课程全文检索接口
目录
1. 基本内容
前后端不分离: https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaonq/p/12363589.html
1.1 安装
pip install drf-haystack # django的开源搜索框架
pip install whoosh # 搜索引擎
pip install jieba # 中文分词Jieba,由于Whoosh自带的是英文单词,对中文的分词支持不是太好
1.2 什么是haystack?
- haystack是django的开源搜索框架,该框架支持
Solr,Elasticsearch,Whoosh,Xapian搜索引擎,不用更改代码,直接切换引擎,减少代码量。 - 搜索引擎使用Whoosh,这是一个由纯Python实现的全文搜索引擎,没有二进制文件,比较小巧,配置比较简单,当然性能自然略低。
- 中文分词Jieba,由于Whoosh自带的是英文分词,对中文的分词支持不是太好,故用jieba替换whoosh的分词组件。
2.配置使用
2.1 syl/settings.py 全文检索配置
'''1.注册app'''
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'haystack', # haystack要放在应用的上面
]
'''2.模板路径'''
TEMPLATES = [
{
`DIRS`: [os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'templates')],
},
]
'''3.全文检索配置'''
HAYSTACK_SEARCH_RESULTS_PER_PAGE = 15 # 搜索出多条数据时需要分页
HAYSTACK_CONNECTIONS = {
'default': {
# 'ENGINE': 'haystack.backends.whoosh_backend.WhooshEngine',
'ENGINE': 'course.whoosh_cn_backend.MyWhooshEngine',
'PATH': os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'whoosh_index'), # 指定倒排索引存放位置
},
}
# # ES引擎
# HAYSTACK_CONNECTIONS = {
# 'default':{
# 'ENGINE':
'haystack.backends.elasticsearch_backend.ElasticsearchSearchEngine',
# 'URL': 'http://10.211.55.15:9200/', # Elasticsearch服务器ip地址,端口号固 定为9200
# 'INDEX_NAME': 'syl', # Elasticsearch建立的反向索引库的名称
# },
# }
# 添加此项,当数据库改变时,会自动更新索引,非常方便
HAYSTACK_SIGNAL_PROCESSOR = 'haystack.signals.RealtimeSignalProcessor'
2.2 在子应用下创建索引文件
-
apps/course/search_indexes.py
# apps/course/search_indexes.py
# 文件名必须是 search_indexes.py
from haystack import indexes
from .models import Course
# 修改此处,类名为模型类的名称+Index,比如模型类为GoodsInfo,则这里类名为GoodsInfoIndex(其实可以随便写)
class CourseIndex(indexes.SearchIndex, indexes.Indexable):
"""
Course索引类
"""
# text为索引字段
# document = True,这代表haystack和搜索引擎将使用此字段的内容作为索引进行检索
# use_template=True 指定根据表中的那些字段建立索引文件的说明放在一个文件中
text = indexes.CharField(document=True, use_template=True)
# 对那张表进行查询
def get_model(self): # 重载get_model方法,必须要有
"""返回建立索引的模型类"""
return Course # 返回这个model
# 建立索引的数据
def index_queryset(self, using=None):
"""返回要建立索引的数据查询集"""
# 这个方法返回什么内容,最终就会对那些方法建立索引,这里是对所有字段建立索引
return self.get_model().objects.all()
2.3 指定索引模板文件
-
templates/search/indexes/course/course_text.txt -
# 创建文件路径命名必须这个规范:templates/search/indexes/应用名称/模型类名称 _text.txt
{{object.id}}
{{object.title}}
{{object.desc}}
2.4 修改为jieba分词中的中文分析器
-
apps/course/whoosh_cn_backend.py
# 更换 text 字段的 分析方式, 变为jieba分词中的中文分析器
from haystack.backends.whoosh_backend import WhooshEngine, WhooshSearchBackend
from whoosh.fields import TEXT
from jieba.analyse import ChineseAnalyzer
class MyWhooshSearchBackend(WhooshSearchBackend):
def build_schema(self, fields):
(content_field_name, schema) = super().build_schema(fields)
# 指定whoosh使用jieba进行分词
schema._fields['text'] = TEXT(stored=True,
analyzer=ChineseAnalyzer(),
field_boost=fields.get('text').boost,
sortable=True)
return (content_field_name, schema)
class MyWhooshEngine(WhooshEngine):
backend = MyWhooshSearchBackend
2.5 课程全文检索接口视图函数
-
course/views.py
from syl import settings
from django.core.paginator import InvalidPage, Paginator
from haystack.forms import ModelSearchForm
from django.http import JsonResponse
# 如果settings.py中配置就是用settings中配置的,否则就每页15条
RESULTS_PER_PAGE = getattr(settings, 'HAYSTACK_SEARCH_RESULTS_PER_PAGE', 15)
def course_index_search(request):
query = request.GET.get('q', None)
page = int(request.GET.get('page', 1)) # 第几页
page_size = int(request.GET.get('page_size', RESULTS_PER_PAGE)) #每页多少条
if query:
form = ModelSearchForm(request.GET, load_all=True) # 将查询条件传递给查询对象
if form.is_valid():
results = form.search() # 查询出来的最终数据
else:
results = []
else:
return JsonResponse({"code": 404, "msg": 'No file found!', "data": []})
# 对结果集进行分页
paginator = Paginator(results, page_size)
try:
page = paginator.page(page) # 从分好的页中拿第几页
except InvalidPage: # 如果分页出错
return JsonResponse({"code": 404, "msg": 'No file found!', "data": []})
jsondata = []
for result in page.object_list: # 分页后的课程查询结果
data = {
'id': result.object.id,
'title': result.object.title,
'desc': result.object.desc,
'img':
request.scheme+'://'+request.META['HTTP_HOST']+result.object.img.url,
#'follower': result.object.follower,
'learner': result.object.learner,
'status': result.object.status,
'course_type': result.object.course_type.id
}
jsondata.append(data)
result = {
"code": 200,
"msg": 'Search successfully!',
"data": {"count": page.paginator.count, "results": jsondata}
}
return JsonResponse(result)
2.6 syl/urls.py 添加路由
urlpatterns = [
path('search/', course_index_search),
]
2.7 命令构建倒排索引
python manage.py rebuild_index
3. 测试课程全文检索
-
测试接口
http://192.168.56.100:8888/search/?q=入门&page=1&page_size=1 -
测试结果
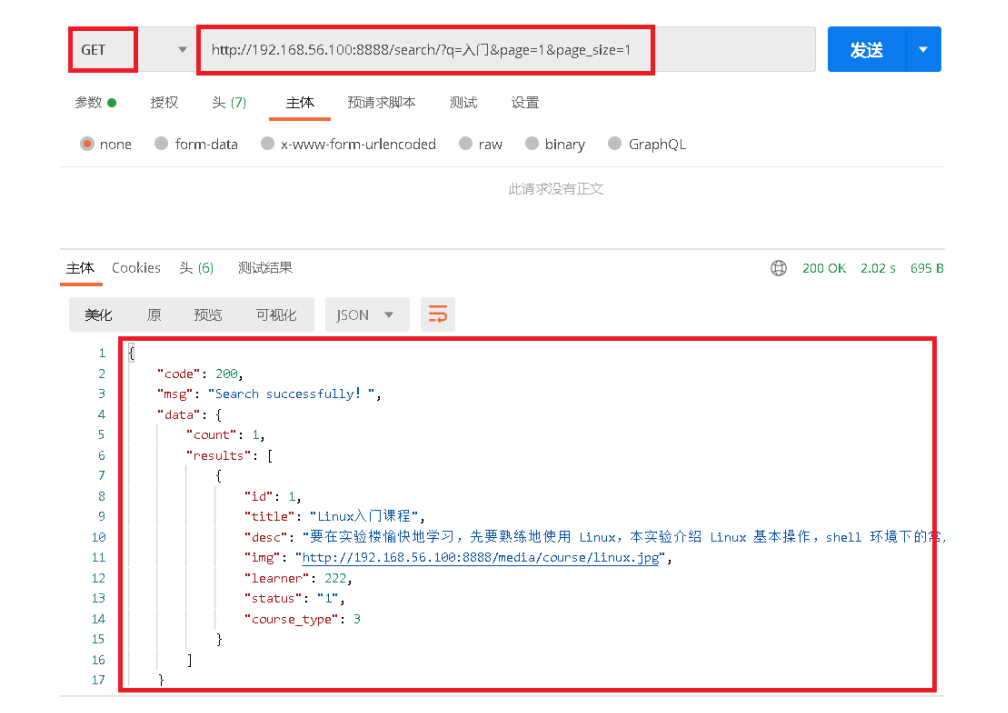
-
返回
{
"code": 200,
"msg": "Search successfully!",
"data": {
"count": 1,
"results": [
{
"id": 1,
"title": "Linux入门课程",
"desc": "要在实验楼愉快地学习,先要熟练地使用 Linux,本实验介绍 Linux 基 本操作,shell 环境下的常用命令。",
"img": "http://192.168.56.100:8888/media/course/linux.jpg",
"learner": 222,
"status": "1",
"course_type": 3
}
}
}
}



