Improved deep reinforcement learning for robotics through distribution-based experience retention
发表时间:2016(IROS 2016)
文章要点:这篇文章提出了experience replay方法的改进,让experience的分布介于当前policy和均匀分布之间,作者做实验发现这个时候的效果是最好的(the ideal distribution is likely to be somewhere between the distribution that results from simply following the most recent policy with some exploration and a uniform distribution over the state-action space.)。
具体的,作者保留了两个buffer,一个是标准的replay buffer \(D_\pi\)。另一个buffer \(D_U\)用同样的样本通过overwritten的方式来近似状态动作空间的均匀分布,相当于避免了在环境中探索就得到了一个均匀分布。然后训练的时候从两个buffer里一起采样。因为训练过程中,探索下降的很快(during the training the amount of exploration is reduced too far, the performance of the controller policy will decrease.),这样既可以保证样本多样性,避免overfitting(RL with deep neural network function approximators can fail when the experiences that are used to train the neural networks are not diverse enough. most minibatch optimization algorithms are based on the assumption of independent and identically distributed data),而且可以减少高的探索带来的危害(Maintaining high levels of exploration might place infeasible demands on physical systems such as robots.)。
而这个用来近似均匀分布的buffer \(D_U\),通过overwritten来实现,具体就是等buffer满了之后,新来的experience会覆盖掉当前buffer里和其他experience最相似的样本。作者通过计算平均相似度得到
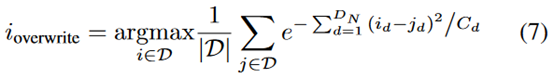
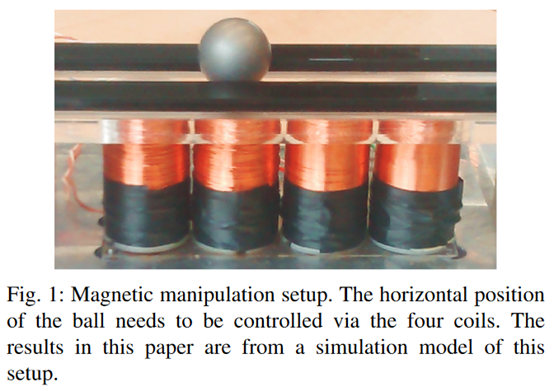
然后采样的时候从\(D_U\)里采\(\alpha\)的比例,从\(D_\pi\)里采\(1-\alpha\)的比例,作者直接取的0.5。作者说,这其实也是generalization和task performance的一种trade-off。作者在一个物理问题上做的实验,效果还可以

最后画了一下状态的分布情况

总结:可能有一定的道理,不过文章的符号有点混乱,有的图也没有解释清楚。
疑问:里面比较了TDE算法,但是没介绍。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号