string在本质上并不是字符串常量,而是一个在运行时运算求值的表达式:
While other string literals always have a constant value, formatted strings are really expressions evaluated at run time.
(与具有恒定值的其它字符串常量不同,格式化字符串实际上是运行时运算求值的表达式。)
—— Python Documentation
f-string在功能方面不逊于传统的%-formatting语句和str.format()函数,同时性能又优于二者,且使用起来也更加简洁明了,因此对于Python3.6及以后的版本,推荐使用f-string进行字符串格式化。
用法
此部分内容主要参考以下资料:
Python Documentation – Formatted String Literals
Python Documentation – Format String Syntax
PEP 498 – Literal String Interpolation
Python 3’s f-Strings: An Improved String Formatting Syntax (Guide)
python3 f-string格式化字符串的高级用法
Python 3: An Intro to f-strings
简单使用
f-string用大括号 {} 表示被替换字段,其中直接填入替换内容:
>>> name = 'Eric' >>> f'Hello, my name is {name}' 'Hello, my name is Eric' >>> number = 7 >>> f'My lucky number is {number}' 'My lucky number is 7' >>> price = 19.99 >>> f'The price of this book is {price}' 'The price of this book is 19.99'
表达式求值与函数调用
f-string的大括号 {} 可以填入表达式或调用函数,Python会求出其结果并填入返回的字符串内:
>>> f'A total number of {24 * 8 + 4}' 'A total number of 196' >>> f'Complex number {(2 + 2j) / (2 - 3j)}' 'Complex number (-0.15384615384615388+0.7692307692307692j)' >>> name = 'ERIC' >>> f'My name is {name.lower()}' 'My name is eric' >>> import math >>> f'The answer is {math.log(math.pi)}' 'The answer is 1.1447298858494002'
引号、大括号与反斜杠
f-string大括号内所用的引号不能和大括号外的引号定界符冲突,可根据情况灵活切换 ' 和 ":
>>> f'I am {"Eric"}' 'I am Eric' >>> f'I am {'Eric'}' File "<stdin>", line 1 f'I am {'Eric'}' ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax
若 ' 和 " 不足以满足要求,还可以使用 ''' 和 """:
>>> f"He said {"I'm Eric"}" File "<stdin>", line 1 f"He said {"I'm Eric"}" ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax >>> f'He said {"I'm Eric"}' File "<stdin>", line 1 f'He said {"I'm Eric"}' ^ SyntaxError: invalid syntax >>> f"""He said {"I'm Eric"}""" "He said I'm Eric" >>> f'''He said {"I'm Eric"}''' "He said I'm Eric"
大括号外的引号还可以使用 \ 转义,但大括号内不能使用 \ 转义:
>>> f'''He\'ll say {"I'm Eric"}''' "He'll say I'm Eric" >>> f'''He'll say {"I\'m Eric"}''' File "<stdin>", line 1 SyntaxError: f-string expression part cannot include a backslash
f-string大括号外如果需要显示大括号,则应输入连续两个大括号 {{ 和 }}:
>>> f'5 {"{stars}"}' '5 {stars}' >>> f'{{5}} {"stars"}' '{5} stars'
上面提到,f-string大括号内不能使用 \ 转义,事实上不仅如此,f-string大括号内根本就不允许出现 \。如果确实需要 \,则应首先将包含 \ 的内容用一个变量表示,再在f-string大括号内填入变量名:
>>> f"newline: {ord('\n')}" File "<stdin>", line 1 SyntaxError: f-string expression part cannot include a backslash >>> newline = ord('\n') >>> f'newline: {newline}' 'newline: 10'
多行f-string
f-string还可用于多行字符串:
>>> name = 'Eric' >>> age = 27 >>> f"Hello!" \ ... f"I'm {name}." \ ... f"I'm {age}." "Hello!I'm Eric.I'm 27." >>> f"""Hello! ... I'm {name}. ... I'm {age}.""" "Hello!\n I'm Eric.\n I'm 27."
自定义格式:对齐、宽度、符号、补零、精度、进制等
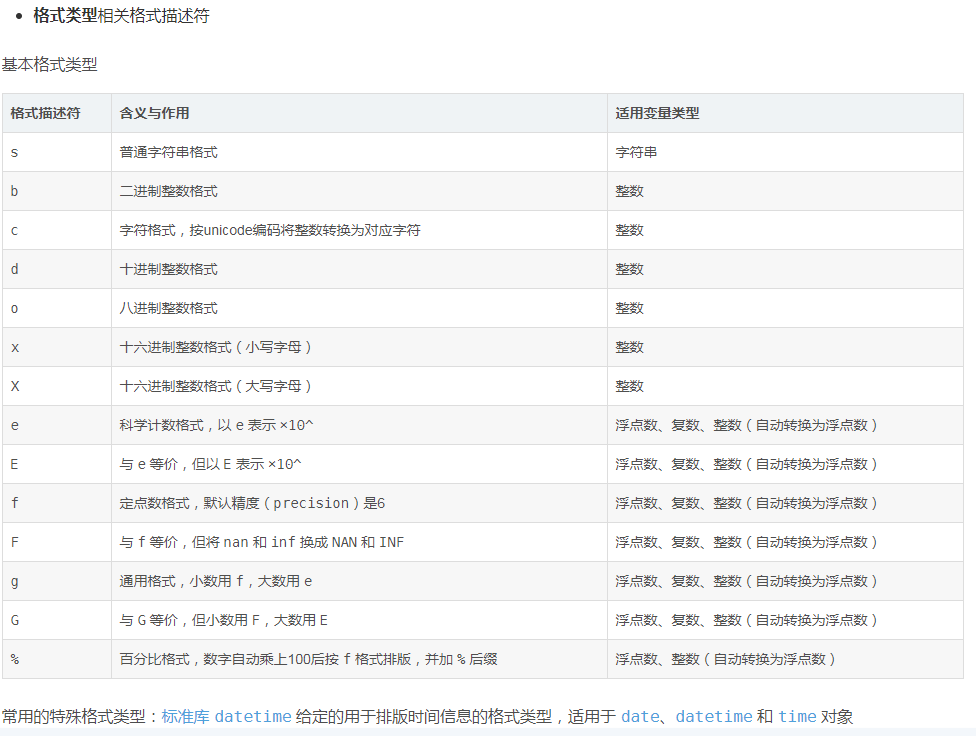
f-string采用 {content:format} 设置字符串格式,其中 content 是替换并填入字符串的内容,可以是变量、表达式或函数等,format是格式描述符。采用默认格式时不必指定 {:format},如上面例子所示只写 {content} 即可。
关于格式描述符的详细语法及含义可查阅Python官方文档,这里按使用时的先后顺序简要介绍常用格式描述符的含义与作用:
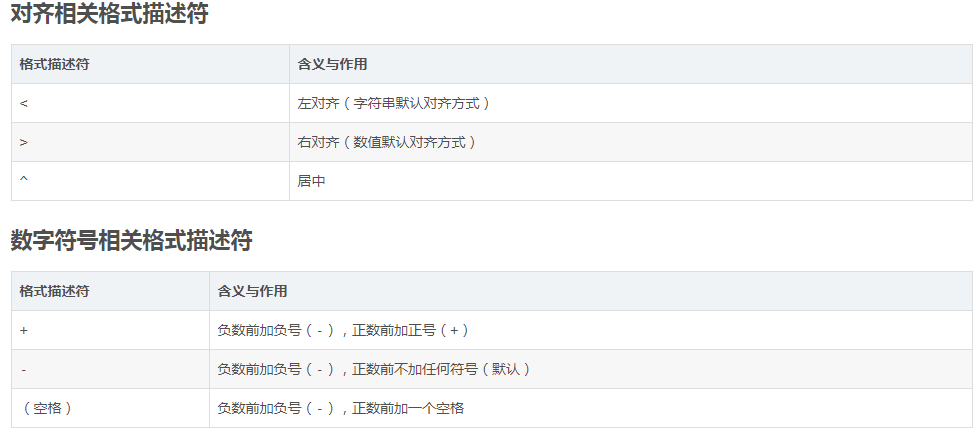
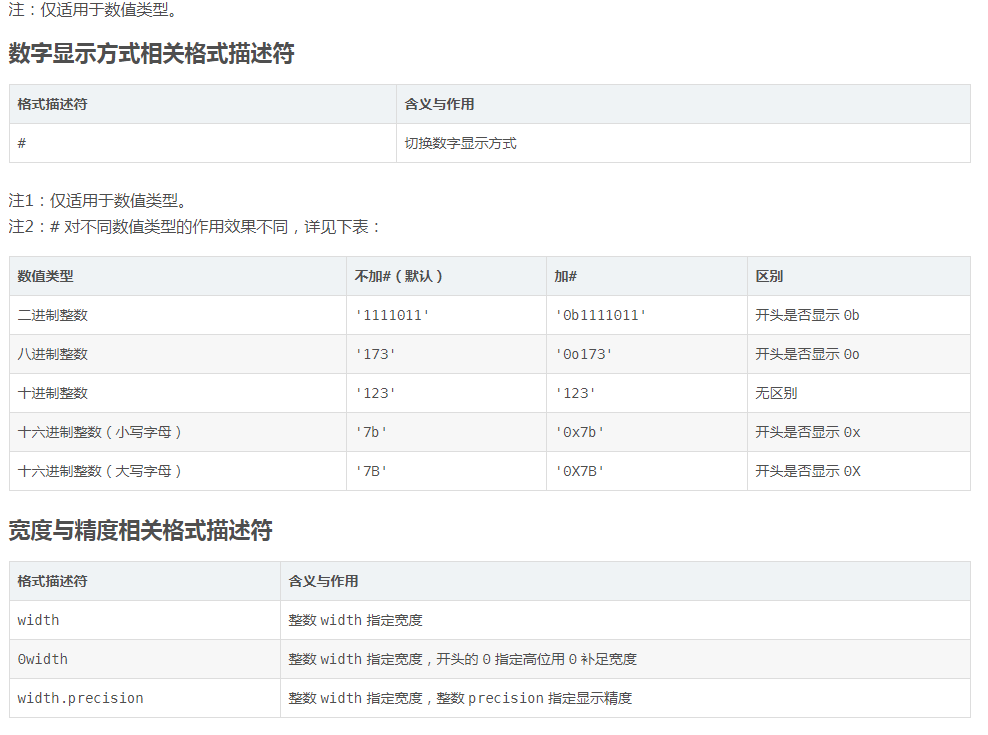
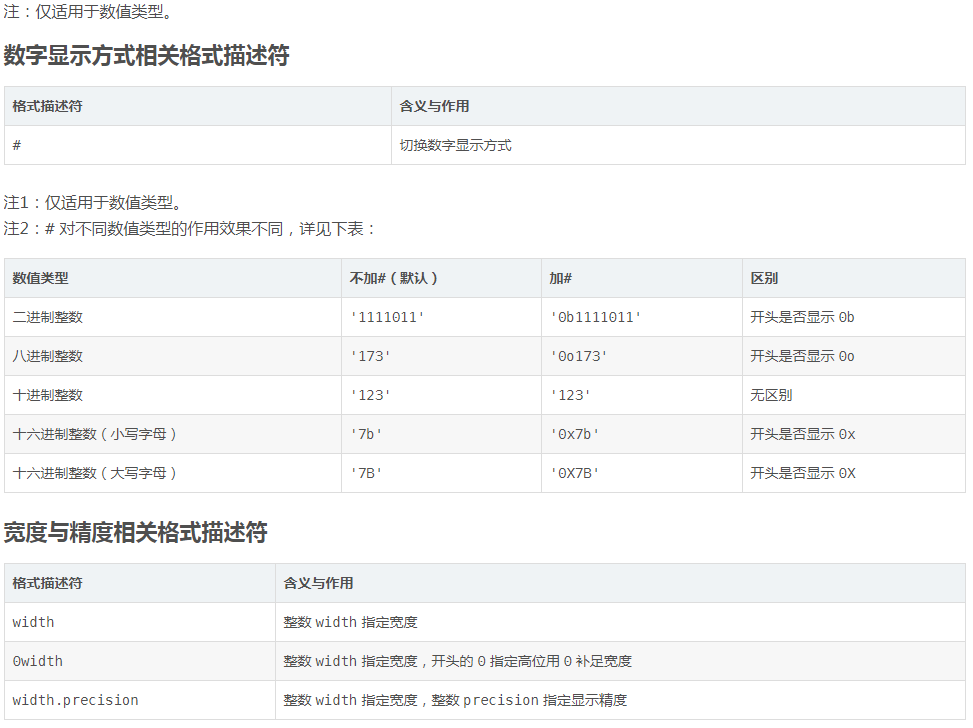
注1:0width 不可用于复数类型和非数值类型,width.precision 不可用于整数类型。
注2:width.precision 用于不同格式类型的浮点数、复数时的含义也不同:用于 f、F、e、E 和 % 时 precision 指定的是小数点后的位数,用于 g 和 G 时 precision 指定的是有效数字位数(小数点前位数+小数点后位数)。
注3:width.precision 除浮点数、复数外还可用于字符串,此时 precision 含义是只使用字符串中前 precision 位字符。
示例:
>>> a = 123.456 >>> f'a is {a:8.2f}' 'a is 123.46' >>> f'a is {a:08.2f}' 'a is 00123.46' >>> f'a is {a:8.2e}' 'a is 1.23e+02' >>> f'a is {a:8.2%}' 'a is 12345.60%' >>> f'a is {a:8.2g}' 'a is 1.2e+02' >>> s = 'hello' >>> f's is {s:8s}' 's is hello ' >>> f's is {s:8.3s}' 's is hel '
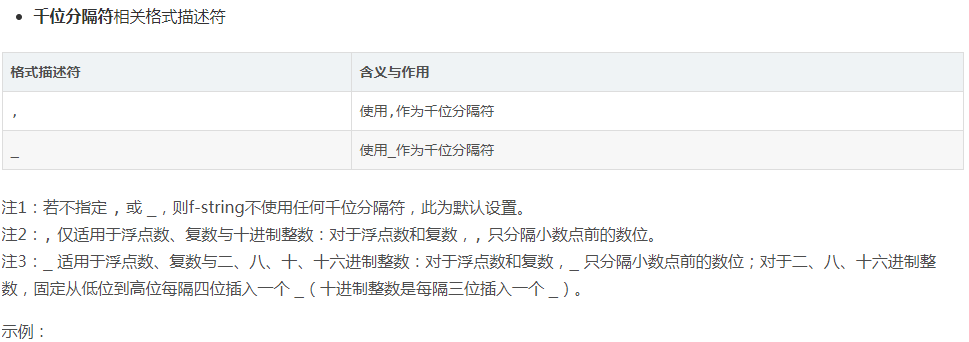
>>> a = 1234567890.098765 >>> f'a is {a:f}' 'a is 1234567890.098765' >>> f'a is {a:,f}' 'a is 1,234,567,890.098765' >>> f'a is {a:_f}' 'a is 1_234_567_890.098765' >>> b = 1234567890 >>> f'b is {b:_b}' 'b is 100_1001_1001_0110_0000_0010_1101_0010' >>> f'b is {b:_o}' 'b is 111_4540_1322' >>> f'b is {b:_d}' 'b is 1_234_567_890' >>> f'b is {b:_x}' 'b is 4996_02d2'
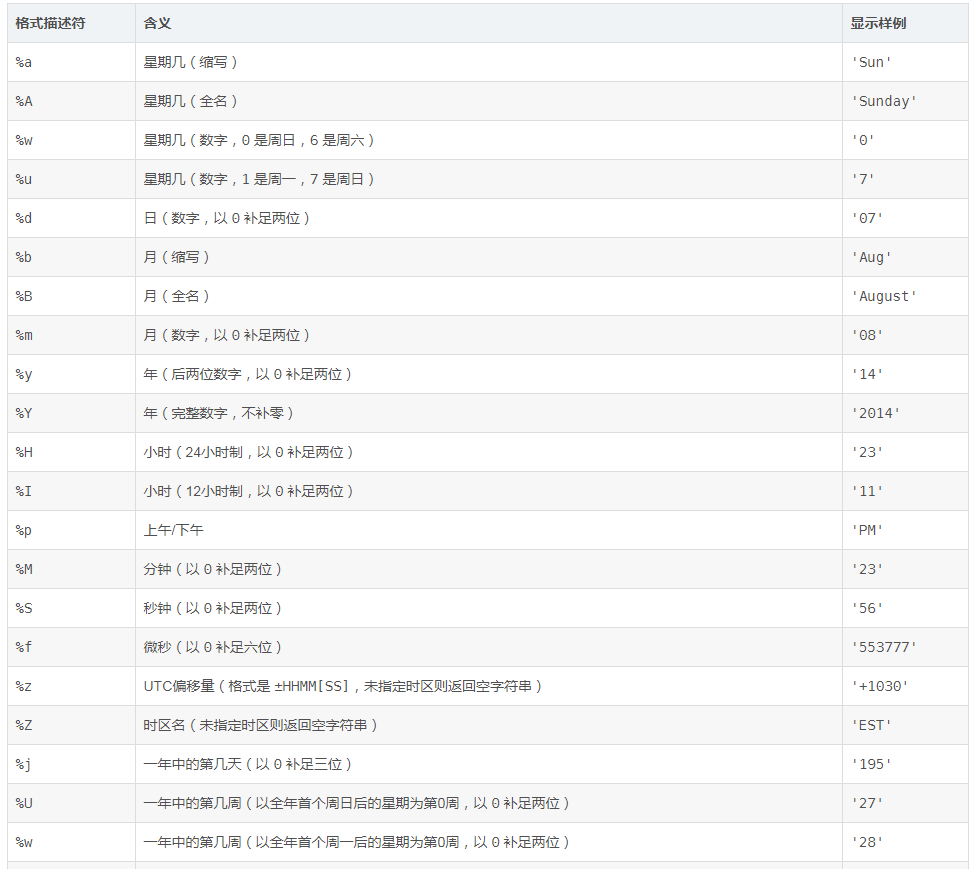

>>> a = 1234 >>> f'a is {a:^#10X}' # 居中,宽度10位,十六进制整数(大写字母),显示0X前缀 'a is 0X4D2 ' >>> b = 1234.5678 >>> f'b is {b:<+10.2f}' # 左对齐,宽度10位,显示正号(+),定点数格式,2位小数 'b is +1234.57 ' >>> c = 12345678 >>> f'c is {c:015,d}' # 高位补零,宽度15位,十进制整数,使用,作为千分分割位 'c is 000,012,345,678' >>> d = 0.5 + 2.5j >>> f'd is {d:30.3e}' # 宽度30位,科学计数法,3位小数 'd is 5.000e-01+2.500e+00j' >>> import datetime >>> e = datetime.datetime.today() >>> f'the time is {e:%Y-%m-%d (%a) %H:%M:%S}' # datetime时间格式 'the time is 2018-07-14 (Sat) 20:46:02'
- lambda表达式
f-string大括号内也可填入lambda表达式,但lambda表达式的 : 会被f-string误认为是表达式与格式描述符之间的分隔符,为避免歧义,需要将lambda表达式置于括号 () 内:
>>> f'result is {lambda x: x ** 2 + 1 (2)}' File "<fstring>", line 1 (lambda x) ^ SyntaxError: unexpected EOF while parsing >>> f'result is {(lambda x: x ** 2 + 1) (2)}' 'result is 5' >>> f'result is {(lambda x: x ** 2 + 1) (2):<+7.2f}'
综合示例
>>> a = 1234
>>> f'a is {a:^#10X}' # 居中,宽度10位,十六进制整数(大写字母),显示0X前缀
'a is 0X4D2 '
>>> b = 1234.5678
>>> f'b is {b:<+10.2f}' # 左对齐,宽度10位,显示正号(+),定点数格式,2位小数
'b is +1234.57 '
>>> c = 12345678
>>> f'c is {c:015,d}' # 高位补零,宽度15位,十进制整数,使用,作为千分分割位
'c is 000,012,345,678'
>>> d = 0.5 + 2.5j
>>> f'd is {d:30.3e}' # 宽度30位,科学计数法,3位小数
'd is 5.000e-01+2.500e+00j'
>>> import datetime
>>> e = datetime.datetime.today()
>>> f'the time is {e:%Y-%m-%d (%a) %H:%M:%S}' # datetime时间格式
'the time is 2018-07-14 (Sat) 20:46:02'
lambda表达式
f-string大括号内也可填入lambda表达式,但lambda表达式的 : 会被f-string误认为是表达式与格式描述符之间的分隔符,为避免歧义,需要将lambda表达式置于括号 () 内:
>>> f'result is {lambda x: x ** 2 + 1 (2)}'
File "<fstring>", line 1
(lambda x)
^
SyntaxError: unexpected EOF while parsing
>>> f'result is {(lambda x: x ** 2 + 1) (2)}'
'result is 5'
>>> f'result is {(lambda x: x ** 2 + 1) (2):<+7.2f}'
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「vitrovitro」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/yizhuanlu9607/java/article/details/89530982





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 震惊!C++程序真的从main开始吗?99%的程序员都答错了
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通
2019-05-27 net start mysql 发生系统错误2 系统找不到指定的文件
2019-05-27 电信说的几兆带宽和自己看到的下载/上传速度有什么关系?
2019-05-27 上传速度计算方法
2019-05-27 shell 判断文件夹或文件是否存在
2019-05-27 Linux查看日志常用命令
2019-05-27 Centos出现-bash: unzip: command not found的解决办法
2019-05-27 物理cpu与逻辑cpu概述