872. Leaf-Similar Trees 叶子顺序遍历是否相等
Consider all the leaves of a binary tree, from left to right order, the values of those leaves form a leaf value sequence.
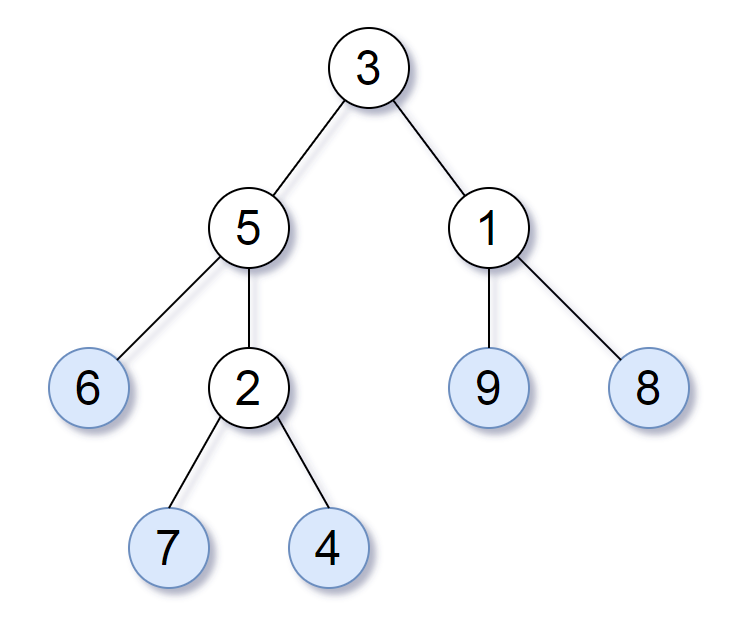
For example, in the given tree above, the leaf value sequence is (6, 7, 4, 9, 8).
Two binary trees are considered leaf-similar if their leaf value sequence is the same.
Return true if and only if the two given trees with head nodes root1 and root2 are leaf-similar.
Example 1:
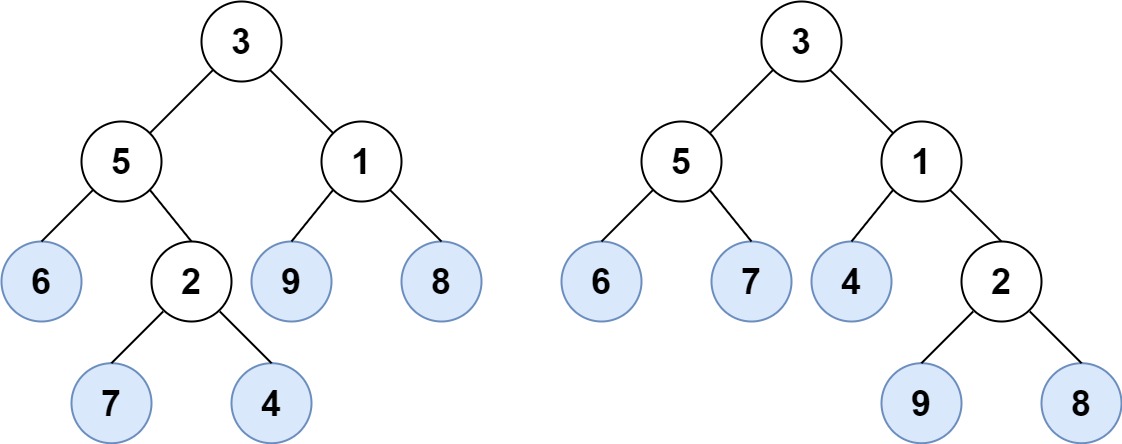
Input: root1 = [3,5,1,6,2,9,8,null,null,7,4], root2 = [3,5,1,6,7,4,2,null,null,null,null,null,null,9,8]
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: root1 = [1], root2 = [1]
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: root1 = [1], root2 = [2]
Output: false
Example 4:
Input: root1 = [1,2], root2 = [2,2]
Output: true
Example 5:
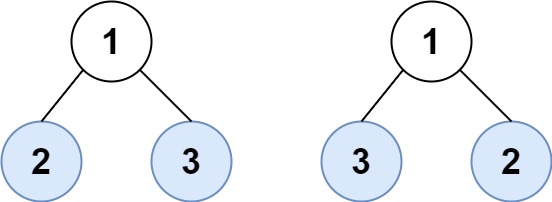
Input: root1 = [1,2,3], root2 = [1,3,2] Output: false
没啥好说的,就是叶子遍历(随便一种遍历顺序)的一个无脑变形罢了……
参考:https://leetcode.com/problems/leaf-similar-trees/discuss/154169/JAVA-very-Easy-understand-solution
class Solution {
public boolean leafSimilar(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList();
ArrayList<Integer> list2 = new ArrayList();
helper(root1, list1);
helper(root2,list2);
if(list1.size() != list2.size()){
return false;
}
for(int i = 0; i < list1.size(); i++){
if(list1.get(i) != list2.get(i)){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private void helper(TreeNode root, ArrayList<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
list.add(root.val);
}
helper(root.left, list);
helper(root.right, list);
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号