[vue]vue双向绑定$on $emit sync-模态框
双向绑定实现($on $emit)
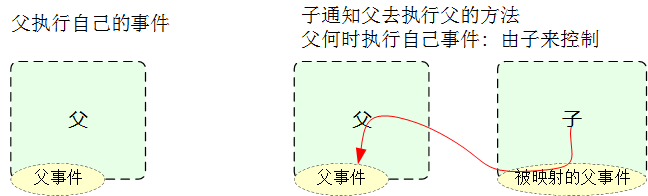
关于父子之间数据更新同步, 如果单向绑定, 子修改了,父却没有修改, 这种一般不符合规范
正常更新数据的套路是:
1. 子通知父更新数据
2. 子自动刷新获取最新数据
- 为实现这个,就会有发布订阅模式
1.特点: 一对多, 一个动作产生,引发一连串行为. 对应到数据结构是:
{失恋:[cry,eat,shopping]}
2.如果失恋产生, 则会触发cry,eat shopping一系列动作执行. 这个思路就是发布订阅模式. 对应到vue,就是子去通知父亲刷新数据后子同步数据.
// 发布 emit 订阅 on {}
function Girl() {
this._events = {}
}
Girl.prototype.on = function (eventName,callback) {
if(this._events[eventName]){ // 不是第一次
this._events[eventName].push(callback); // {失恋:[cry,eat,shopping]}
}else{
this._events[eventName] = [callback] //{失恋:[cry]}
}
};
Girl.prototype.emit = function (eventName,...args) { //[我,你,他]
// [].slice.call(arguments,1);
// Array.from(arguments).slice(1);
if(this._events[eventName]){
this._events[eventName].forEach(cb=>cb(...args));
}
};
let girl = new Girl();
let girl1 = new Girl();
let cry = (who) =>{console.log(who+'哭');};
let shopping = (who) =>{console.log(who+'购物');};
let eat = (who) =>{console.log(who+'吃');};
girl.on('失恋',cry); // {失恋:[cry]}
girl.on('失恋',eat); // {失恋:[cry,eat]}
girl.on('失恋',shopping); // {失恋:[cry,eat,shopping]}
girl1.emit('失恋');
本文思路:
- 先实现子获取父数据(单向绑定)
- 然后实现双向数据更新($on $emit)
1.给父亲写改money的方法(但不要注册到父上)
2.将父改money方法传给子,$on
3.子一旦想改数据,即会发射信息$emit给父,提示父该执行动作了.
- 双向更新简化: sync
1.直接实现
2.语法糖简化
<div id="app">
money:{{money}} <br>
<awsome :childmoney="money"></awsome>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
money: 700,
},
components: {
awsome: {
data: function () {
return {count: 0}
},
props:['childmoney'],
template: "<button @click='childmoney++'>childmoney: {{childmoney}}</button>"
}
}
})
</script>
- 双向绑定3步走
// 1. 父亲定义更改自己money事件
methods: {getMoney() {this.$emit('childthings', 1400);}
// 2. 父将事件传给子,
childthings.$on('childthings',things)
// 3, 子在这里(相当于)触发父方法在父上执行
awsome.$emit('childthings', 1400);
<div id="app">
money:{{money}} <br>
<!--2,父将事件传给子,
childthings.$on('childthings',things)-->
<awsome :childmoney="money" @childthings="things"></awsome>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
//1. 单向数据更新不应该发生
//2. 子想改变数据,应该通知父先改变, 父改变后,子自动刷新
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
money: 700,
},
methods: {
things(val) { // 1.父亲定义更改自己money事件
alert(val);
this.money = val;
}
},
components: {
awsome: {
data: function () {
return {count: 0}
},
props: ['childmoney'],
methods: {
getMoney() {
this.$emit('childthings', 1400); // 3, 子在这里(相当于)触发父方法在父上执行(函数名+参数)
}
},
template: "<button @click='getMoney'>childmoney: {{childmoney}}</button>"
}
}
})
</script>
- 双向绑定的简写: sync
<div id="app">
money:{{money}} <br>
<h1>sync双向绑定1-1:</h1>
<awsome :childmoney="money" @update:childmoeny="val=>this.money=val"></awsome>
<h1>sync双向绑定1-2:</h1>
<awsome :childmoney="money" @update:childmoeny="things"></awsome>
<h1>sync双向绑定1-3: 简化写法</h1>
<awsome :childmoney.sync="money"></awsome>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
money: 700,
},
methods: {
things(val) {
alert(val);
this.money = val;
}
},
components: {
awsome: {
data: function () {
return {count: 0}
},
props: ['childmoney'],
methods: {
getMoney() {
this.$emit('update:childmoney', 1400); // 这里需要改成和上面父给子注册方法时相同的名字
}
},
template: "<button @click='getMoney'>childmoney: {{childmoney}}</button>"
}
}
})
</script>
- 最简单的写法
<div id="app">
{{money}}
<awsome :childmoney.sync="money"></awsome>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
money: 700,
},
components: {
awsome: {
props:['childmoney'],
/* methods:{
getMoney(){
this.$emit('update:childmoney',1400);
}
},*/
template: `<button @click="()=>this.$emit('update:childmoney',1400)">{{childmoney}}</button>`
}
}
})
</script>
模态框案例
- 1.父传数据给子, 父将flag=true传给子,实现点按钮弹出
- 2.子远程替父调用方法,修改flag=false,实现点关闭按钮关闭.
<div id="app">
<button @click="flag=true">模态框</button>
<!--<motal :childflag="flag" @close="()=>flag=false"></motal>-->
<motal :childflag="flag" @childthings="things"></motal>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
flag: false,
},
methods: {
things(val) {
this.flag = val;
}
},
components: {
motal: {
props: ['childflag'],
methods: {
shutdown() {
this.$emit('childthings');
}
},
template: `
<div class="mask" v-show="childflag">
<div class="dialog">
<button @click="shutdown">关闭</button>
</div>
</div>`,
},
}
})
</script>
较为抽象的代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.mask {
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
position: fixed;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, .35);
top: 0;
left: 0
}
.dialog {
width: 400px;
height: 150px;
background: #fff;
position: fixed;
top: 50%;
left: 50%;
transform: translate3d(-50%, -50%, 0)
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<button @click="flag=true">弹</button>
<!--如果show的值是true则显示 如果是false则隐藏 @close对应的函数是点击关闭按钮时触发的函数-->
<modal :childflag="flag" @childthings="()=>flag=false"></modal>
</div>
<template id="dialog">
<div class="mask" v-show="childflag">
<div class="dialog">
<button @click="shutdown">关闭</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let modal = { //接收了父组件的属性
props: ['childflag'],
template: '#dialog',
methods: {
shutdown() {
this.$emit('childthings');
}
}
};
let vm = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {flag: false},
components: {
modal // 名字不能叫dialog 原生中已经占用了这个名字
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
mounted里refs实现父类触发子类的方法.
加载中...页在加载完成后会被销毁, 谁来触发他销毁? 一般是父类. 映射到vue就是父类触发子类的方法.
1.给要获取子组件添加ref标识
2.mounted阶段调用,如this.$refs.load.hide()
注: ref放在组件上获取的是vue实例(VueComponent), 而非dom元素, 但可以通过实例在全局调用子元素的方法.
<div id="app">
<loading ref="load"></loading>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
let vm = new Vue({
el: "#app",
data: {
msg: 'hi'
},
mounted() {
console.log(this.$refs.load);
this.$refs.load.hide(); //获取到的是vm实例,但可以操控里面的方法.
},
components: {
loading: {
methods: {
hide() {
console.log('hide func被触发');
}
},
template: "<h1>sucess!</h1>",
}
}
})
</script>
- 学习知识一贯的做法是,先理解骨干使用套路, 然后结合栗子来揣摩知识点的设计理念(用来解决啥问题)
下面是ref一个栗子页面loading.
<div id="app">
<loading ref="load"></loading>
</div>
<script src="node_modules/vue/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
// 父组件调用子组件的方法
let loading = {
data(){
return {flag:true}
},
template:'<div v-show="flag">疯狂加载中。。。</div>',
methods:{
hide(){
this.flag = false;
}
}
};
let vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
mounted(){ // ref 如果放在组件上 获取的是组件的实例 并不是组件的dom元素
// this.$refs.load.hide()
// this.$refs.load.$el.style.background = 'red'
},
data:{},
components:{
loading
}
})
</script>

