.NET中Dictionary<TKey, TValue>浅析
.NET中Dictionary<TKey, Tvalue>是非常常用的key-value的数据结构,也就是其实就是传说中的哈希表。.NET中还有一个叫做Hashtable的类型,两个类型都是哈希表。这两个类型都可以实现键值对存储的功能,区别就是一个是泛型一个不是并且内部实现有一些不同。今天就研究一下.NET中的Dictionary<TKey, TValue>以及一些相关问题。
guid:33b4b911-2068-4513-9d98-31b2dab4f70c
文中如有错误,望指出。
什么是哈希表
Wikipedia中对于Hash table的定义是这样的:
In computing, a hash table (also hash map) is a data structure used to implement an associative array, a structure that can map keys to values.
它是一个通过关键字直接访问内存存储位置的数据结构,这是一个所有数据结构教科书里都会有的一个数据结构,这里不做太多的研究。但是有几个概念还是要提一下,因为对于我们理解Dictionary的内部实现很大作用。
更多哈希表的内容:Wikipedia,Hashtable 博客
碰撞(Collision)及处理
由于我们在数据结构中采用的哈希算法不是一个完美的哈希算法,同时我们会限制我们用来存储的内存空间。所以发生碰撞是不可能避免的,所以很处理如何碰撞就是设计哈希表的时候需要考虑的一个很重要的因素。
处理碰撞有很多方法,例如开放寻址法(Open Adressing),分离链接法(Separate chaining)。Dictionary中采用的是一个叫做Separate chaining with linked lists的方法。
通过下面这个Wikipedia上的图就可以很清楚的认识到这是一个什么样子的方法。
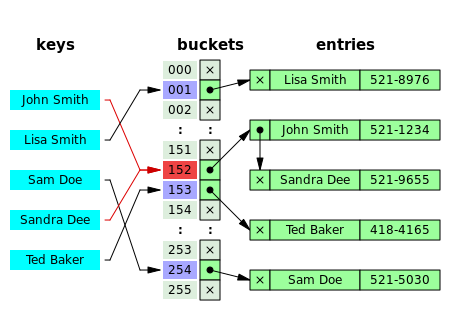
利用两个数组,buckets数组只保存一个地址,这个地址指向的是entries数组中的一个实例(entry)。当哈希值冲突的时候则需要往当前指向的那个实例的链表的末端添加一个新实例即可。
装填因子(Load Factor)
装填因子的存在是因为在开放定址方法中,当数组中的内容越来越多的时候则冲突的概率就会越来越大,而在开放定址方法中冲突的解决方案是采用探测法,而这种冲突会带来性能的极大损失。wikipedia中的这张图比较了分散链接和线性探测法在不同装填因子的情况下CPU缓存不命中的对应关系。

在Dictionary采用的这种方法里,装填因子并不是一个重要的因素不会对性能有太大影响,所以Dictionary默认使用了1并认为没有必要提供任何接口去设置这个值。
Dictionary内部如何实现
先来介绍几个在Dictionary中重要的变量:
int[] buckets和Entry[] entriesIEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer
.
- 这两个就是在上面提到的两个数组,所谓的 Separate chaining with linked lists。
- 在往Dictionary中添加一对新值的时候需要计算key的Hashcode,冲突的时候也需要判断两个value是不是相等。这个comparer就是来做这个事情的,那么这里为什么不直接调用key重载的GetHashCode和Equal方法呢?这个会在下文中讲到。
插入
通过一个例子来说明Dictionary在插入的时候做了什么。
Dictionary<int, string=""> dict = new Dictionary<int, string="">(); dict.Add(0, "zero"); dict.Add(12, "twelve"); dict.Add(15, "fiften"); dict.Add(4, "four");
下面这张“图”能够看出两个数组在插入操作中的变化,结合源代码细细品味就能知道发生了什么。
--------- --------- |buckets| |entries| |-------| |-------| | 0 | | -->| hashcode=0,key=0,next=-1,value="zero" |-------| |-------| | -1 | | empty | |-------| |-------| | -1 | | empty | |-------| |-------| --------- --------- |buckets| |entries| |-------| |-------| | 1 | | -->| hashcode=0,key=0,next=-1,value="zero" |-------| |-------| | -1 | | -->| hashcode=12,key=12,next=0,value="twelve" |-------| |-------| | -1 | | empty | |-------| |-------| --------- --------- |buckets| |entries| |-------| |-------| | 2 | | -->| hashcode=0,key=0,next=-1,value="zero" |-------| |-------| | -1 | | -->| hashcode=12,key=12,next=0,value="twelve" |-------| |-------| | -1 | | -->| hashcode=15,key=15,next=1,value="fiften" |-------| |-------| --------- --------- |buckets| |entries| |-------| |-------| | 0 | | -->| hashcode=0,key=0,next=-1,value="zero" |-------| |-------| | 2 | | -->| hashcode=12,key=12,next=-1,value="twelve" |-------| |-------| | -1 | | -->| hashcode=15,key=15,next=-1,value="fiften" |-------| |-------| | -1 | | -->| hashcode=4,key=4,next=-1,value="four" |-------| |-------| | 3 | | empty | |-------| |-------| | 1 | | empty | |-------| |-------| | -1 | | empty | |-------| |-------|
扩容
上面例子中最后一个插入时,Dictionary就做了一次扩容。它将Dictionary的size从原有的3扩展到了7。可以看到entries中的元素在扩容的时候变化不大,只是next有了些变化,这是因为扩容以后他们的哈希值%length不再映射到同一个值上了,也就不需要共享一个值啦。我觉得这里有两点值得一提。
- 扩容的下一个size是如何得到的,在上面的例子中为什么是7?
- 扩容是两个数组的变化。
对于第一个问题,因为Dictionary中数组长度有限,所以是通过key.GetHashCode() % length来获得一个bucket数组中的位置然后更改entry的next。那么我们就要保证尽可能的减少取模带来的冲突次数,那么素数就能够很好的保证取模以后能够尽可能的分散在数组的各处。
Dictionary扩容的时候会先把当前的容量*2,然后再在一个素数表中找到比这个值大的最近的一个素数。这个素数表是长这样子的:
public static readonly int[] primes = {
3, 7, 11, 17, 23, 29, 37, 47, 59, 71, 89, 107, 131, 163, 197, 239, 293, 353, 431, 521, 631, 761, 919,
1103, 1327, 1597, 1931, 2333, 2801, 3371, 4049, 4861, 5839, 7013, 8419, 10103, 12143, 14591,
17519, 21023, 25229, 30293, 36353, 43627, 52361, 62851, 75431, 90523, 108631, 130363, 156437,
187751, 225307, 270371, 324449, 389357, 467237, 560689, 672827, 807403, 968897, 1162687, 1395263,
1674319, 2009191, 2411033, 2893249, 3471899, 4166287, 4999559, 5999471, 7199369};
至于第二个问题,我们在上文中也提到过了,这个方法在扩容的时候是不需要对哈希表中存储的内容进行重新哈希。我们只需要将bucket中的分布的元素所对应的哈希值重新进行取模运算,然后放到新的位置上即可,这个操作是极快的。
查找
key.GetHashCode() % length --> 遍历链表找到equal的key
删除
同查找。
几个注意事项
性能问题
我们使用Dictionary的时候一般的习惯应该就跟代码1中那样,这种使用方法在我们使用内置的类型当key的时候没有问题,但是如果我们需要将一个自定义的值类型(struct)当作key的时候就需要注意了。这里有一个很容易忽略的问题,会导致使用Dictionary的时候带来大量不必要的性能开销。
当我们需要定义一些自定义结构并且要把这些实例放在集合中的时候我们往往会采用值类型而不会定义成一个类,如果这些类型只存在数据的话值类型在性能上比类要好很多。(Choosing Between Class and Struct)
我们先做一个实验来比较一下值类型和类作为key的性能有多大的差距。实验代码如下,这段代码中我插入1000个到10000个数据来得到所需要的时间。
public class/struct CustomKey
{
public int Field1;
public int Field2;
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return Field1.GetHashCode() ^
Field2.GetHashCode();
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
CustomKey key = (CustomKey)obj;
return this.Field1 == key.Field1 &&
this.Field2 == key.Field2;
}
}
Dictionary<CustomKey, int> dict = new Dictionary<CustomKey, int>();
int tryCount = 50;
double totalTime = 0.0;
for (int count = 1000; count < 10000; count += 1000)
{
for (int j = 0; j < tryCount; j++)
{
Stopwatch watcher = Stopwatch.StartNew();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
CustomKey key = new CustomKey() { Field1 = i * 2, Field2 = i * 2 + 1 };
dict.Add(key, i);
}
watcher.Stop();
dict.Clear();
totalTime += watcher.ElapsedMilliseconds;
}
Console.WriteLine("{0},{1}", count, totalTime / tryCount);
}
结果是这样子的:
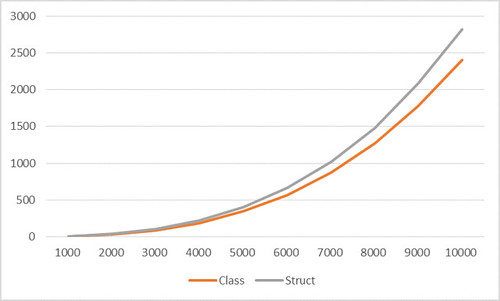
WTF?为什么和我的预期不一样,不是应该值类型要快才对不是么?orz....
这里就要提到刚刚在上文中提到的那个IEqualityComparer<TKey> comparer,Dictioanry内部的比较都是通过这个实例来进行的。但是我们没有指定它,那么它使用的就是EqualityComparer<TKey>.Default。让我们看一下源代码来了解一下这个Default到底是怎么来的,在CreateComparer我们可以看到如果我们的类型不是byte、没实现IEquatable<T>接口、不是Nullable<T>、不是enum的话,会默认给我们创建一个ObjectEqualityComparer<T>()。
而ObjectEqualityComparer<T>()中的Equal和GetHashCode方法看上去也没啥问题,那到底问题出在哪里呢?
跟值类型有关的性能问题,马上能够想到的就是装箱和拆箱所带来的性能损耗。这里那里存在这种操作呢?我们来看一下下面的两段代码就明白了。
ObjectEqualityComparer.Equals(T x, T y)的IL代码
// Methods
.method public hidebysig virtual
instance bool Equals (
!T x,
!T y
) cil managed
{
// Method begins at RVA 0x62a39
// Code size 50 (0x32)
.maxstack 8
IL_0000: ldarg.1
IL_0001: box !T
IL_0006: brfalse.s IL_0026
IL_0008: ldarg.2
IL_0009: box !T
IL_000e: brfalse.s IL_0024
IL_0010: ldarga.s x
IL_0012: ldarg.2
IL_0013: box !T
IL_0018: constrained. !T
IL_001e: callvirt instance bool System.Object::Equals(object)
IL_0023: ret
IL_0024: ldc.i4.0
IL_0025: ret
IL_0026: ldarg.2
IL_0027: box !T
IL_002c: brfalse.s IL_0030
IL_002e: ldc.i4.0
IL_002f: ret
IL_0030: ldc.i4.1
IL_0031: ret
} // end of method ObjectEqualityComparer`1::Equals
ObjectEqualityComparer.Equals(T x, T y)的IL代码
.method public hidebysig virtual
instance int32 GetHashCode (
!T obj
) cil managed
{
.custom instance void System.Runtime.TargetedPatchingOptOutAttribute::.ctor(string) = (
01 00 3b 50 65 72 66 6f 72 6d 61 6e 63 65 20 63
72 69 74 69 63 61 6c 20 74 6f 20 69 6e 6c 69 6e
65 20 61 63 72 6f 73 73 20 4e 47 65 6e 20 69 6d
61 67 65 20 62 6f 75 6e 64 61 72 69 65 73 00 00
)
// Method begins at RVA 0x62a6c
// Code size 24 (0x18)
.maxstack 8
IL_0000: ldarg.1
IL_0001: box !T
IL_0006: brtrue.s IL_000a
IL_0008: ldc.i4.0
IL_0009: ret
IL_000a: ldarga.s obj
IL_000c: constrained. !T
IL_0012: callvirt instance int32 System.Object::GetHashCode()
IL_0017: ret
} // end of method ObjectEqualityComparer`1::GetHashCode
从上面两段代码中可以看到在ObjectEqualityComparer的默认实现中会存在着很多的box(见高亮行)操作,它是用来将值类型装箱成引用类型的。这个操作是很耗时的,因为它需要创建一个object并将值类型中的值拷贝到新创建的对象中。(CustomKey.Equal方法中也有一个unbox操作)。
怎么破?
我觉得只要避免装箱不就行了,那我们自己创建一个Comparer。
public class MykeyComparer : IEqualityComparer
{
#region IEqualityComparer Members
public bool Equals(CustomKey x, CustomKey y)
{
return x.Field1 == y.Field1 &&
x.Field2 == y.Field2;
}
public int GetHashCode(CustomKey obj)
{
return obj.Field1.GetHashCode() ^
obj.Field2.GetHashCode();
}
#endregion
}
那我们将实验代码稍作修改(Dictionary<CustomKey, int> dict = new Dictionary<CustomKey, int>(new MykeyComparer());)在测试一把。这次的结果显示性能提高了很多。

线程安全
这货不是线程安全的,需要多线程操作要么自己维护同步要么使用线程安全的Dictionary-->ConcurrentDictionary<TKey, TValue>
先到这里吧


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号