三次握手和常用状态码
1、软件测试的金字塔模型:
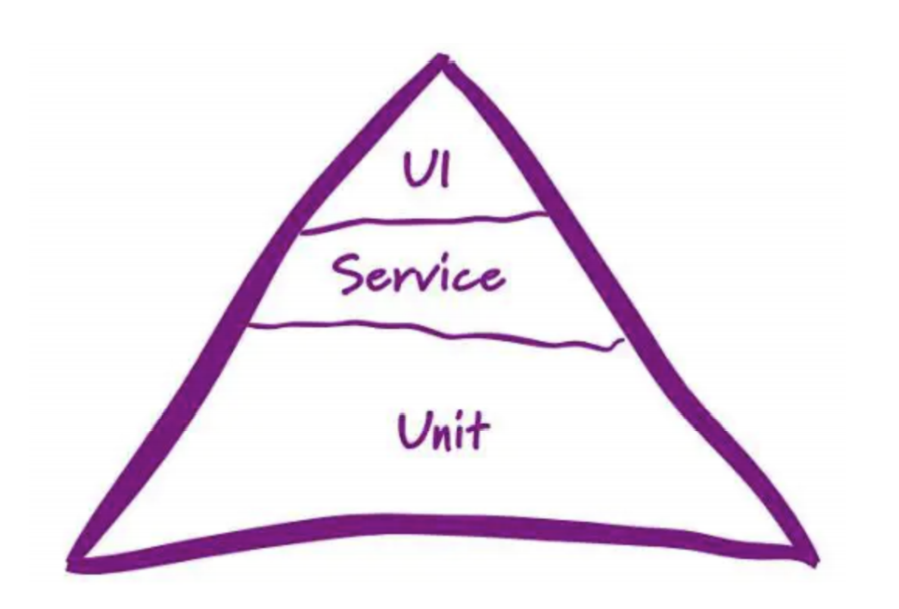
在金字塔的模型中,分别是单元,服务和UI三个层级。这地方主要的说下服务层的测试,在服务层的测试维度中,主要针对的是业务接口的测试,来验证接口功能是否完整,如内部逻辑,异常处理。这样的目的是验证接口它是否稳定,所以接口的测试相对而言比较容易而且更加高效,测试用例的维护成本也低。
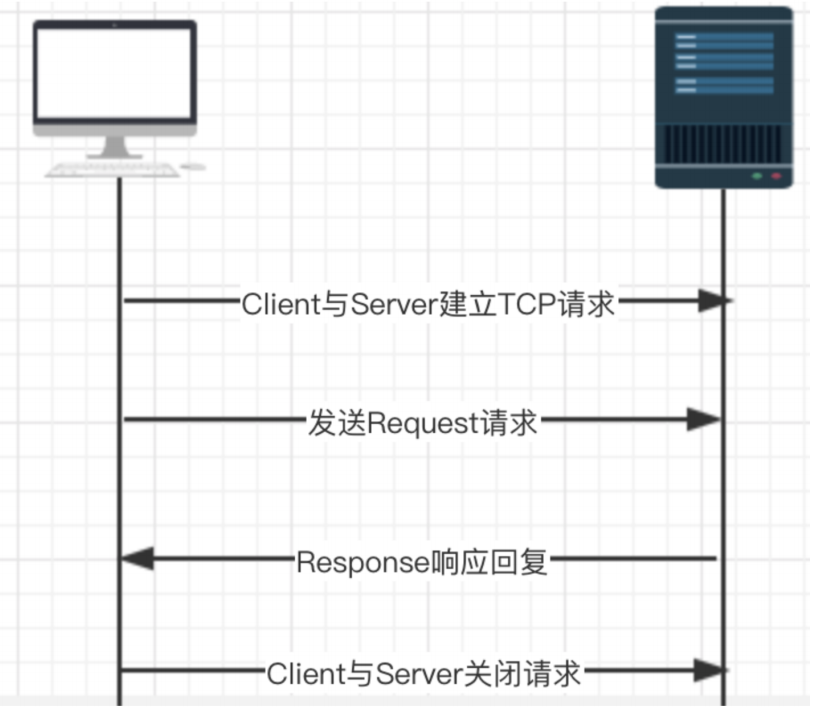
2、http完整请求(三次握手协议):
客户端与服务端之间建立TCP的链接请求
客户服务端服务发送Request的请求(请求地址,请求方法(增删改查),请求头,请求参数)
服务端Response相应回复给客户端(协议状态码(Status Code),响应头,响应数据)
客户端与服务端之间关闭TCP的连接请求
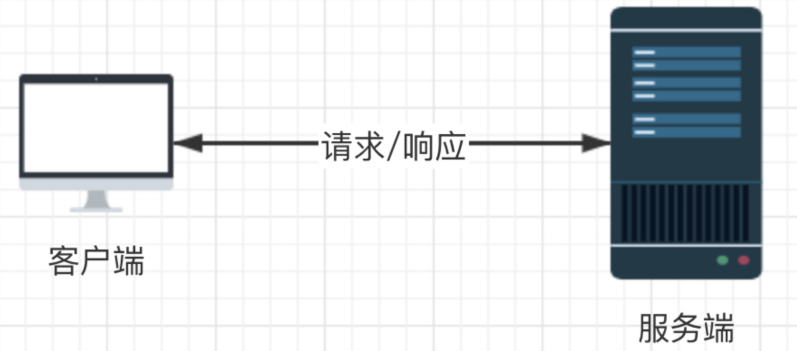
3、通信模式:(客户端和服务端都必须存在)
同步请求:客户端发送请求,服务端必须回应客户端的请求。(缺点:容易超时,客服端发送请求,服务端迟迟不回应客户端的请求;
如果请求是存在大的计算量和逻辑存在问题,就会导致请求堵塞,不回复就容易堵塞;)
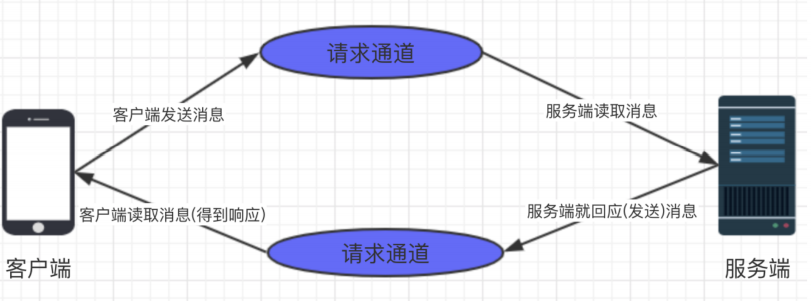
异步请求:由于同步交互存在超市以及堵塞的情况,所以有了异步交互,在异步交互中,客户端和服务端互相不需要关注对方的存在,
只需要关注对应的MQ的消息,客户端与服务端的交互主要是通过MQ的消息中间作为传递。
4、常用的请求方法:
get:请求指定页面信息,并返回实体主体。
post:向指定的资源提交数据进行处理请求(提交表单、上传文件),有时候可以添加或者删除
put:从客户端向服务端传送的数据取代指定的文件(上传文件)
delete:请求服务端删除指定的页面
5、常用状态码:
200:请求成功
301:永久重定向
302:临时重定向
(4开头的错误都是客户端的问题)
400:客户端请求错误(请求方法、请求头和请求参数错误)
401:Unauthorized
403:Forbidden
404:请求资源不存在
405:不被允许的请求方法
(5开头都是服务端的问题,假死:电脑能用但是很卡)
500:服务器内部错误
504:GateWay Timeout
6、请求头/响应头:
Cookie:维持当前访问会话
Referer:标识这个请求是从那个页面发送过来的
User-Agent:可以使服务器能够识别客户使用的操作系统版本,浏览器以及信息版本
Content-Type:互联网媒体类型或者MIME类型
Content-Encoding:响应内容的编码
Server:服务器信息
Content-Type:指定返回的数据格式
Set-Cookie:设置Cookie,响应头里面的Set-Cookie告诉客户端把内容放在Cookie中,下次请求携带Cookie的请求
7、常用请求数据格式:
application/x-www-from-urlencoded 表单数据
multipart/form-json 表单文件上传
Application/json 序列化JSON格式数据
Text/xml XML数据
实战:
login.py文件
#!/usr/bin/env python
#!coding:utf-8
from flask import Flask,jsonify
from flask_restful import Api,Resource,reqparse
app=Flask(__name__)
api=Api(app)
class LoginView(Resource):
def get(self):
return {'status':0,'msg':'ok','data':'this is a login page'}
def post(self):
parser=reqparse.RequestParser()
parser.add_argument('username', type=str, required=True, help='用户名不能为空')
parser.add_argument('password',type=str,required=True,help='账户密码不能为空')
parser.add_argument('age',type=int,help='年龄必须为正正数')
parser.add_argument('sex',type=str,help='性别只能是男或者女',choices=['女','男'])
args=parser.parse_args()
return jsonify(args)
api.add_resource(LoginView,'/login',endpoint='login')
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True,port=5000)
api.文件
import requests
import json
import unittest
# r=requests.get(
# url='http://localhost:5000/login'
# )
# print('协议状态码:',r.status_code)
# print('响应头:',r.headers)
# #响应类型是json时,才使用
# print('响应数据:',r.json())
# print('响应内容:',r.text)
# print('响应二进制的内容:',r.content)
# print('响应时间:',r.elapsed.total_seconds())
# print('cookie:',r.cookies)
# r=requests.post(
# url='http://localhost:5000/login',
# #data是str类型,所以需要json序列化(就是把python转为str)
# # data=json.dumps({'username':'lyl','password':123,'age':18,'sex':'女'}),
# json={'username':'lyl','password':123,'age':18,'sex':'女'},
# headers={'content_type':'application/json'})
# print(r.status_code)
# print(r.json())
class ApiTest(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self) -> None:
self.url='http://localhost:5000/login'
self.data={'username':'lyl','password':123,'age':18,'sex':'女'}
self.headers={'content_type':'application/json'}
def test_login_get(self):
r=requests.get(url=self.url)
self.assertEqual(r.status_code,200)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['status'],0)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['data'],'this is a login page')
def test_login_post(self):
r=requests.post(
url=self.url,
json=self.data,
headers=self.headers)
self.assertEqual(r.status_code,200)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['username'],'lyl')
def test_login_username_null(self):
'''login服务验证:username参数为空的校验'''
r=requests.post(
url=self.url,
json={'password':123,'age':18,'sex':'女'},
headers=self.headers)
self.assertEqual(r.status_code, 400)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['message']['username'], '用户名不能为空')
def test_login_password_null(self):
'''login服务验证:username参数为空的校验'''
r=requests.post(
url=self.url,
json={'username':'lyl','age':18,'sex':'女'},
headers=self.headers)
self.assertEqual(r.status_code, 400)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['message']['password'], '账户密码不能为空')
def test_login_age_null(self):
'''login服务验证:username参数为空的校验'''
r=requests.post(
url=self.url,
json={'username':'lyl','password':123,'age':"etrestr",'sex':'女'},
headers=self.headers)
self.assertEqual(r.status_code, 400)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['message']['age'], '年龄必须为正正数')
def test_login_sex_null(self):
'''login服务验证:username参数为空的校验'''
r=requests.post(
url=self.url,
json={'username':'lyl','password':123,'age':18,"sex":"aefrtyu"},
headers=self.headers)
self.assertEqual(r.status_code, 400)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['message']['sex'], '性别只能是男或者女')
def test_cunYou_001(self):
r=requests.post(
url='http://m.cyw.com/Home/ComSearch/search',
data={'k':'天沐温泉'},
headers={'content-type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8',
'user-agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.159 Safari/537.36'})
self.assertEqual(r.status_code,200)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['procedure'],9)
def test_cunYu_002(self):
r=requests.post(
url='http://m.cyw.com/Home/ComSearch/search',
data={'k':'烧烤'},
headers={'content-type':'application/x-www-form-urlencoded; charset=UTF-8',
'user-agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/92.0.4515.159 Safari/537.36'})
self.assertEqual(r.status_code,200)
self.assertEqual(r.json()['procedure'],6)
# print(r.json())
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main(verbosity=2)


