[2021 Spring] CS61A 学习笔记 lecture 11 Sequences (II) and Data Abstraction
课本: http://composingprograms.com/pages/22-data-abstraction.html
这节课主要内容是序列的特性和数据抽象。
目录
Sequence(II)
Multiple Variables
for循环中的迭代变量就像是赋值语句的左半边式子:

Two Iterations at Once!(zip函数)
zip函数可以将多个序列进行组合,实际上返回一个生成器

Modifying Lists
列表是可变序列,可以分配元素和切片。

List Comprehensions
列表的完整形式:
[<expression> for <var> in <sequence expression> if <boolean expression>]

exercise
def matches(a, b):
"""Return the number of values k such that A[k] == B[k].
>>> matches([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [3, 2, 3, 0, 5])
3
>>> matches("abdomens", "indolence")
4
>>> matches("abcd", "dcba")
0
>>> matches("abcde", "edcba")
1
>>> matches("abcdefg", "edcba")
1
"""
return sum([1 for x, y in zip(a, b) if x==y])
def triangle(n):
"""Assuming N >= 0, return the list consisting of N lists:
[1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3], ... [1, 2, ... N].
>>> triangle(0)
[]
>>> triangle(1)
[[1]]
>>> triangle(5)
[[1], [1, 2], [1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]
"""
return [list(range(1, i + 1)) for i in range(1, n+1)]
Data Abstraction
Philosophy
ADT(abstract data type): 抽象数据类型

Classification
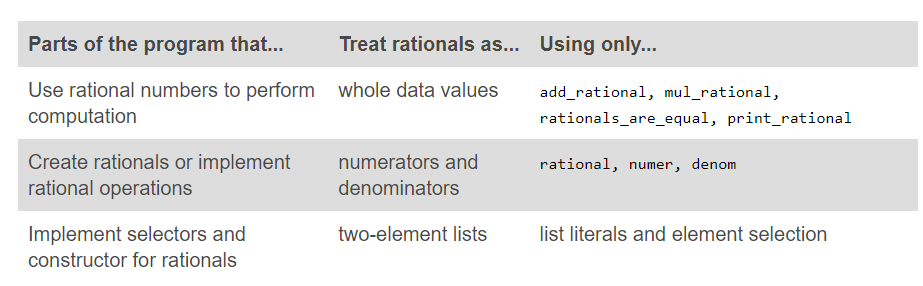
分类:构造器、访问器、修改器

Rational Numbers
书中将有理数作为ADT的例子。
# Rationals
from math import gcd
def make_rat(n, d):
"""The rational number N/D, assuming N, D are integers, D!=0"""
g = gcd(n, d)
n //= g; d //= g
return (n, d)
def numer(r):
"""The numerator of rational number R in lowest terms."""
return r[0]
def denom(r):
"""The denominator of rational number R in lowest terms.
Always positive."""
return r[1]
def add_rat(x, y):
return make_rat(numer(x) * denom(y) + numer(y) * denom(x),
denom(x) * denom(y))
def mul_rat(x, y):
return make_rat(numer(x) * numer(y), denom(x) * denom(y))
def str_rat(r): # (For fun: a little new Python string magic)
return str(numer(r)) if denom(r) == 1 else f"{numer(r)}/{denom(r)}"
def equal_rat(x, y):
return numer(x) * denom(y) == numer(y) * denom(x)
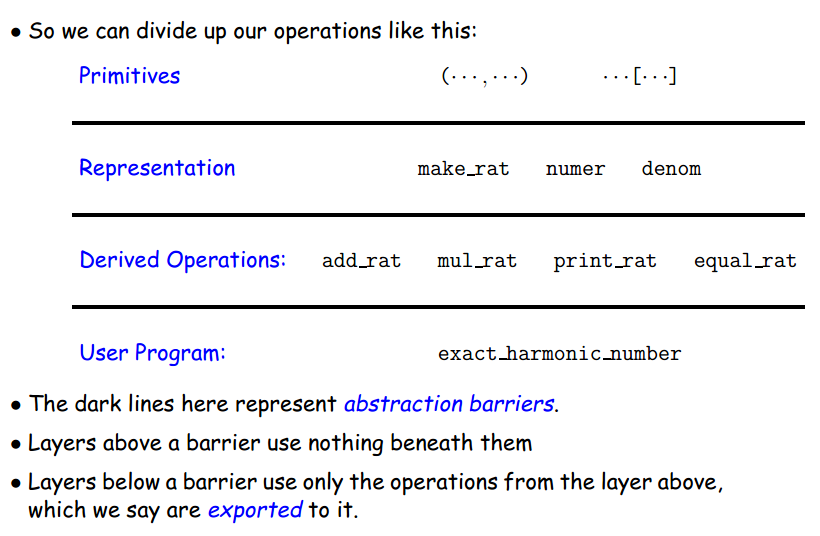
Layers of Abstraction
抽象界限:界限上层不会用到下层的操作,界限下层只用到上一层的操作。