Model-based Reinforcement Learning: A Survey

发表时间:2021
文章要点:一篇综述,主要从dynamics model learning,planning-learning integration和implicit model-based RL三个方面介绍。dynamics model learning包括stochasticity, uncertainty, partial observability, non-stationarity, state abstraction, and temporal abstraction等问题,integration of planning and learning主要讲如何把model和问题结合起来,用planning解决问题,implicit approach to model-based RL主要介绍如何学习planning,就是说planning不是一个固定的规则,也是通过优化的方式学出来的。最后文章还介绍了一点model based RL的优点,比如data efficiency, targeted exploration, stability, transfer, safety and explainability。
文章把具体方法分成Model-based RL with a learned model,Model-based RL with a known model和Planning over a learned model

这里Planning over a learned model就是说学了model之后就只有planning,没有RL的部分,所以有的也不把这个类别当成model based RL,因为只有model based planning。
对于model来说,有三个类型Forward model,Backward/reverse model,Inverse model。
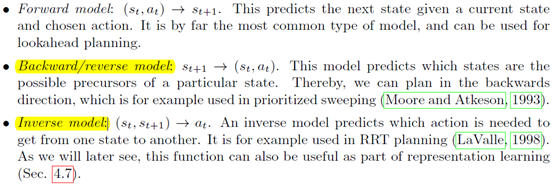
这里一个reverse一个inverse还挺容易搞混。
Model的估计方法作者区分了parametric and non-parametric methods,以及exact and approximate methods。通常有统计假设的都算是参数方法,比如线性回归这些,没有参数假设的都算是非参方法,比如高斯过程这种。然后exact就是指准确的值,比如查表的方法,或者replay buffer全存下来这种。approximate methods顾名思义就比如线性回归,神经网络这种的。
然后就引出了model的一系列问题,比如Region in which the model is valid,Stochasticity,Uncertainty,Partial observability,Non-stationarity,Multi-step Prediction,State abstraction。
然后下一部分就是介绍怎么把planning用上去。
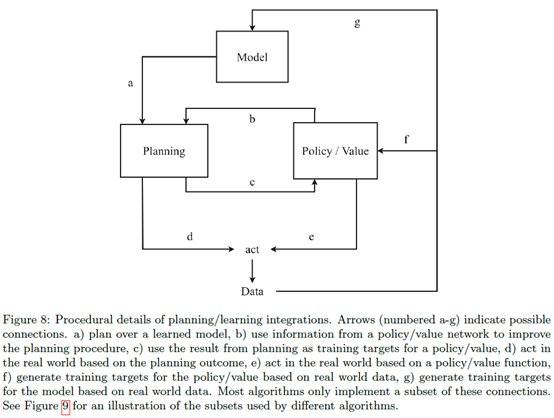
这部分回答了四个问题

比较常见的几个问题,里面提到的做法也是很常见
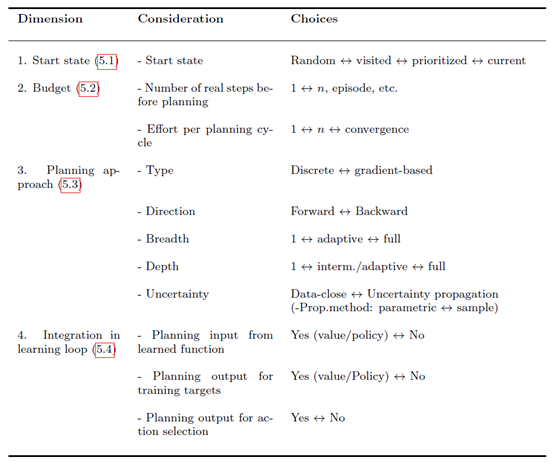
这里我觉得第二个问题是很值得做一做的,这个trade off有点意思。这个问题又可以分成两个问题,When to start planning? How much time to spend on planning?
最后Implicit Model-based Reinforcement Learning这部分,提出了一个隐式学习的观点,比如整个问题都可以看做是model free方法,里面的各个模块只是来解决这个问题的隐式方法,我们并不需要作区分(In other words, the entire model based RL procedure (model learning, planning, and possibly integration in value/policy approximation) can from the outside be seen as a model-free RL problem)。
这就引出了implicit model-based RL,比如Value equivalent models是说模型是隐式的/抽象的,我不管你具体怎么做,只要value对的上就行(forward dynamics might be complicated to learn, but the aspects of the dynamics that are relevant for value prediction might be much smoother and easier to learn)。文中举的例子是Value Iteration Networks (VIN)和Universal Planning Networks (UPN)。
再比如Learning to plan,就是说planning也不是制定好的方式,比如MCTS之类的,而是像policy一样去学出来的(The idea is to optimize our planner over a sequence of tasks to eventually obtain a better planning algorithm, which is a form of meta-learning)。文中举的例子是MCTSNets,Imagination-augmented agents (I2A) 和Imagination-based planner (IBP)。
最后就是结合起来,model和planning一起学(If we specify a parameterized differentiable model and a parameterized differentiable planning procedure, then we can optimize the resulting computational graph jointly for the model and the planning operations.)。文中举的例子是TreeQN和Deep Repeated ConvLSTM (DRC)。
最后结尾说了下model based RL的好处
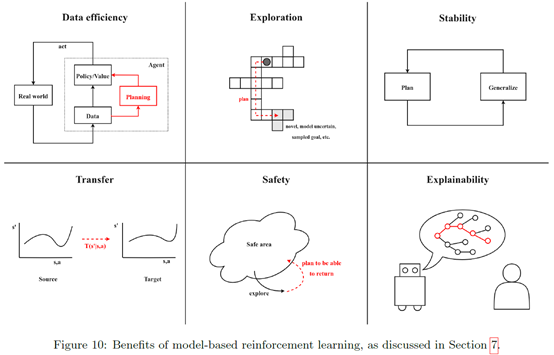
以及一些劣势,比如additional computation,unstable due to uncertainty and approximation errors in the model.
总结:很新的一篇综述,各个方向基本都列全了的。有启发的一点是可以用model去做exploration,发现option,或者subgoal,感觉这也是一个很好的点子,毕竟model里面是safe的。而且planning可以看成一种deep exploration,而像ϵ-greedy这种就是local exploration,显然deep exploration会在某些情况下有优势(Planning may identify temporally correlated action sequences that perform deep exploration towards new reward regions, which local exploration methods would fail to identify due to jittering behaviour)。
然后How much planning budget do we allocate for planning and real data collection这个问题也值得做。
疑问:里面这个Gaussian processes算非参数方法,这个要去看看具体是怎么分类参数和非参的。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号